5 Ways to Master Lewis Dot Structures Easily
The mastery of Lewis dot structures is an invaluable skill for students and chemists alike, enabling a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and molecular structure. This blog post offers a comprehensive guide to mastering Lewis dot structures through five effective methods, making this often-intimidating topic accessible to everyone.
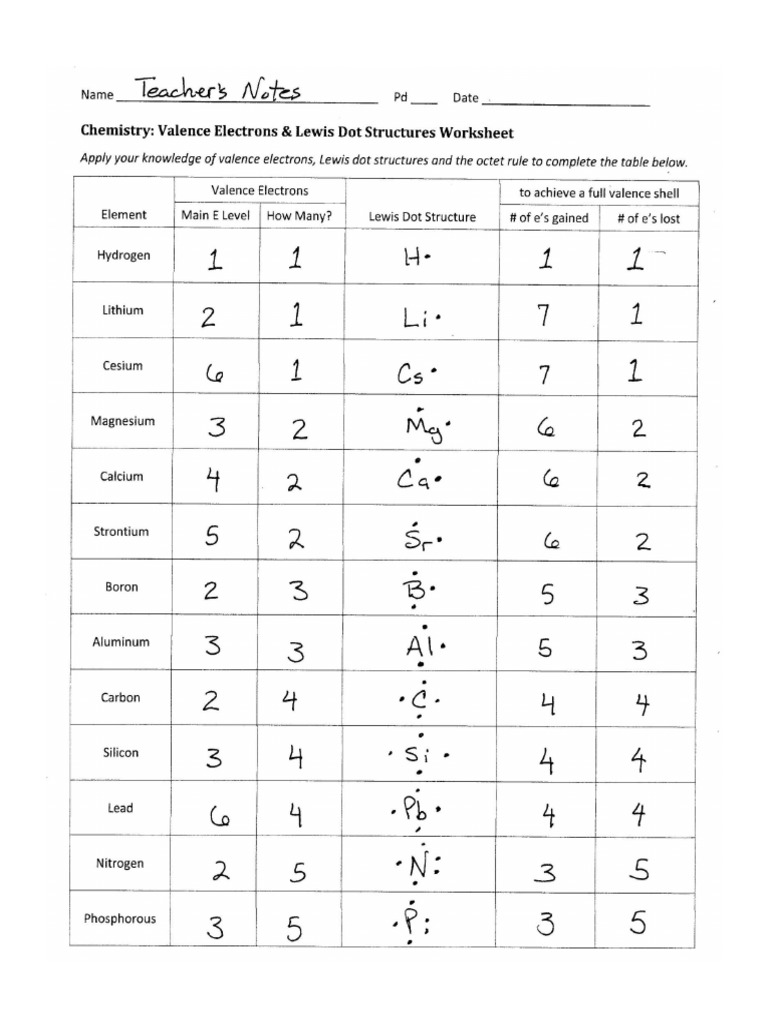
1. Understanding the Basics of Atomic Structure
Before diving into Lewis structures, one must first grasp the basic principles of atomic structure. Here’s a quick primer:
- Electrons: These negatively charged particles orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
- Nucleus: Composed of protons and neutrons; it’s the core around which electrons orbit.
- Valence Electrons: The electrons in the outermost shell are pivotal for chemical bonding.
💡 Note: Recognizing the number of valence electrons is key since these are the electrons involved in the formation of chemical bonds.
2. The Octet Rule - Your Roadmap to Bonding

At the heart of Lewis structures lies the octet rule, which posits that atoms tend to:
- Combine in such a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell to achieve stability similar to that of the noble gases.
- Exceptions exist, notably with hydrogen (2 electrons) and some elements with expanded octets or incomplete octets.
Learning this rule simplifies the process of drawing Lewis structures significantly, providing a clear guideline for determining bonding possibilities.
3. Practice with Simple Molecules

Start your journey by focusing on straightforward molecules like:
- H2 (Hydrogen)
- F2 (Fluorine)
- CH4 (Methane)
Follow these steps:
- Count Valence Electrons: Sum the valence electrons for all atoms in the molecule.
- Determine the Skeleton: Use the elements’ periodic table positions to infer atom connectivity.
- Arrange Electrons: Begin with single bonds, then distribute the remaining electrons to achieve octets.
- Check Octets: Ensure each atom has 8 electrons, except for hydrogen, which only needs 2.
💡 Note: Practice makes perfect. Start with simple molecules and gradually increase complexity as you become more comfortable.
4. Leveraging Formal Charges

