Louisiana Purchase 1803: Map Worksheet Answers Revealed

The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 was one of the most significant land acquisitions in the history of the United States. With a stroke of the pen, America doubled in size, adding vast territories to the nation and securing its future as a continental power. In this blog post, we delve into this monumental event by exploring a worksheet designed to deepen understanding of the Louisiana Purchase map and its implications.
The Historical Context of the Louisiana Purchase

To appreciate the significance of the Louisiana Purchase, one must understand its historical backdrop:
- French Control: Initially, the territory was under French control, known as French Louisiana, until it was ceded to Spain in the Treaty of Paris in 1763.
- Return to France: By 1800, Napoleon Bonaparte, who was restoring French colonial power, pressured Spain to return Louisiana in the secret Treaty of San Ildefonso.
- Unforeseen Challenges: Economic troubles in France, including failure in Saint-Domingue (modern-day Haiti) and mounting costs of European wars, made it advantageous for Napoleon to sell Louisiana to the United States.
Map Worksheet: Key Elements
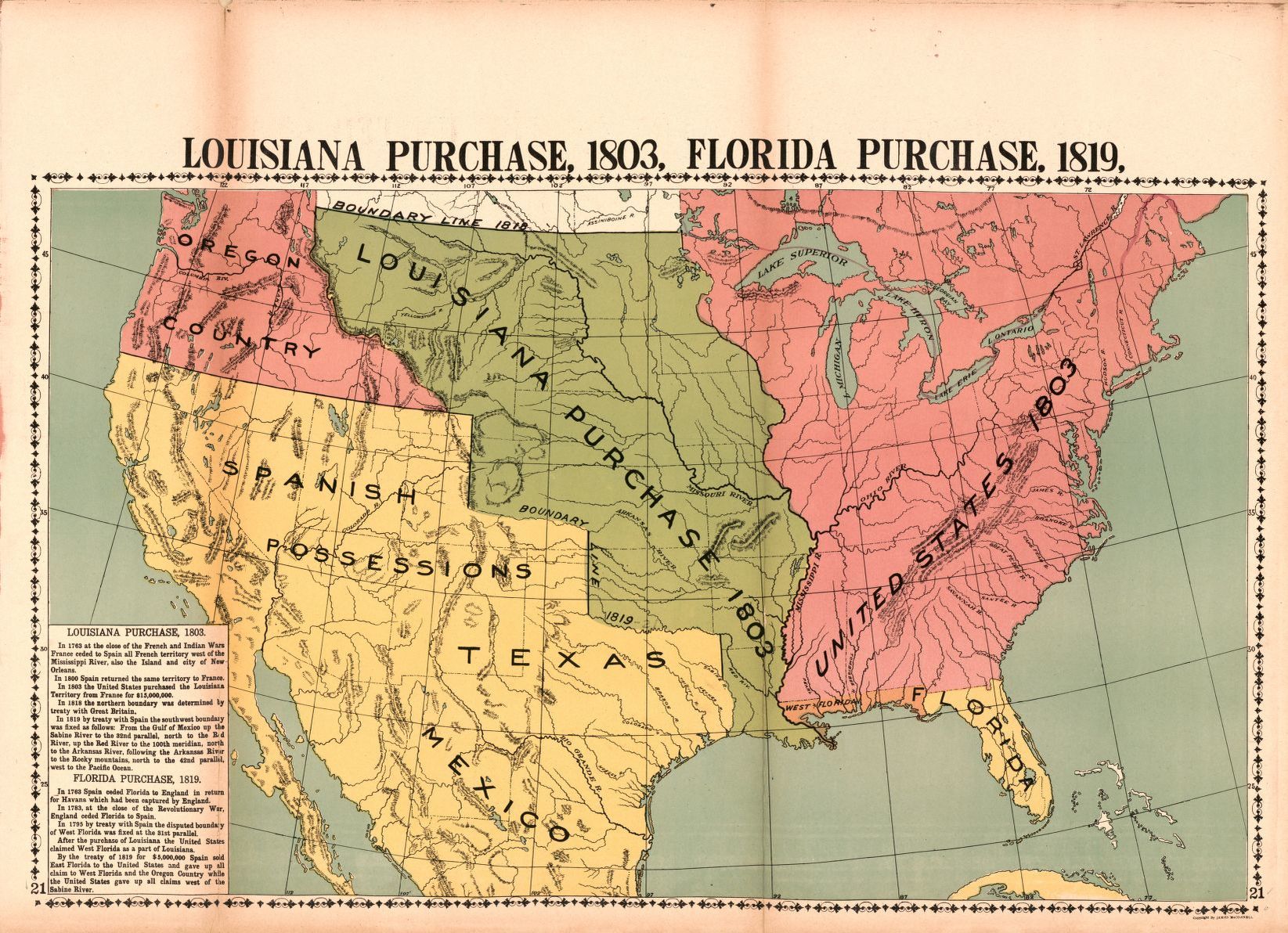
Let's examine the map worksheet that outlines the changes in Louisiana's boundaries and control:
| Year | Region | Control | Key Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1763 | French Louisiana | France to Spain | Treaty of Paris ends Seven Years' War |
| 1800 | Louisiana | Spain to France | Secret Treaty of San Ildefonso |
| 1803 | Louisiana | France to USA | Louisiana Purchase signed |

