Lewis Structure Worksheet

Introduction to Lewis Structures

Lewis structures are a way to represent the covalent bonds between atoms in a molecule. They are used to predict the shape of a molecule and to identify the types of bonds that are present. A Lewis structure is a two-dimensional representation of a molecule that shows the arrangement of electrons around the atoms.
How to Draw Lewis Structures

To draw a Lewis structure, you need to follow these steps: * Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. * Draw the skeleton of the molecule, showing the arrangement of the atoms. * Add electrons to the molecule, starting with the atoms that have the lowest electronegativity. * Use single bonds to connect the atoms, and add lone pairs to the atoms that have more electrons than they need to form bonds. * Check the octet rule to make sure that each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell.
Types of Lewis Structures
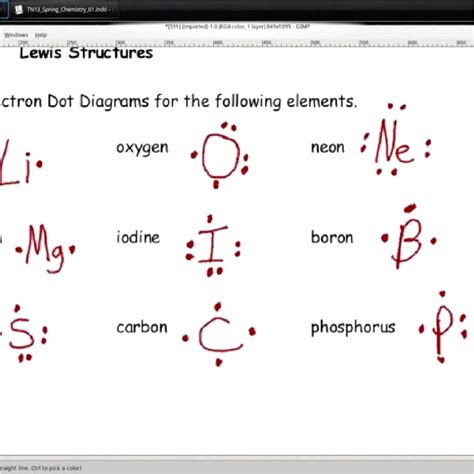
There are several types of Lewis structures, including: * Skeletal structures, which show the arrangement of the atoms in the molecule. * Expanded structures, which show all of the electrons in the molecule. * Condensed structures, which show the arrangement of the atoms and the bonds between them, but do not show all of the electrons.
Practice Drawing Lewis Structures
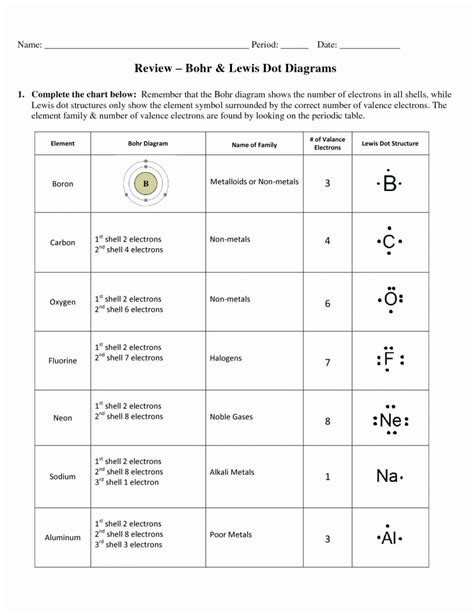
Here are some examples of molecules to practice drawing Lewis structures: * CO2 (carbon dioxide) * H2O (water) * CH4 (methane) * NH3 (ammonia) * C2H4 (ethylene)
💡 Note: When drawing Lewis structures, make sure to follow the octet rule and to show all of the electrons in the molecule.
Tips for Drawing Lewis Structures
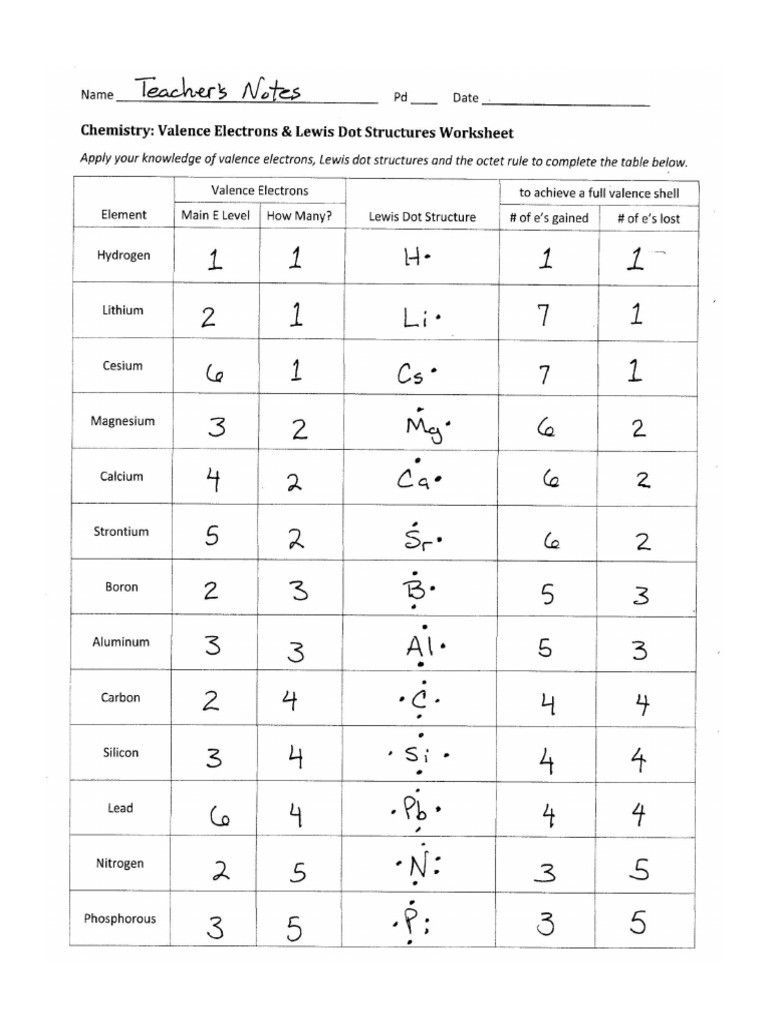
Here are some tips to keep in mind when drawing Lewis structures: * Always start by drawing the skeleton of the molecule. * Use single bonds to connect the atoms, and add lone pairs to the atoms that have more electrons than they need to form bonds. * Check the octet rule to make sure that each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell. * Use brackets to indicate the presence of ions or charges in the molecule. * Use arrows to indicate the direction of electron movement in the molecule.
| Molecule | Number of Valence Electrons | Number of Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 16 | 4 |
| H2O | 8 | 2 |
| CH4 | 8 | 4 |
| NH3 | 8 | 3 |
| C2H4 | 12 | 5 |

In summary, Lewis structures are a powerful tool for understanding the arrangement of electrons in a molecule. By following the steps outlined above and practicing with different molecules, you can become proficient in drawing Lewis structures and using them to predict the shape and properties of molecules. The key points to remember are to always follow the octet rule, to use single bonds and lone pairs to represent the electrons in the molecule, and to check your work carefully to make sure that the Lewis structure is correct.
What is the purpose of drawing Lewis structures?

+
The purpose of drawing Lewis structures is to represent the covalent bonds between atoms in a molecule and to predict the shape of the molecule.
How do I determine the number of valence electrons in a molecule?

+
To determine the number of valence electrons in a molecule, you need to count the number of valence electrons for each atom in the molecule and add them together.
What is the octet rule?

+
The octet rule states that each atom in a molecule should have eight electrons in its outer shell, which is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of a noble gas atom.