5 Tips for Perfect Muscle Labelling Worksheets
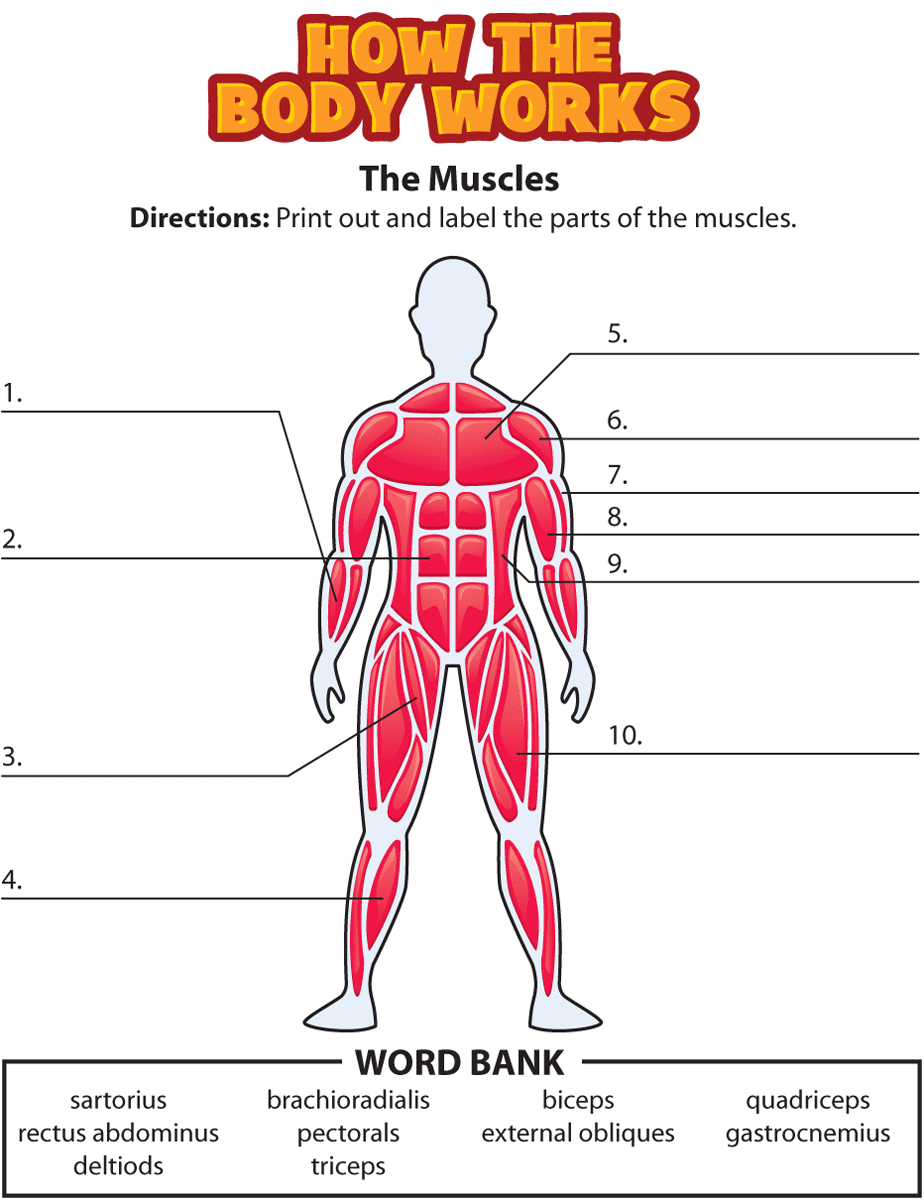
Creating muscle labelling worksheets can be an excellent educational tool for students studying anatomy or anyone interested in the human musculoskeletal system. These worksheets not only help in memorizing muscle names and locations but also aid in understanding the relationships and functions of these muscles. Here are five detailed tips to ensure your muscle labelling worksheets are both educational and engaging.
1. Accuracy in Muscle Depiction