🔍 Note: The map above is a simplified version. The actual boundaries were subject to dispute and negotiation over the years.
Significance of the Louisiana Purchase

The Louisiana Purchase had far-reaching effects:
- Expansion of Territory: It expanded U.S. territory from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains, effectively doubling its landmass.
- Westward Expansion: It fueled westward expansion, sparking the period known as "Manifest Destiny."
- Economic Growth: The purchase ensured control of the Mississippi River, crucial for commerce and navigation.
Impact on Native American Tribes

The acquisition wasn't without its controversies:
- Native American Displacement: As settlers moved west, Native American tribes were increasingly pushed off their ancestral lands, leading to conflicts and the eventual displacement of many tribes.
- Legal and Ethical Concerns: The treaty negotiations did not include consultations with the indigenous peoples, raising ethical questions about land rights and sovereignty.
Key Players in the Louisiana Purchase

Here are the individuals who played pivotal roles in this historical event:
- Napoleon Bonaparte: As the leader of France, Napoleon decided to sell Louisiana to the United States due to financial difficulties.
- Thomas Jefferson: The President at the time, Jefferson pushed for the purchase, initially concerned about its constitutionality but seeing its strategic importance.
- James Monroe: Sent to France as an emissary by Jefferson, Monroe played a key role in negotiating the purchase.
- Robert Livingston: Served as the U.S. Minister to France and was instrumental in finalizing the deal with Monroe.
📚 Note: Jefferson believed the purchase would be beneficial for agriculture, with visions of creating an "agrarian republic."
Legacy of the Louisiana Purchase

The Louisiana Purchase left a lasting legacy on the United States:
- Nation Building: It set the stage for westward expansion and the building of a nation.
- Foreign Relations: It altered the balance of power in North America, weakening French influence and cementing American strength.
- Legal and Constitutional Impact: The acquisition raised questions about presidential powers and the interpretation of the Constitution, leading to debates on the extent of federal authority.
🌍 Note: The map detailing the Louisiana Purchase was instrumental in cartography and territorial claims of the era.
In summary, the Louisiana Purchase of 1803 was more than a real estate deal; it was a catalyst for national growth, economic development, and a precedent for future land acquisitions. Understanding its map and the key players involved offers a glimpse into the shaping of the modern United States.
What was the main reason France decided to sell Louisiana?

+
France faced economic challenges, including the failure to retain control over Saint-Domingue (Haiti) and the need to finance their ongoing European wars. Selling Louisiana to the United States provided immediate funds and reduced the cost of maintaining the territory.
How did the Louisiana Purchase affect Native American tribes?

+
The purchase led to increased European American settlement, often at the expense of Native American lands. Many tribes were displaced from their ancestral territories as the U.S. government and settlers expanded westward, resulting in conflicts and broken treaties.
Was the Louisiana Purchase legal under the U.S. Constitution?
+
At the time, Thomas Jefferson believed the Constitution did not explicitly give him the power to acquire foreign territory. However, to ensure the purchase, Jefferson and his supporters interpreted the Constitution loosely, especially under the “necessary and proper” clause, which allowed for actions deemed essential for the country’s interests.
What were the implications for French influence in North America?

+
The sale marked the end of French colonial ambitions in North America, significantly reducing their presence and influence in the region. It allowed the United States to consolidate its position as a major power on the continent.
How was the Louisiana Purchase paid for?

+
The United States purchased Louisiana for $15 million, which was paid in a combination of stocks held by U.S. banks and cash, financed through bonds issued by the U.S. government.


