Karyotype Layout Worksheet: Beginner's Guide to Chromosomal Mapping

Understanding the intricate world of genetics is essential for anyone involved in the fields of biology, medicine, or any life science research. One of the foundational techniques for genetic analysis is chromosomal mapping through the creation of a karyotype. A karyotype layout worksheet serves as an invaluable tool for students, scientists, and hobbyists alike to explore the chromosomal makeup of species, identify chromosomal abnormalities, and research genetic traits. This guide will delve into the nuances of creating and interpreting karyotype layout worksheets, providing both theoretical knowledge and practical advice.
What is a Karyotype?
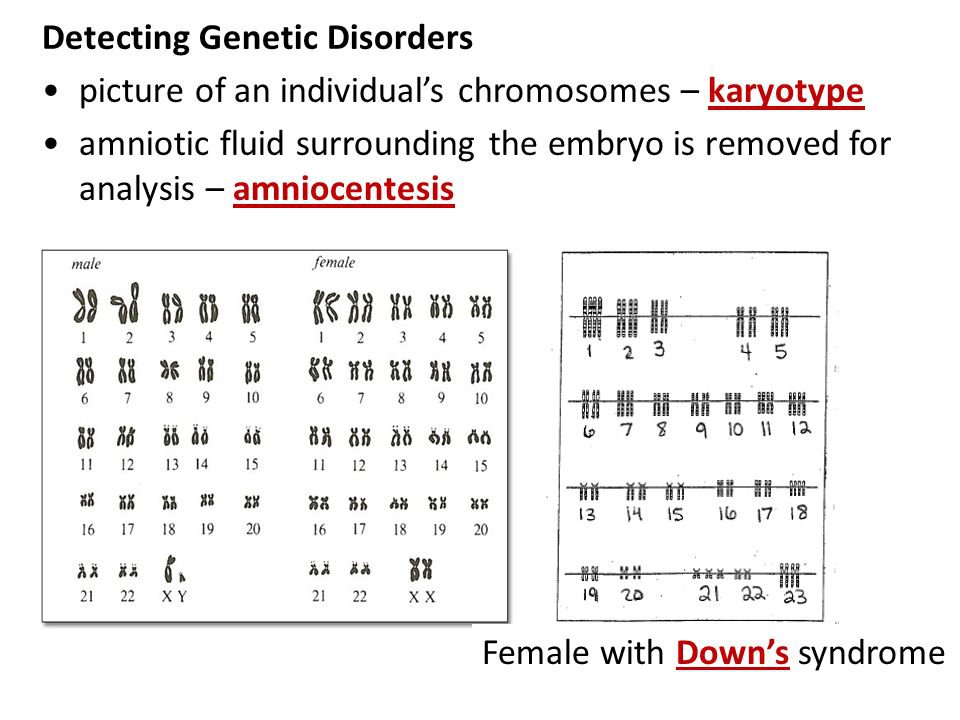
A karyotype is an organized profile of an individual’s chromosomes. Each chromosome is stained to produce bands, which are then arranged in pairs, starting from the largest to the smallest. Here’s how you can begin:
- Chromosome Staining: Chromosomes are stained to differentiate the banding patterns.
- Ordering: Arranged in a standard format, usually by length, with the sex chromosomes last.
Preparing Your Karyotype Layout Worksheet

Creating a karyotype involves several steps to ensure accuracy and reliability:
- Cell Culture and Division: Grow cells in culture media, synchronize the cell cycle to harvest cells in metaphase, and treat them with colchicine to arrest mitosis at metaphase.
- Chromosome Preparation: Isolate and spread chromosomes on a slide, staining them with Giemsa (G-banding) for clear visibility.
- Capturing Images: Use a microscope with a digital camera to capture clear images of chromosomes.
- Software Analysis: Use karyotyping software to match, pair, and arrange chromosomes according to size, banding pattern, and centromere position.
🔬 Note: Make sure to observe cells in metaphase for the best chromosome morphology.
