5 Tips for Solving Limiting Reactant Problems Fast

5 Proven Strategies to Solve Limiting Reactant Problems Faster

Chemistry can be a challenging subject, but understanding how to quickly solve limiting reactant problems can make it much less daunting. These calculations are fundamental in stoichiometry, a key area in chemistry education. This guide will present you with five effective tips to streamline your approach to solving these problems, allowing you to conquer them with confidence.
Understand The Concept

Before diving into tips for quick solutions, let’s briefly review what a limiting reactant is. A limiting reactant is the reactant in a chemical reaction that is completely consumed, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. Here’s how you can understand this better:
- Identify the chemical equation: Know the balanced equation of the reaction.
- Determine the moles: Convert given masses to moles using molar mass.
- Compare ratios: Use the coefficients from the balanced equation to find the mole ratio.
Tip #1: Start with a Molar Ratio
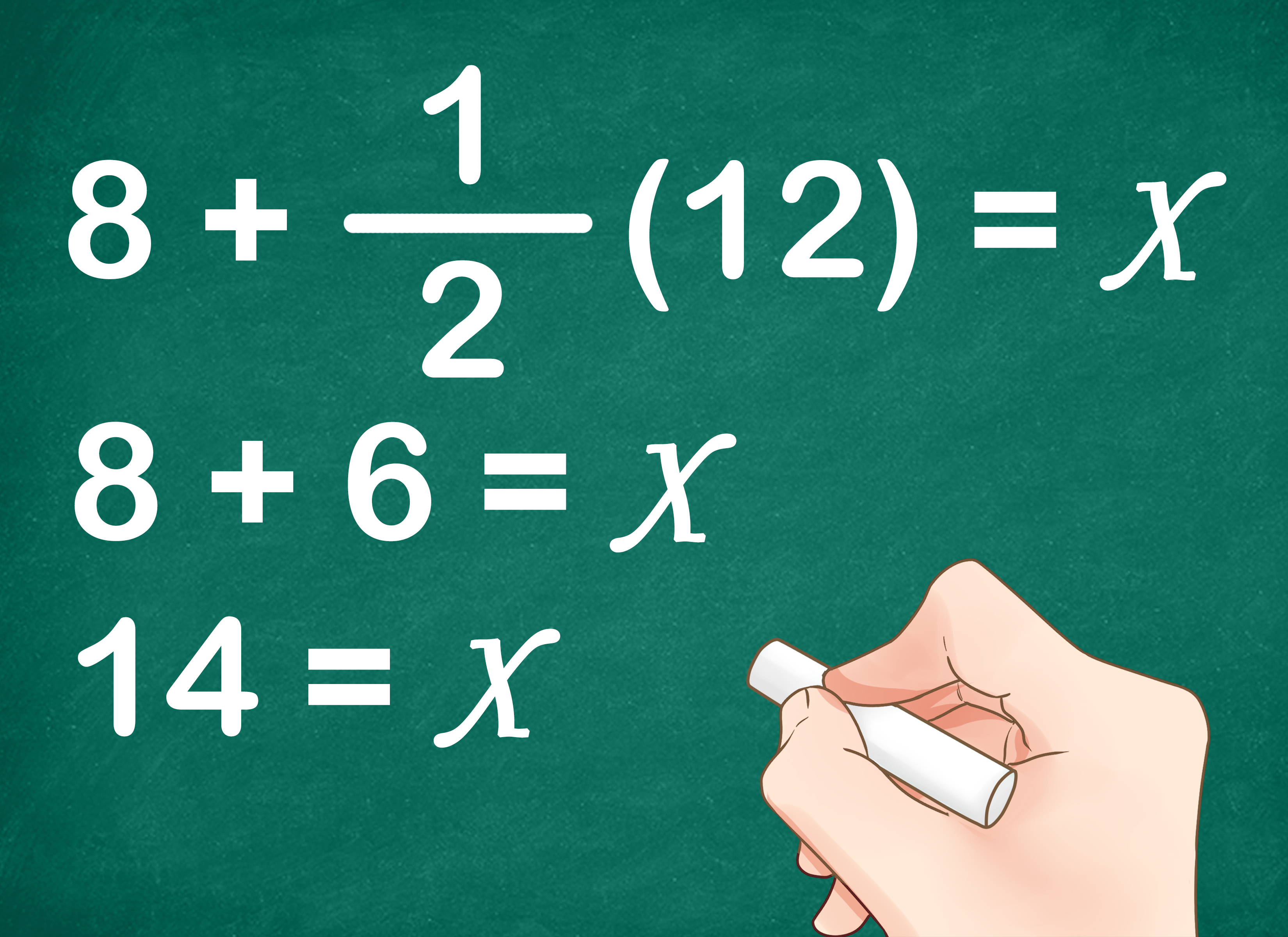
Immediately converting the quantities of reactants to moles and using the balanced equation to calculate the molar ratio is an effective start. This strategy helps in:
- Quickly comparing how much product each reactant can produce.
- Identifying which reactant runs out first, hence limiting the reaction.
- Streamlining your calculations by avoiding unnecessary steps.
Tip #2: Use Dimensional Analysis