When creating worksheets for muscle labelling, accuracy should be your top priority. Here’s how you can ensure this:
- Use High-Quality Images: Employ clear, high-resolution images of human anatomy. These could be from anatomical atlases, professional photographic sources, or detailed illustrations. Make sure that the images depict the muscles accurately, showing them in their correct anatomical positions.
- Consult Anatomical References: Always cross-reference your images with reliable anatomical textbooks or digital resources. This will help in ensuring that muscles are correctly labelled, with no anatomical discrepancies or errors.
- Anatomical Markers: Use clear markers like points, lines, or colored zones to differentiate muscles, especially where they overlap or when depicting deep muscles beneath superficial ones.
📘 Note: While accuracy is vital, do not compromise the aesthetic appeal, as an engaging visual will encourage better learning outcomes.
2. Tailor to Audience Knowledge

Adjust the complexity of your worksheets based on the educational level of your audience:
- Beginner Worksheets: Label larger, prominent muscles like biceps, triceps, pectorals, etc. Use fewer labels and include hints or cues.
- Intermediate: Introduce more complex muscles, naming conventions, and include small annotations about muscle actions or origins.
- Advanced: Challenge learners with detailed dissections, including deep muscles, muscular actions, and functional anatomy.
Always ensure that the complexity of information correlates with the learner’s knowledge level to make the learning experience effective and enjoyable.
3. Interactive Learning Elements
To make muscle labelling more than just a static exercise:
- Interactive Fill-ins: Provide worksheets where students can drag labels onto the correct muscles or fill in blanks. This active participation reinforces memory and understanding.
- Color Coding: Use different colors to represent different muscle groups or functions, helping students to categorize and remember better.
- Multiple Choice: Include questions where students must choose the correct muscle from a set of options, fostering a deeper understanding of anatomical landmarks.
📕 Note: Interactive elements not only engage students but also make the process of learning more dynamic and fun, which can lead to better retention.
4. Provide Additional Information

