7 Simple Tips for Line Graphs Worksheets

Understanding Line Graphs
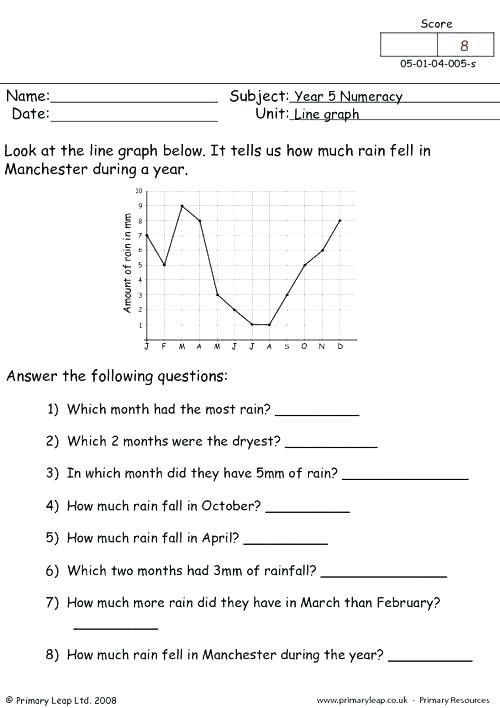
Line graphs are a pivotal tool in visual data representation, particularly when tracking changes over continuous intervals such as time. Whether in business, science, or finance, line graphs provide a clear way to see trends, fluctuations, and patterns at a glance. This post will guide you through seven simple tips to ensure your line graphs worksheets are both effective and engaging for all audiences.
Tip #1: Keep Your Data Focused
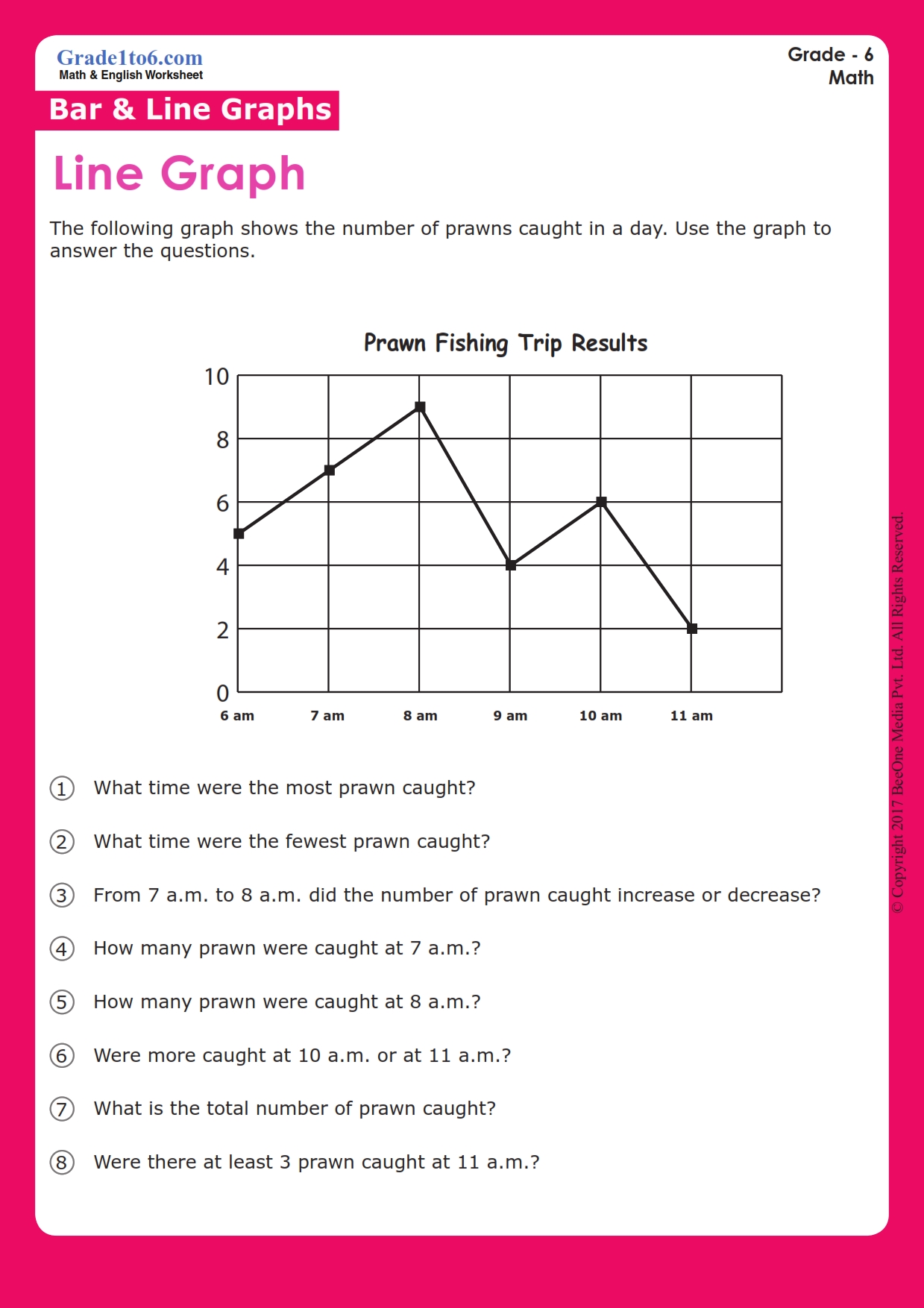

