Master Line Plot Fractions with Our Fun Worksheet

Line plots, often referred to as dot plots, are a vital tool for understanding data distribution, frequency, and patterns. Whether you're a teacher, student, or data enthusiast, mastering line plot fractions can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and represent data. This blog post will guide you through the fascinating world of line plots, providing you with practical worksheets and tips to master this statistical representation.
Why Line Plots are Essential

Line plots are one of the simplest yet most effective ways to visually represent data:
- Visual Representation: They provide an immediate visual of data distribution, which is easier to interpret than raw data.
- Spotting Patterns: Trends, gaps, clusters, or outliers become evident at a glance.
- Simplicity: Their construction and interpretation require minimal mathematical sophistication.
Understanding Line Plot Fractions
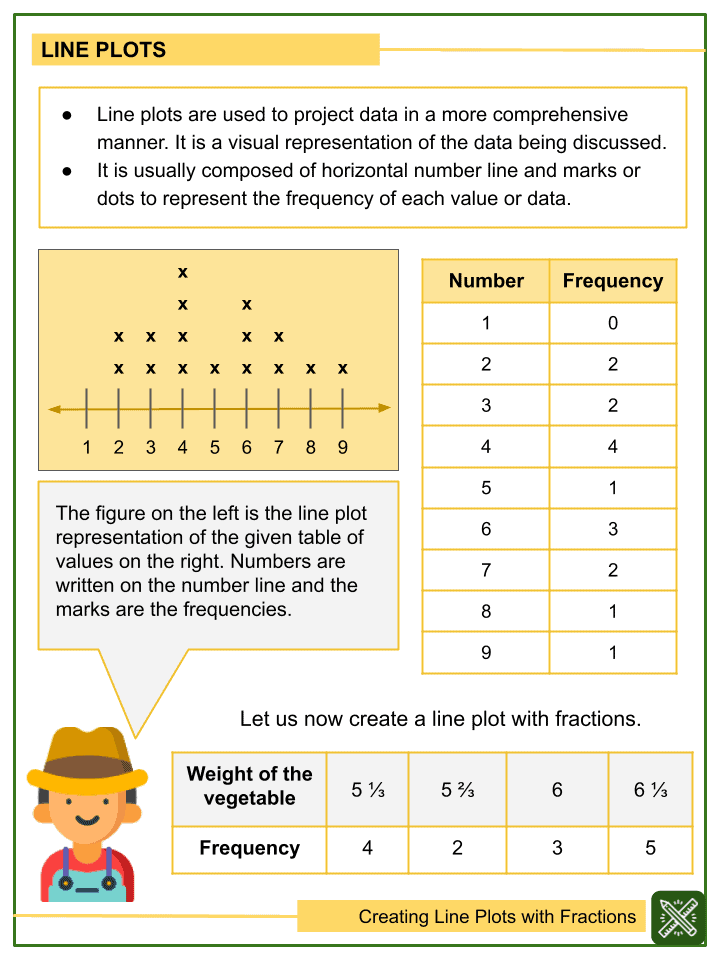
Line plots involve marking data points on a number line, often dealing with fractions. Here’s how you can understand and create line plots:
- Gather Data: Start with a set of data, typically fractional numbers.
- Number Line: Create a horizontal line and mark intervals.
- Plot Data: Each data point is represented by placing an "x" above the appropriate number on the line.
- Label Axes: Clearly label your number line to ensure readability.
Practical Worksheet for Line Plot Fractions

| Step | Activity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Collection | Ask students to measure the length of leaves they find, recording the measurements in fractions of an inch. |
| 2 | Constructing the Plot | Create a number line from 0 to 1 in increments of 1/4 inches. Place each measurement on the line. |
| 3 | Analysis | Discuss what the plot reveals about the data. Look for clusters or patterns. |

Here's a sample line plot worksheet:
Let’s say students measure leaf lengths and get the following: 3/4, 1/2, 3/4, 1/4, 1/2, 1/4, 5/8, 1/2.
0 1/4 1/2 3/4 1
x x xxx xx
Tips for Mastering Line Plot Fractions

- Use Real Data: Real-world measurements make the concept tangible and engaging.
- Label Correctly: Make sure your labels are clear to avoid confusion.
- Scale Appropriately: Choose increments on the number line that best represent your data set's range.
- Encourage Discussion: Use the line plot as a discussion point to draw insights.
📚 Note: When working with line plots, encourage students to explain their findings, fostering a deeper understanding of data analysis.
In summary, line plots are a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding fractional data. Through practical worksheets, like the one provided, and by applying the tips shared, both students and educators can master the art of line plot fractions, making data analysis both fun and educational.
What is the difference between a line plot and a bar chart?

+
A line plot uses a number line to display individual data points while a bar chart uses vertical or horizontal bars to show categorical or continuous data comparison.
Can I use decimal numbers instead of fractions in a line plot?

+
Yes, line plots can also use decimals for precision. However, using fractions might be more intuitive for visualizing parts of a whole.
How do line plots help in understanding data distribution?

+
Line plots visually depict the frequency of each value, allowing you to see where data points cluster, any gaps, and the overall shape of data distribution.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating line plots?

+
Common mistakes include not scaling the number line correctly, misplacing points, and failing to label the axis clearly, which can mislead the viewer’s interpretation of the data.
How can I use line plots in everyday life?

+
Line plots can be used for tracking daily expenses, analyzing test scores, recording weather data, or even to show how often you accomplish certain tasks over time.