5 Steps Long Division

Introduction to Long Division

Long division is a method for dividing one number by another, and it is a fundamental concept in mathematics. It involves a series of steps that help us find the quotient and remainder when one number is divided by another. In this article, we will explore the 5 steps of long division, and provide examples to illustrate each step.
Step 1: Write the Dividend, Divisor, and Quotient
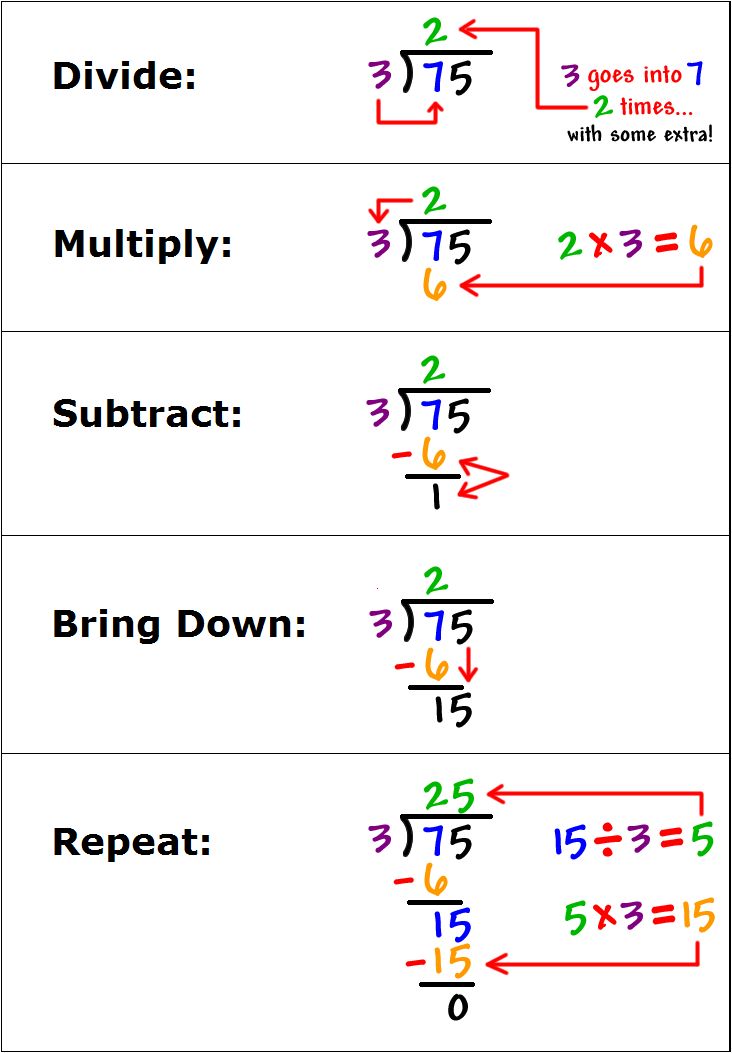
The first step in long division is to write the dividend (the number being divided), the divisor (the number by which we are dividing), and the quotient (the result of the division). We start by writing the dividend on top of a line, and the divisor below it. The quotient will be written above the line. For example, if we want to divide 432 by 12, we would write:
| ___ | 12 |
| 432 |

Step 2: Divide the First Digit of the Dividend

The next step is to divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor. In our example, we would divide 4 (the first digit of 432) by 12. Since 12 does not go into 4, we would write 0 on top of the line, and multiply 12 by 0 to get 0. We would then subtract 0 from 4, and write the result below the line.
| 0 | 12 |
| 432 | |
| -0 | |
| 4 |
Step 3: Bring Down the Next Digit

The next step is to bring down the next digit of the dividend. In our example, we would bring down the 3, and add it to the result from the previous step. We would then divide the new number by the divisor, and write the result on top of the line.
| __ | 12 |
| 432 | |
| -0 | |
| 43 |
Step 4: Multiply and Subtract

The next step is to multiply the divisor by the result from the previous step, and subtract the product from the new number. In our example, we would multiply 12 by 3 (the result from the previous step), and subtract the product from 43. We would then write the result below the line.
| 3 | 12 |
| 432 | |
| -36 | |
| 7 |
Step 5: Bring Down the Next Digit and Repeat

The final step is to bring down the next digit of the dividend, and repeat the process. In our example, we would bring down the 2, and add it to the result from the previous step. We would then divide the new number by the divisor, and write the result on top of the line.
| 36 | 12 |
| 432 | |
| -360 | |
| 72 |
📝 Note: The result of the division is 36, with a remainder of 0.
As we can see, long division involves a series of steps that help us find the quotient and remainder when one number is divided by another. By following these 5 steps, we can perform long division with ease and accuracy.
To summarize, the key points of long division are: * Write the dividend, divisor, and quotient * Divide the first digit of the dividend * Bring down the next digit and repeat * Multiply and subtract * Bring down the next digit and repeat
These steps will help you master the concept of long division and solve problems with ease.
What is the purpose of long division?

+
The purpose of long division is to find the quotient and remainder when one number is divided by another.
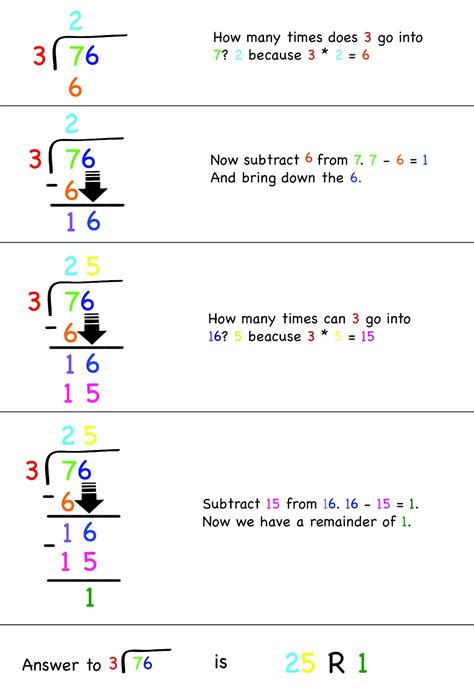
How many steps are involved in long division?
+
There are 5 steps involved in long division: write the dividend, divisor, and quotient, divide the first digit of the dividend, bring down the next digit, multiply and subtract, and bring down the next digit and repeat.
What is the result of the division in the example above?

+
The result of the division is 36, with a remainder of 0.