Dimensional analysis, or the factor-label method, is an indispensable tool for quick calculations in chemistry. Here’s how you can apply it:
- Set up your calculations so that units cancel out.
- Work from the known quantity to the unknown using conversion factors derived from the balanced equation.
- Example: Converting grams to moles, moles to grams, etc., ensuring that the units you need end up in the final answer.
Tip #3: Memorize Common Stoichiometric Ratios

Many reactions have commonly occurring stoichiometric ratios. Knowing these by heart can expedite your problem-solving:
- Combustion reactions typically have a 1:3 or 1:2 ratio of hydrocarbon to oxygen.
- Acid-base neutralization often follows a 1:1 stoichiometry.
💡 Note: While memorizing is useful, ensure you can apply these ratios accurately in context.
Tip #4: Utilize Calculators or Apps

In the age of technology, using calculators or apps designed for stoichiometric calculations can save time. Here are some steps to consider:
- Input the balanced equation directly into the app or calculator.
- Let the technology perform complex calculations for you, ensuring accuracy.
- Focus on interpreting results rather than doing all the math by hand.
Tip #5: Practice with Different Scenarios

Finally, the key to mastering any type of problem in chemistry is practice. Here’s how to make it efficient:
- Use online resources or textbooks for a variety of problems.
- Work through problems under timed conditions to simulate exam pressure.
- Revise common pitfalls like forgetting to balance the equation or misinterpreting units.
💡 Note: Diversify your practice scenarios to enhance your problem-solving versatility.
By applying these tips, you're setting yourself up for success in tackling limiting reactant problems swiftly and accurately. Understanding the theoretical foundations alongside mastering these practical strategies will ensure you not only perform well in exams but also build a solid understanding of chemistry. In summary, the journey involves recognizing the importance of quick conversion to moles, leveraging dimensional analysis for clear and correct calculations, committing common stoichiometries to memory, embracing technology, and honing your skills through varied practice. With these strategies, you're well-equipped to solve limiting reactant problems with confidence and speed.
Why is the concept of a limiting reactant important in stoichiometry?

+
The concept of a limiting reactant is vital because it determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed in a chemical reaction. It also helps in understanding reaction efficiency and identifying which reagent controls the overall reaction rate and yield.
Can I use a calculator for all types of stoichiometric calculations?

+
Yes, but understanding the underlying principles is crucial. Calculators and apps are tools to aid your work, not replace your knowledge. They can perform complex operations quickly, but you should know how to interpret the results and set up the problems correctly.
What is the quickest way to identify the limiting reactant in a problem?
+
One of the quickest ways is to convert the quantities of all reactants to moles and compare the mole ratio from the balanced chemical equation. The reactant that produces the least amount of product based on this ratio is typically the limiting reactant.