5 Ways to Teach Ancient China with Maps

Exploring the ancient civilizations of China opens up a world of rich history, diverse cultures, and extensive developments that have shaped the modern world. One of the most engaging ways to teach students about this fascinating era is through the use of maps. Here are five ways to incorporate maps into your lessons on Ancient China:
Understanding Dynasties through Time Maps

Each dynasty in China contributed uniquely to the region’s development, and using time maps can help students visualize these changes:
- Shang Dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BCE): Introduce students to the earliest dynasty with its oracle bones, bronze vessels, and early writing system.
- Zhou Dynasty (1046–256 BCE): Highlight the period of feudalism, the rise of Confucianism, and the concept of the Mandate of Heaven.
- Qin Dynasty (221–206 BCE): Show the unification of China and the construction of the Great Wall.
- Han Dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE): Discuss the expansion of territory, the Silk Road, and advancements in agriculture and technology.
- Other Significant Dynasties: Include maps for the Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties, focusing on their territorial expansions, cultural achievements, and contributions to science and arts.
📝 Note: By overlaying each dynasty’s territory on the same base map, students can see the progression of China’s borders and understand the continuity and changes in governance.
Cultural and Trade Networks

Maps can depict not only political borders but also cultural diffusion and trade routes:
- The Silk Road: Illustrate the network of trade routes connecting China with the Middle East and Europe, highlighting significant cities and commodities exchanged.
- Tea-Horse Road: Explain this important trade route between China and Tibet, focused on tea and horses.
- Maritime Silk Route: Show how trade by sea influenced ancient Chinese society, leading to the development of navigation and maritime technology.
🚂 Note: Use interactive maps where students can click on trade routes to learn about specific goods and their cultural impact.
Geographic Influence on Civilizations

Discuss how geography shaped Chinese history:
- Natural Barriers: Maps can show mountains like the Himalayas, deserts like the Gobi, and rivers like the Yellow and Yangtze, illustrating how these features acted as barriers or cradles for civilization.
- Agricultural Zones: Explain how river systems facilitated agriculture, leading to the development of dense populations and early states.
- Climate Impact: Maps highlighting monsoon seasons and other climatic factors can demonstrate how weather patterns influenced ancient Chinese agriculture and settlement patterns.
Economic Mapping

Use maps to explore economic developments:
| Economic Era | Key Features | Map Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Early Bronze Age | Bronze Casting, Early Irrigation | Regions of earliest metallurgical activities |
| Iron Age | Advanced Agriculture, Trade | Distribution of iron tools and trade cities |
| Classical Era | Paper Making, Silk Production | Manufacturing hubs and raw material sources |
| Medieval Period | Porcelain Production, Maritime Trade | Port cities and distribution of goods |

