Mach 2 Speed in MPH: What's the Magic Number

The Speed of Sound: A Fundamental Concept in Aerodynamics

When we talk about speed, we often think about how fast an object can move. But have you ever wondered what the speed of sound is? The speed of sound, also known as Mach 1, is a fundamental concept in aerodynamics that has fascinated scientists and engineers for centuries. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of supersonic speeds and explore the magic number that represents Mach 2 in miles per hour.
What is Mach 1?

Mach 1, also known as the speed of sound, is the speed at which sound waves propagate through the air. At sea level, in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius), the speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h). This speed is the threshold beyond which an object is considered supersonic.
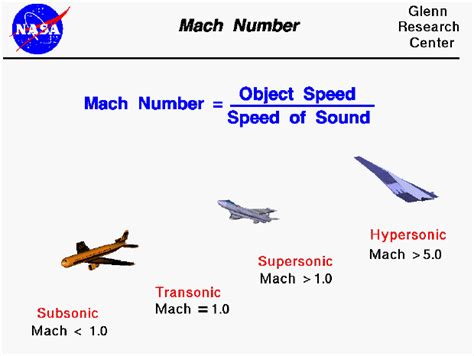
Mach Numbers: A Measure of Supersonic Speed
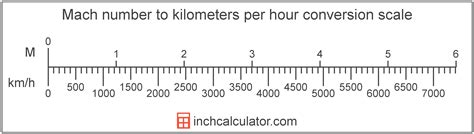
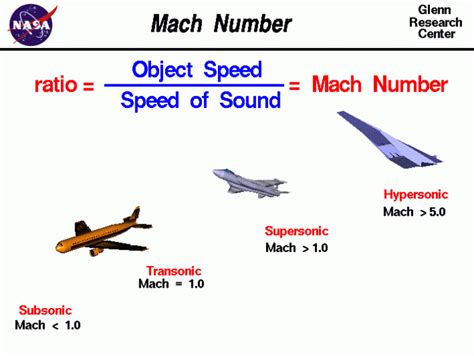
Mach numbers are used to express the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound. A Mach number is defined as the ratio of the object’s speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. For example, an object traveling at Mach 1 is moving at the speed of sound, while an object traveling at Mach 2 is moving at twice the speed of sound.
Mach 2: The Magic Number

So, what is the magic number that represents Mach 2 in miles per hour? To calculate this, we need to multiply the speed of sound by 2.
768 mph (Mach 1) x 2 = 1,536 mph
Therefore, Mach 2 is equivalent to approximately 1,536 miles per hour.
Supersonic Flight: Breaking the Sound Barrier
Supersonic flight, which involves flying faster than the speed of sound, is a complex phenomenon that requires careful consideration of aerodynamics and materials science. When an object breaks the sound barrier, it produces a sonic boom, which is a shockwave that travels through the air and produces a loud noise.
🚀 Note: The sonic boom is not just a simple noise; it's a shockwave that can cause damage to structures and injure people if they are too close to the flight path.
Applications of Supersonic Flight

Supersonic flight has several applications in fields such as:
- Military aviation: Supersonic aircraft are used for reconnaissance, intercept, and combat missions.
- Space exploration: Supersonic speeds are required to reach orbit and escape Earth’s atmosphere.
- Commercial aviation: Supersonic business jets are being developed to reduce travel times between cities.
Challenges of Supersonic Flight
While supersonic flight has many benefits, it also poses significant challenges, including:
- Aerodynamic heating: Supersonic speeds generate high temperatures, which can cause structural damage to the aircraft.
- Sonic booms: Supersonic flight produces sonic booms, which can be a nuisance and cause damage to structures.
- Fuel efficiency: Supersonic flight requires a lot of energy, which can reduce fuel efficiency and increase operating costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mach 2 represents a significant milestone in the world of aerodynamics, marking a speed of approximately 1,536 miles per hour. While supersonic flight has many applications, it also poses significant challenges that require careful consideration of aerodynamics, materials science, and engineering.
What is the speed of sound?
+
The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level, in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
What is Mach 2?

+
Mach 2 is a speed of approximately 1,536 miles per hour, which is twice the speed of sound.
What are the challenges of supersonic flight?

+
Supersonic flight poses several challenges, including aerodynamic heating, sonic booms, and reduced fuel efficiency.
Related Terms:
- Mach 1 speed
- Kecepatan Mach 2
- mach 2 speed in km h
- 1 mach km h
- Mach 3 speed
- Mach 10