Interpreting Your Karyotype Worksheet
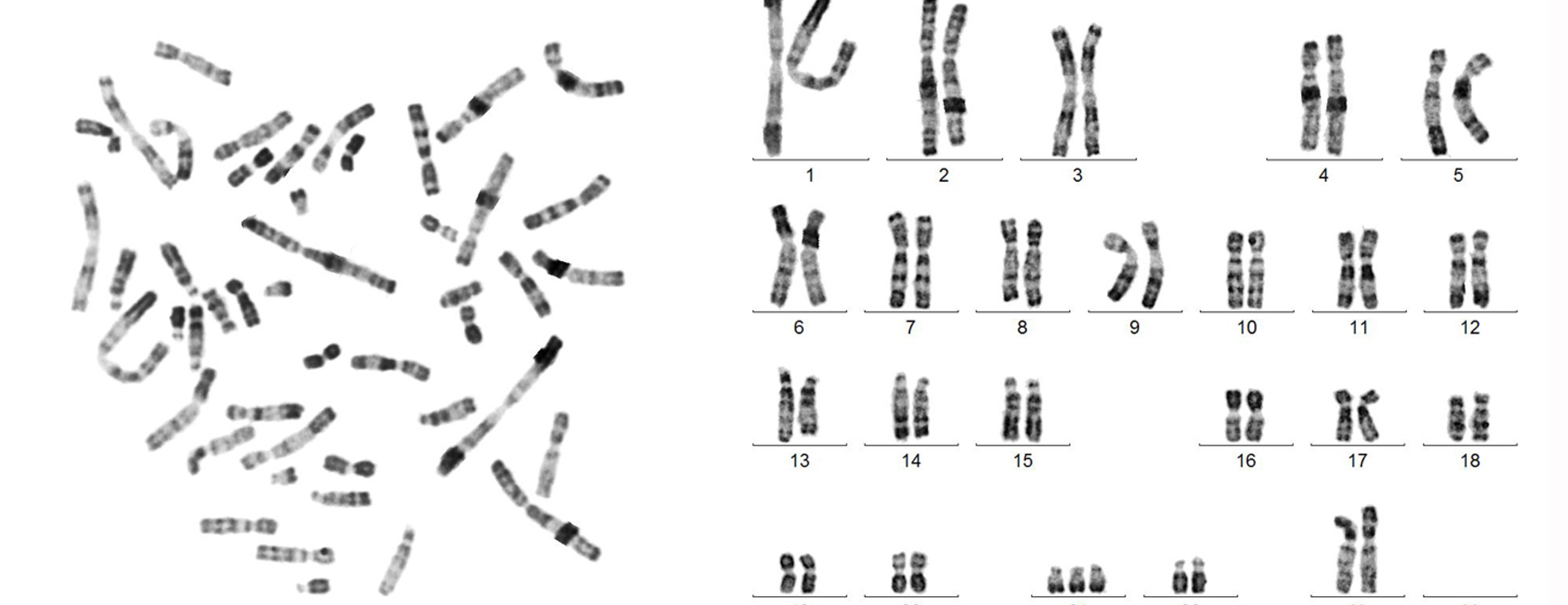
Once you’ve prepared your karyotype:
- Counting Chromosomes: Verify the number of chromosomes. For humans, a normal count is 46 (23 pairs).
- Identifying Structural Abnormalities: Look for deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations.