Innovations and Inventions
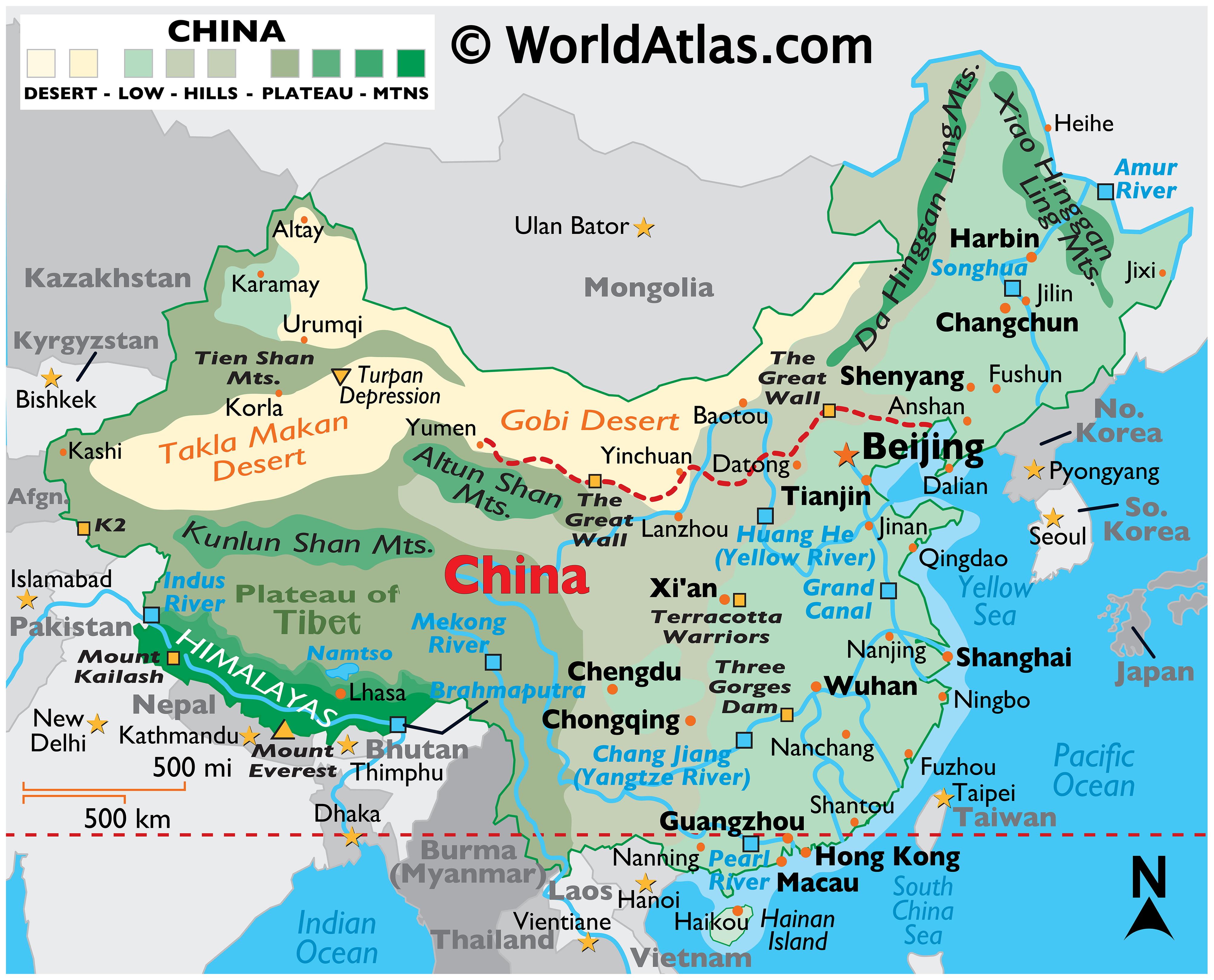
Highlight China’s contributions to science and technology through thematic maps:
- Compass: Trace the spread of the compass from its Chinese origin to the rest of the world.
- Gunpowder: Map the development and spread of gunpowder, impacting military technology and fireworks.
- Printing: Show the diffusion of movable type printing from China to Europe, revolutionizing knowledge dissemination.
Teaching Ancient China through maps not only makes history more tangible but also engaging, allowing students to visually connect with the past. By visualizing dynasties, trade networks, geographic influences, economic changes, and technological innovations, learners gain a deeper appreciation of how ancient Chinese civilization evolved and influenced the world. Maps are not just tools for navigation; they are windows into the complexities of human history, culture, and development.
How can maps be used effectively in the classroom for teaching Ancient China?

+
Maps can be used to illustrate historical events, geographic influences, cultural exchanges, and economic developments. By allowing students to interact with maps, they can explore how different factors contributed to the rise and fall of dynasties, the expansion of territories, and the spread of innovations. This visual aid helps make abstract historical concepts more concrete.
What are some key maps to focus on when teaching Ancient China?

+
Focus on maps that show the territorial extent of various Chinese dynasties, trade routes like the Silk Road, agricultural zones shaped by natural features, and thematic maps showing the spread of Chinese inventions and cultural influences.
Why is geographic influence important in understanding ancient Chinese history?

+
Geography played a pivotal role in shaping Chinese civilization. Mountains, rivers, deserts, and climatic conditions influenced trade, agriculture, warfare, and settlement patterns. Understanding these aspects provides insight into why certain events occurred and why certain cultural practices developed.