Enrich your worksheets with supplemental information:
- Muscle Actions: Describe what each muscle does, like flexion, extension, abduction, etc. This helps in contextual understanding of the muscle’s role in movement.
- Origin and Insertion: Mention where the muscle originates from and where it inserts, as this is crucial for understanding biomechanics.
- Common Injuries: Include notes on typical injuries or conditions associated with specific muscles, giving practical relevance to the anatomy.
| Muscle | Action | Origin | Insertion | Common Injuries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deltoid | Shoulder abduction | Clavicle, scapula | Humerus | Rotator cuff tears |
| Biceps Brachii | Flexion of forearm | Scapula | Radius | Tendon ruptures |
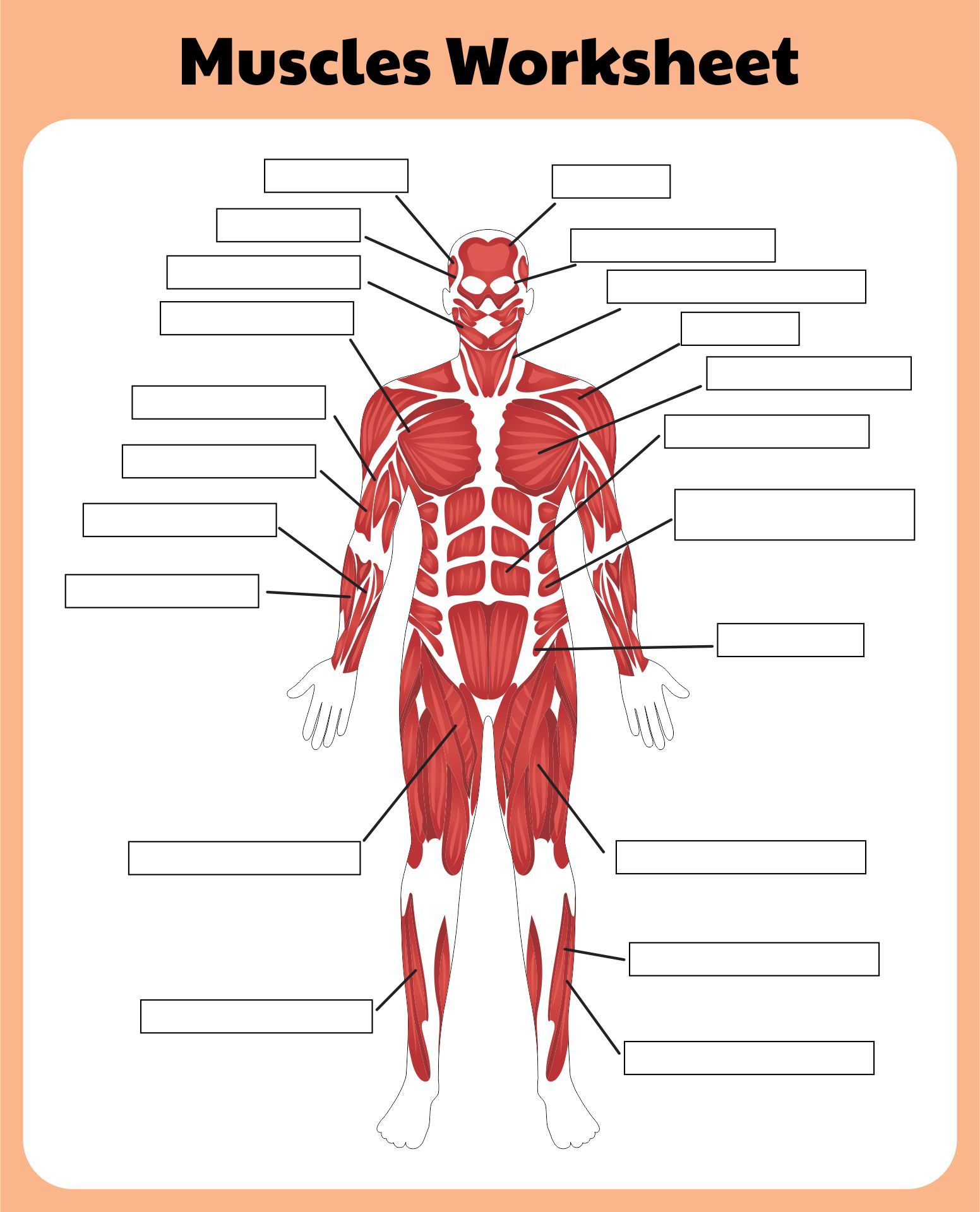
5. Feedback and Assessment

Include ways for learners to get feedback:
- Self-Assessment Keys: Provide answer keys or self-check tools where students can review their answers independently.
- Quizzes and Tests: Design quizzes that can be completed post-worksheet to gauge understanding. These could be in the form of fill-in-the-blanks, matching, or diagram labelling.
- Peer Review: Encourage students to exchange worksheets for peer review, which promotes collaborative learning and can highlight different interpretations or approaches to muscle anatomy.
💡 Note: Feedback is essential for reinforcing learning. It helps learners to see where they excel and where they need improvement.
In summary, by focusing on accuracy, tailoring content to the audience, incorporating interactive elements, enriching worksheets with useful information, and providing mechanisms for feedback, you can create muscle labelling worksheets that are not just educational but also engaging. These practices ensure that students retain more information, understand the complexity of muscle anatomy better, and apply this knowledge in practical scenarios.
How can I ensure the anatomical accuracy of my worksheets?

+
To ensure anatomical accuracy, use reliable anatomical sources for reference, cross-check labels, and consider consulting with an anatomist or a knowledgeable professional in the field of anatomy.
Are there tools or software that can help in creating interactive worksheets?

+
Yes, tools like Adobe Illustrator, Microsoft PowerPoint, or online platforms like Quizlet or Kahoot can be used to design interactive anatomical diagrams and labels.
How can I make muscle labelling interesting for younger students?

+
Incorporate fun elements like puzzles, games, or interactive activities. For instance, you can create a treasure hunt where students label muscles to find clues, making the learning process an adventure.
What are some strategies to cater to students with different learning styles?

+
Include visual aids for visual learners, provide written descriptions for reading/writing learners, and hands-on activities or kinesthetic learning options for tactile learners. Interactive quizzes can also engage auditory learners.



