Kinematics Motion Graphs Worksheet Answers Revealed!
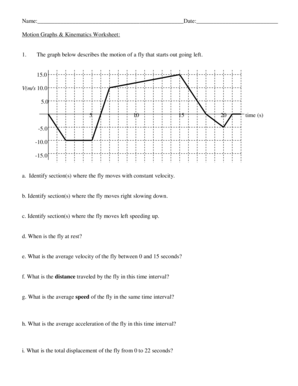
Graphical representation in physics, particularly kinematics, is an invaluable tool for understanding motion dynamics without calculus. Kinematics motion graphs provide a visual snapshot of how objects move over time. This blog post dives deep into the kinematics motion graphs worksheet answers, offering explanations, insights, and step-by-step solutions to better grasp these fundamental concepts.
What are Kinematics Motion Graphs?


Kinematics motion graphs, such as distance-time and velocity-time graphs, are used to depict how position, velocity, and acceleration change over time. Here’s a quick overview:
- Distance-Time Graph: Shows the change in position of an object relative to time. The slope at any point on this graph represents the object’s instantaneous velocity.
- Velocity-Time Graph: Illustrates how an object’s velocity varies with time. The slope here gives the object’s acceleration, and the area under the curve represents the total distance traveled.
- Acceleration-Time Graph: While less common, this graph shows the change in acceleration, where the area under the curve gives the change in velocity.
Analyzing Distance-Time Graphs
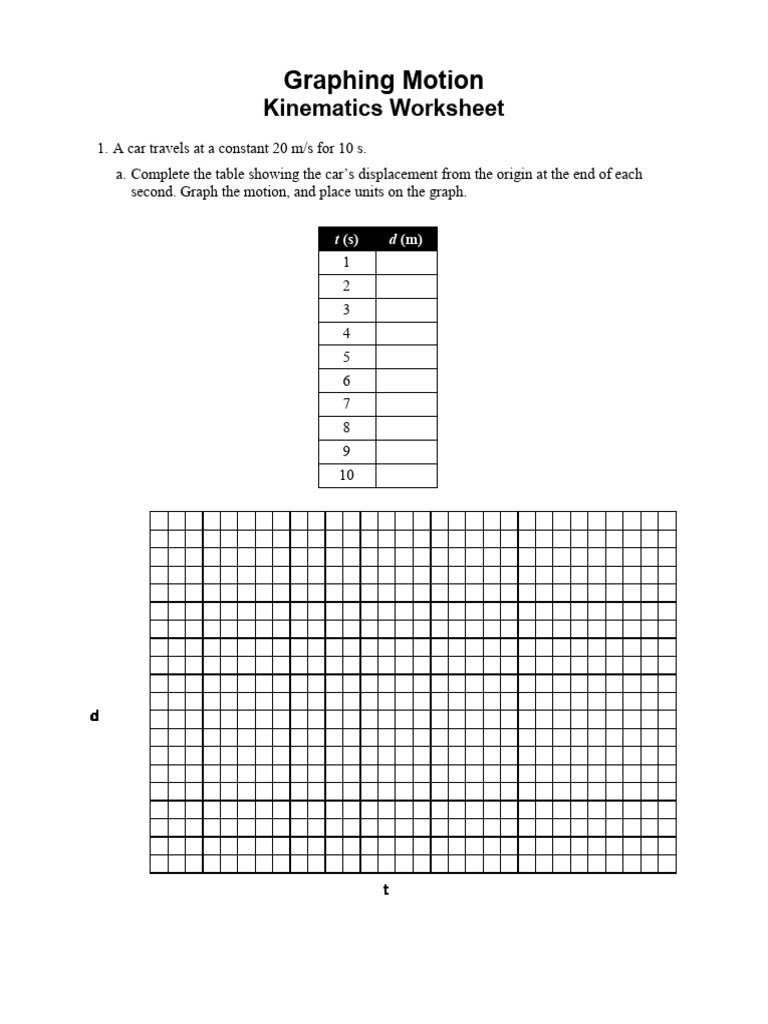
Let’s examine a few sample questions from the kinematics motion graphs worksheet:
| Question | Graph Type | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| What does a straight, slanted line on a distance-time graph indicate? | Distance-Time | Constant velocity |
| What happens if the line curves upward? | Distance-Time | Increasing velocity (acceleration) |
| What does a horizontal line mean? | Distance-Time | Object is stationary |

💡 Note: Remember that the steeper the slope, the greater the velocity of the object.
Understanding Velocity-Time Graphs


Here are some common scenarios on a velocity-time graph:
- A horizontal line indicates constant velocity.
- A straight line with a positive slope means constant positive acceleration.
- A curved line (parabolic shape) can represent changing acceleration.
- The area under the curve gives the displacement.
Practice Examples

Let’s look at some worksheet questions to understand how to read these graphs:
- Question: An object travels at a constant velocity of 4 m/s for 10 seconds. Sketch the velocity-time graph.
- Answer: Plot a horizontal line at 4 m/s from 0 to 10 seconds.
- Question: What is the acceleration of the object if its velocity changes from 3 m/s to 7 m/s over 4 seconds?
- Answer: Use the acceleration formula, (a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}). Here, (a = \frac{7 - 3}{4} = 1 \, \text{m/s}^2).
💡 Note: Always ensure the units are consistent when calculating acceleration from velocity changes.
Mistakes to Avoid

When working with kinematics motion graphs, here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Confusing velocity with speed; remember, velocity has direction.
- Misinterpreting the slope’s meaning on different types of graphs.
- Incorrectly calculating the area under the velocity-time graph for distance when the velocity changes.
Wrapping Up

Analyzing kinematics motion graphs is a key skill for mastering physics. By understanding the relationship between time, distance, velocity, and acceleration, you can predict and explain an object’s motion in various scenarios. This post has provided a comprehensive guide through different graph types, how to interpret them, and common errors to watch out for. With practice, these graphs become an intuitive way to visualize and analyze motion, helping you solve complex problems with ease.
What does a horizontal line on a velocity-time graph represent?

