Label the Parts of an Animal Cell: Interactive Worksheet
In the fascinating world of biology, understanding the structure of a cell is fundamental to grasping how life functions at its most basic level. An animal cell, unlike plant cells, lacks a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles. Instead, it has unique organelles and features that perform specific functions essential for the cell's survival. Let's dive deep into the animal cell and identify its key components through an interactive worksheet designed to educate and engage students in learning biology interactively.
Overview of Animal Cells

Before we get into labeling the parts, let’s briefly cover what makes an animal cell unique:
- Cell Membrane: Acts as a protective barrier controlling the influx and efflux of substances.
- Cytoplasm: Gel-like substance where cell organelles reside and where most metabolic activities occur.
- Nucleus: Stores genetic material in the form of DNA, directing the cell’s activities.
- Organelles: Special structures within the cell, each with a specific function.
Parts of an Animal Cell

Here’s a table to summarize the main parts of an animal cell:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Protection, boundary control, and communication |
| Nucleus | Contains DNA, controls cell’s activities |
| Cytoplasm | Houses organelles, site of cellular reactions |
| Mitochondria | Powerhouse of the cell, ATP production |
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) | Protein synthesis, modification, and transport |
| Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) | Lipid synthesis, detoxification, calcium storage |
| Golgi Apparatus | Packaging and shipping of cellular products |
| Lysosomes | Breakdown of waste materials and cellular debris |
| Centrioles | Cell division, microtubule organization |
| Endosomes | Sorting and routing of endocytosed materials |

📝 Note: This is not an exhaustive list. Cells vary, and other organelles like peroxisomes, ribosomes, and the cytoskeleton also play crucial roles in cellular functions.
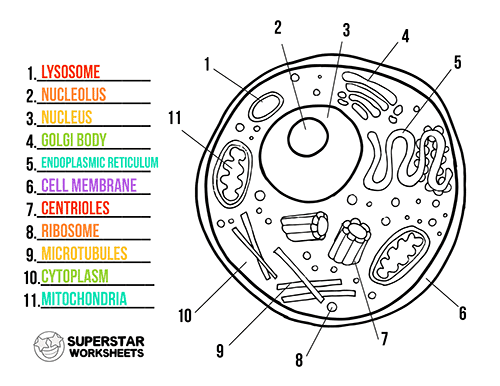
Interactive Labeling Worksheet

Below, you’ll find an interactive worksheet to test your understanding of the parts of an animal cell:
Drag and drop labels to their correct location on the cell:
- Cell Membrane
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Centrioles
- Endosomes
As you engage with this worksheet, remember:
- Cell structures can appear different under various magnifications and preparations for viewing.
- Some organelles are not visible in all cell types.
- Cell biology involves dynamic interactions, not static labels.
Enhancing Learning through Interactive Media

Interactive worksheets, like the one above, serve multiple educational purposes:
- Engagement: Interactive elements make learning more engaging and memorable.
- Understanding: By physically labeling parts, learners better understand the spatial arrangement and function of organelles.
- Feedback: Immediate feedback on label placement enhances learning efficiency.
Summarily, the exploration of an animal cell through interactive learning not only acquaints students with cellular anatomy but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life at the cellular level. The cell, with its intricate organization and dynamic processes, truly is the basic unit of life, where countless biochemical interactions occur to sustain life. This interactive journey through an animal cell elucidates how these tiny structures are paramount in the grandeur of biology, making the microscopic world tangible and exciting for learners of all ages.
Why do cells have membranes?

+
Cell membranes act as selective barriers, protecting the cell from its environment while allowing necessary substances to pass in and out, like nutrients, waste, and signaling molecules.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?

+
The nucleus is like the control center of the cell, storing DNA which contains instructions for cellular functions, growth, repair, and reproduction.
How does the mitochondria generate energy?

+
Mitochondria produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through cellular respiration, a process involving the breakdown of glucose to release energy, often called the “powerhouse” of the cell.
Can animal cells survive without lysosomes?

+
Lysosomes are crucial for breaking down waste materials and cellular debris; their absence can lead to various cellular dysfunctions, but cells have compensatory mechanisms to survive in some conditions.
Why is it important to study cell biology?

+
Understanding cell biology is essential for comprehending how diseases develop, designing targeted therapies, advancing biotechnology, and exploring the origins of life itself.