Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet Answers Revealed
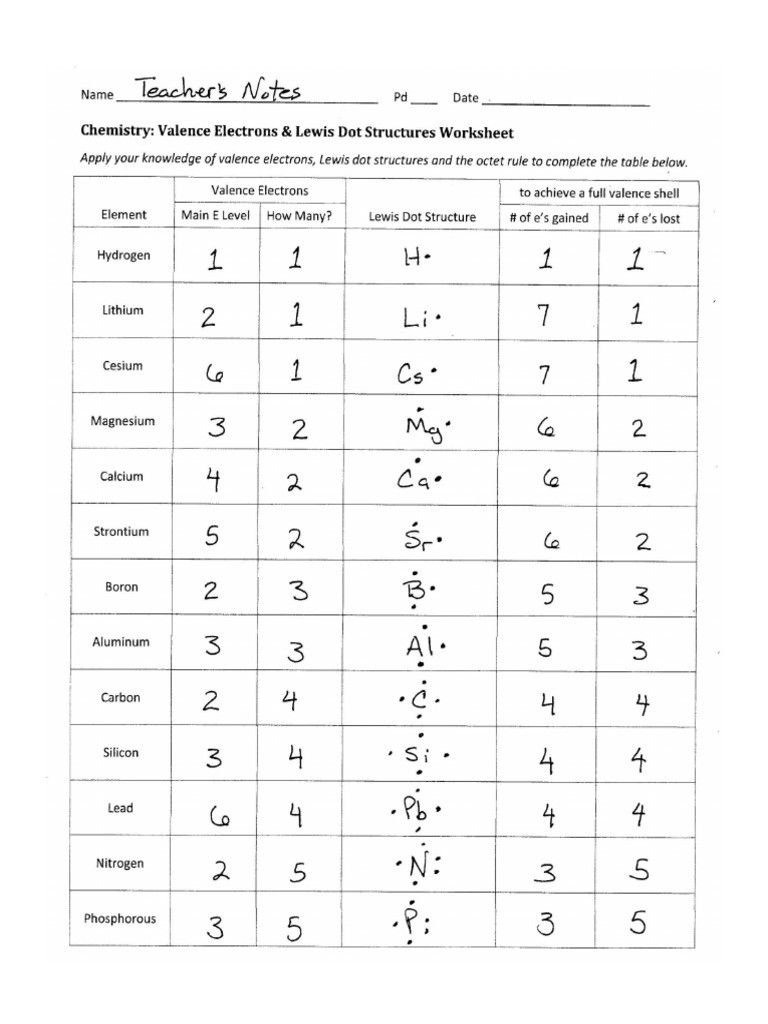
Lewis dot diagrams, also known as Lewis structures or electron dot structures, are fundamental in chemistry for depicting the valence electrons surrounding atoms, molecules, or ions. Understanding how to construct these diagrams not only helps in visualizing chemical bonding but also in predicting molecular behavior. This article will guide you through creating Lewis dot diagrams, provide you with detailed answers for common elements, and explain why this knowledge is vital for students and professionals alike.
What is a Lewis Dot Diagram?

A Lewis dot diagram is a graphical representation used to visualize the arrangement of atoms and the bonding between them. Here’s what you need to know:
- Valence Electrons: These are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which are crucial in chemical reactions.
- Electron Dots: Each dot represents one valence electron, placed around the symbol of the atom in pairs or singly.
- Octet Rule: Most atoms aim to achieve a full octet of electrons (8 electrons) to become stable, similar to the noble gases.

Constructing a Lewis Dot Diagram

To draw a Lewis dot diagram, follow these steps:
- Determine the number of valence electrons by identifying the element’s group number from the periodic table.
- Write the atomic symbol in the center.
- Place the valence electrons as dots around the atomic symbol, starting from the top and moving clockwise. Fill in each side before pairing.
🎓 Note: Keep in mind that for elements in group 1 and 2, you might not need to pair up any electrons as they have fewer than four valence electrons.
Examples of Lewis Dot Diagrams for Common Elements

Let’s look at some Lewis dot diagrams for commonly encountered elements:
- Hydrogen (H): Has 1 valence electron. Thus, its diagram is simply:
H · 
- Helium (He): This noble gas has a full shell with 2 valence electrons:
· · He - Carbon ©: With 4 valence electrons, carbon’s diagram shows these electrons in pairs:
· · C · · - Oxygen (O): Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. Its structure would look like:
· · · O · · ·
Why Lewis Dot Diagrams Matter
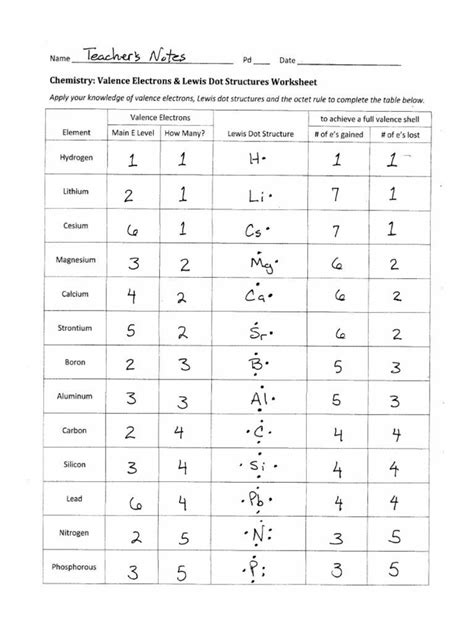
Understanding Lewis dot diagrams:
- Helps predict chemical reactivity based on the electron configuration.
- Assists in visualizing bonding—single, double, or triple bonds in molecules.
- Enables the determination of the shape of molecules (VSEPR theory).
- Is crucial in teaching basic chemical principles to new learners.
⚠️ Note: Be careful not to exceed the octet rule unless dealing with elements like boron or phosphorus which can handle an extended octet.
Common Mistakes in Lewis Structures

Here are some frequent errors to avoid:
- Overfilling Shells: Remember to limit the valence electrons to 8 unless dealing with exceptions.
- Underestimating Shared Electrons: Each bond counts for two electrons in the valence shell.
- Misplacing Dots: Always place lone pairs first before bonds.
- Forgetting Formal Charges: Especially important when dealing with ions or compounds like oxides.
In wrapping up, Lewis dot diagrams serve as a visual tool to better understand the basics of molecular structure, bonding, and chemical reactivity. By mastering these diagrams, students and chemists can more easily navigate the complex world of chemical reactions, molecule shape, and behavior. Remember, practice makes perfect in drawing accurate Lewis structures, and understanding the fundamental concepts behind them will enhance your overall comprehension of chemistry. Now, with this in-depth knowledge, you're well-equipped to handle even the most intricate of chemical problems.
Why do atoms follow the octet rule?
+
Atoms follow the octet rule to achieve stability similar to the noble gases, which have a full outer shell of electrons. This leads to lower energy states and thus, greater stability.
How do you determine the number of valence electrons for an element?

+
The number of valence electrons for an element can be determined by looking at the group number in the periodic table. For most elements, the group number equals the number of valence electrons, except for the transition metals where it’s more complex.
What do unpaired electrons signify in a Lewis dot diagram?

+
Unpaired electrons in a Lewis dot diagram represent electrons available for bonding. An atom with unpaired electrons will generally participate in chemical reactions to bond with other atoms and achieve a more stable configuration.