Formal charges help to:
- Determine which Lewis structure is most plausible when multiple configurations exist.
- Identify the atom’s electron environment and anticipate potential chemical behavior.
Calculate formal charges with this formula:
- Formal Charge = Valence electrons - Non-bonding electrons - 1⁄2(Bonding electrons)
Optimal structures have:
- Formal charges closest to zero for each atom.
- Formal charges distributed in a way that reflects electronegativity (more negative charges on more electronegative atoms).
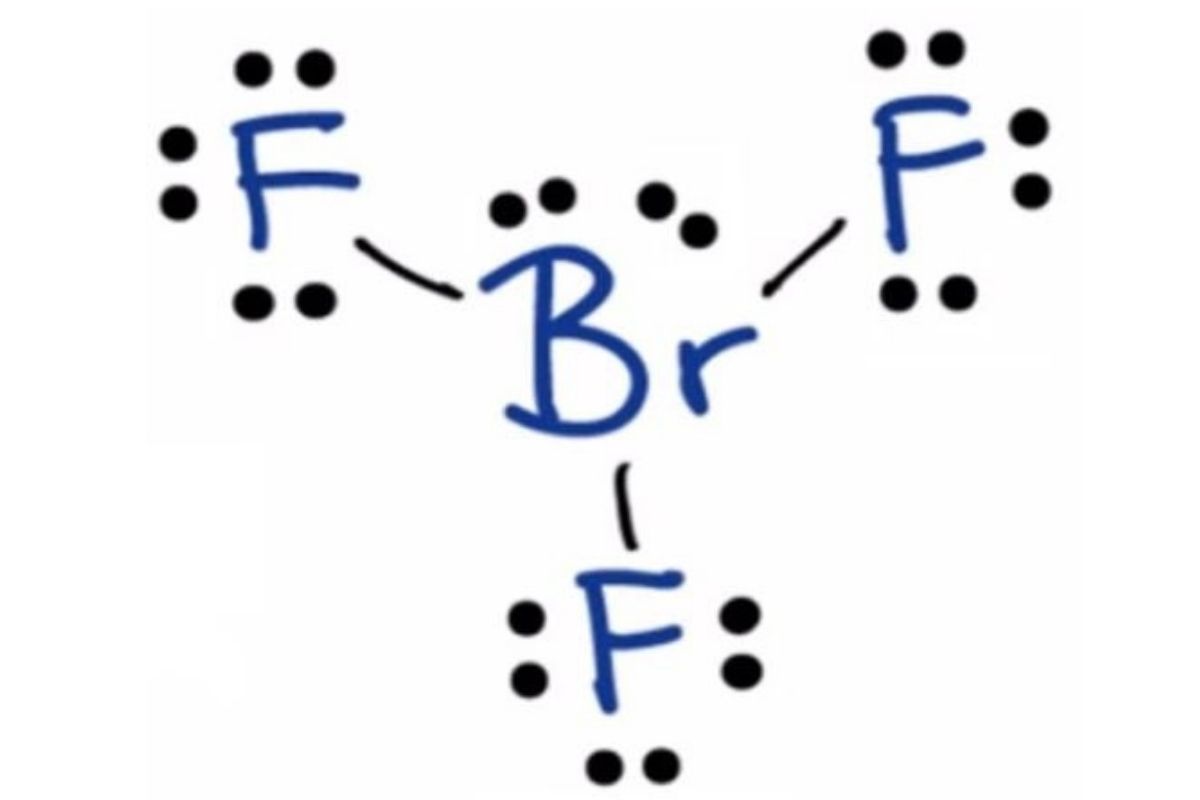
5. Expand Your Toolbox - Additional Techniques

To further enhance your mastery over Lewis dot structures, consider these additional techniques:
- Resonance Structures: Understand how multiple valid Lewis structures can exist for some molecules to minimize formal charges and achieve octets where possible.
- Radical Species: Recognize that not all molecules follow the octet rule; free radicals have an unpaired electron.
- Expanded Octets: For elements beyond the second row, allow for more than 8 electrons, like sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
💡 Note: Mastering these techniques requires practice, but they’ll make you versatile in handling diverse chemical scenarios.
In summary, mastering Lewis dot structures involves understanding atomic basics, adhering to the octet rule, practicing with simple to complex molecules, using formal charges to refine structures, and expanding your knowledge with additional concepts. These five methods provide a structured approach to mastering a topic fundamental to chemistry, paving the way for a deeper comprehension of molecular structure and reactivity.
What is the importance of valence electrons in Lewis structures?

+
Valence electrons are crucial in Lewis structures as they determine the atom’s capacity to form bonds. Only these electrons participate in chemical bonding, influencing the molecule’s shape and reactivity.
Why doesn’t the octet rule always apply?

+
While the octet rule simplifies the drawing of Lewis structures, it has exceptions due to elements’ unique electron configurations or molecular geometry constraints, like hydrogen needing only two electrons or expanded octets in some molecules.
How can I practice drawing Lewis structures effectively?

+
Practice by starting with simple molecules, gradually increasing complexity. Reviewing your work against accurate models or molecular simulations can help refine your technique.