Start by selecting data that is relevant to the story you wish to tell. Clutter can make graphs difficult to interpret. Here’s how to maintain focus:
- Choose Relevant Variables: Ensure each variable shown is crucial to your narrative.
- Limit Time Frame: Avoid long timelines unless necessary. Shorter periods can help highlight trends more effectively.
- Use Filtering: If dealing with large datasets, apply filters to show only pertinent information.
💡 Note: Less is more; a graph with fewer lines can convey trends more clearly.
Tip #2: Choose an Appropriate Scale
| Scale Type | When to Use |
|---|---|
| Linear Scale | When data points are evenly spaced |
| Logarithmic Scale | For data showing exponential growth or decline |
| Broken Axis | To handle a few outliers without losing the overall trend |
Selecting the right scale ensures that your line graph accurately reflects the data’s nature:
- Assess Data Distribution: Look for skewness or exponential patterns before deciding on the scale.
- Start Axis at Zero: This prevents exaggeration of fluctuations unless there’s a strong reason to do otherwise.
Tip #3: Use Consistent Colors and Markers


Visual consistency helps in reducing cognitive load for viewers:
- Choose a Color Palette: Use similar color tones for related data points.
- Marker Styles: Differentiate lines with unique marker styles (circles, squares, etc.)
- Color Blindness: Ensure your colors are distinguishable for color-blind individuals.
Tip #4: Label Clearly

Good labeling is essential for quick understanding:
- Data Labels: Include labels for critical points or key data sets.
- Axis Titles: Make them brief yet informative, indicating units of measure.
- Legend Placement: Place the legend in a way that does not overlap with data or disrupt the graph’s readability.
Tip #5: Add Context with Annotations

Annotations provide context, making your graph tell a story:
- Highlight Significant Events: Use arrows or text boxes to point out key events or changes.
- Date Markers: Add vertical lines or points to show significant dates or periods.
- Notes: Provide brief explanatory notes where necessary.
🛑 Note: Keep annotations concise to avoid cluttering the graph.
Tip #6: Maintain Clean Presentation


Your line graph should be visually appealing and easy to interpret:
- Avoid Chart Junk: Remove unnecessary grid lines, shadows, or 3D effects.
- Consistent Font: Use a readable font size and style throughout the graph.
- Background: Keep it clean and white; if needed, use a subtle color gradient for distinction.
Tip #7: Utilize Interactive Elements

In today’s digital age, interactive elements can enhance data exploration:
- Hover Information: Implement tooltips to show exact values on hover.
- Zoom and Pan: Allow users to zoom in or pan to explore data in detail.
- Dynamic Filters: Offer filters to let users view specific parts of the data.
In wrapping up, mastering the creation of line graphs worksheets requires attention to detail in every aspect, from choosing relevant data to ensuring interactive elements enhance user engagement. By adhering to these seven tips, you’ll not only create graphs that are visually appealing but also charts that effectively communicate insights and trends, making them useful in reports, presentations, and even educational settings. Remember, the key to successful line graphs lies in clarity, simplicity, and the ability to tell a compelling story through data visualization.
Why should I use a logarithmic scale in my line graph?

+
A logarithmic scale is particularly useful when dealing with data that shows exponential growth or decline. It helps in visualizing large differences in magnitude without skewing the interpretation of the data.
How do I handle outliers in a line graph?

+
Outliers can be handled by using a broken axis to focus on the primary trend while still indicating where outliers occur. Another approach is to use secondary axes or annotations to point out these outliers without affecting the main graph’s scale.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when creating line graphs?
+
Common pitfalls include overcomplicating the graph with too many variables, using non-representative scales, neglecting clear labeling, and not providing enough context. Clutter and chart junk can also detract from the graph’s clarity and effectiveness.