+
A horizontal line on a velocity-time graph indicates that the object is moving with constant velocity. There is no change in velocity, hence no acceleration.
How do you calculate displacement from a velocity-time graph?
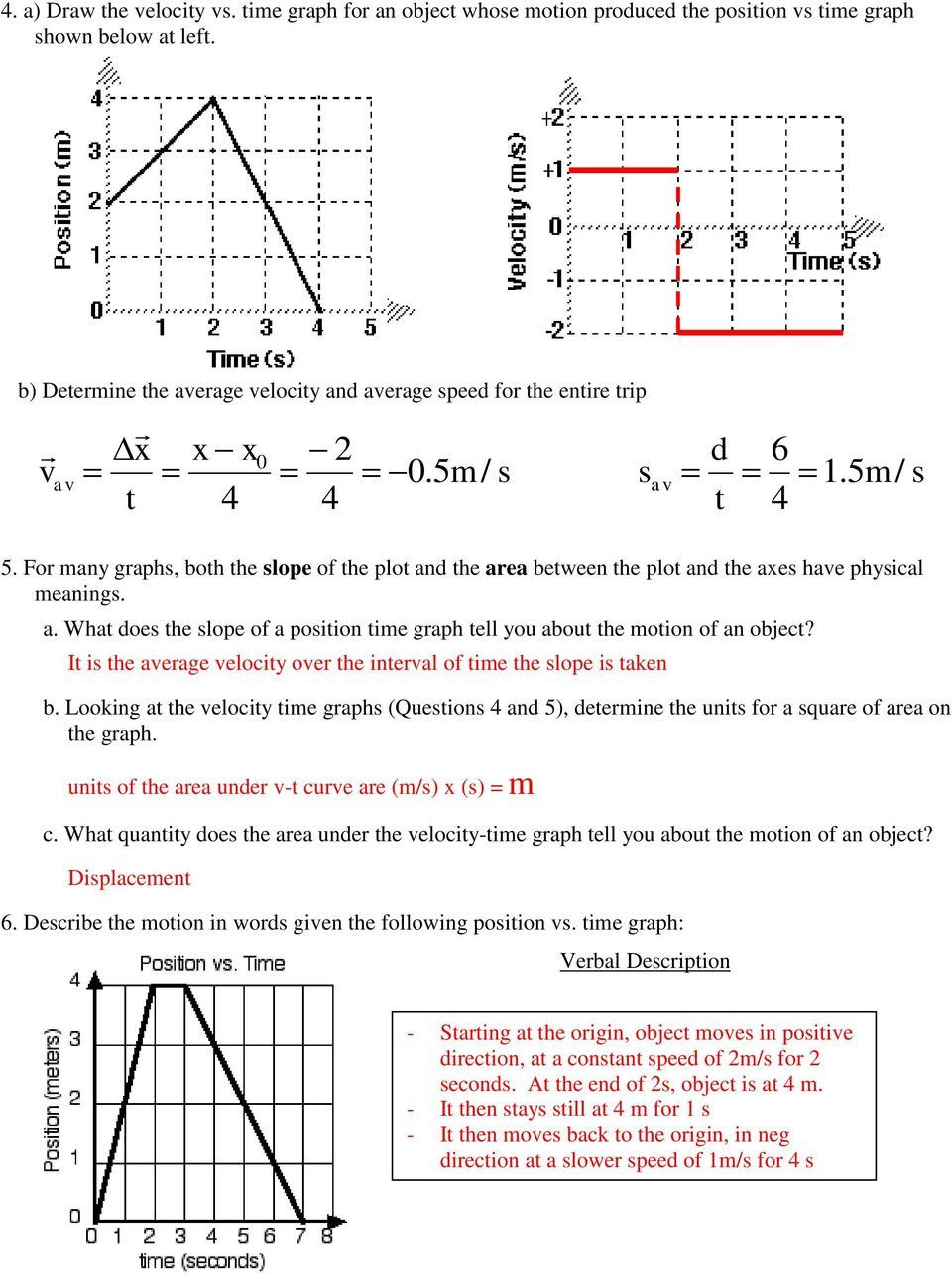
+
The displacement of an object can be found by calculating the area under the velocity-time graph. This area can be a rectangle or a triangle (or both) depending on whether the velocity is constant or changing.
Why is the slope of a distance-time graph important?
+
The slope of a distance-time graph gives the instantaneous velocity of the object at any given time. A steeper slope indicates faster motion, while a flat line means the object isn’t moving.
Can you have a negative acceleration on a velocity-time graph?

+
Yes, negative acceleration (deceleration) is represented by a negative slope on a velocity-time graph. This means the object is slowing down in its forward motion or accelerating in the opposite direction.
What does a curved line on a velocity-time graph indicate?

+
A curved line on a velocity-time graph indicates changing acceleration, where the velocity of the object is increasing at a non-constant rate.