- Spotting Aneuploidy: Check for extra or missing chromosomes like in Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Using Karyotype Layout Worksheets in Education

Karyotype layout worksheets are excellent educational tools:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Teaching Genetic Concepts | Helps students visualize chromosome structure and genetic abnormalities. |
| Diagnosis Simulation | Allows students to simulate the process of diagnosing genetic conditions. |
| Comparative Studies | Comparing human and non-human species karyotypes to understand evolution and speciation. |
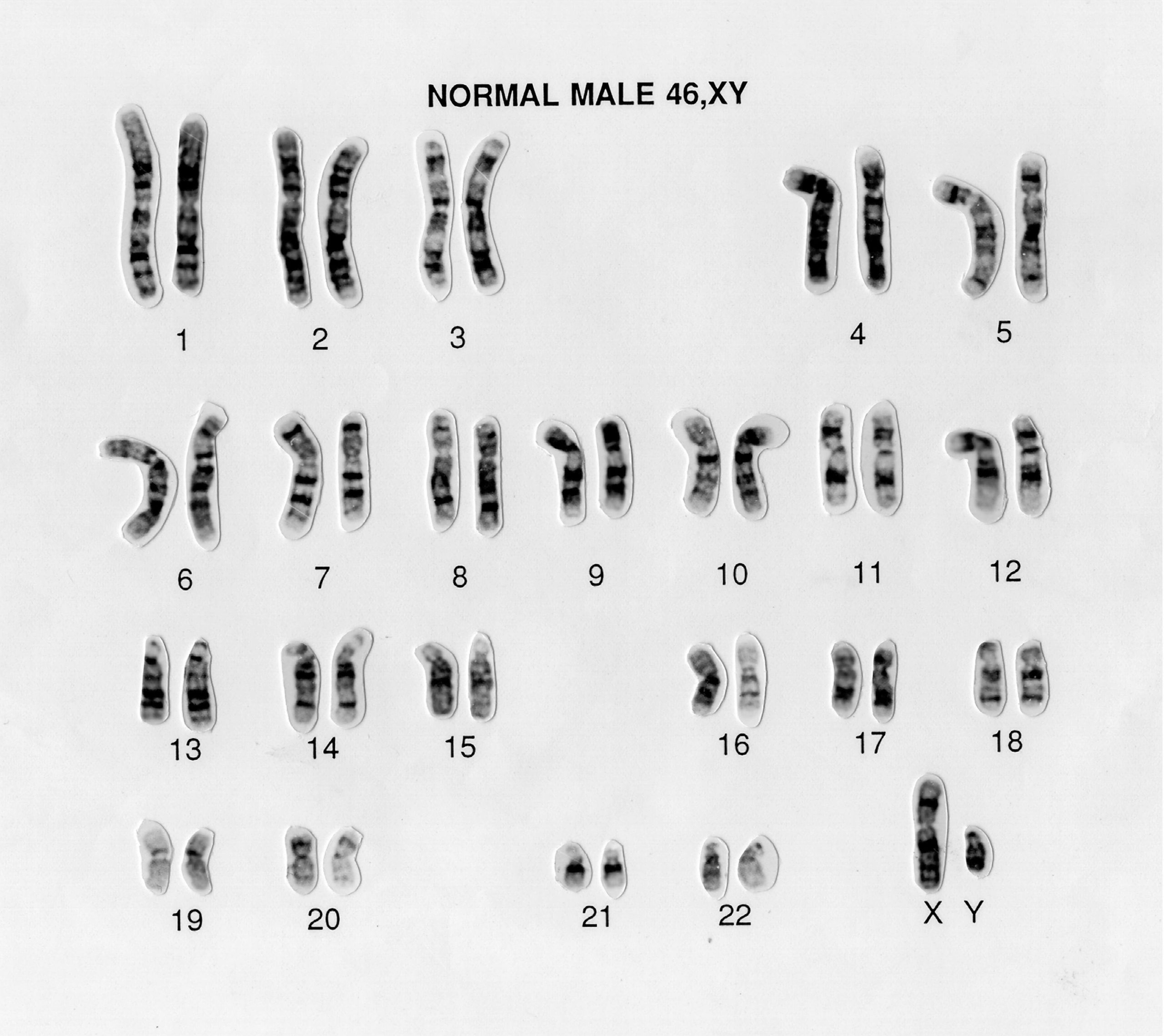
📚 Note: Worksheets can be used to simulate genetic screenings, teaching students to identify syndromes like Klinefelter or Turner.
Challenges and Considerations

There are several challenges when working with karyotype layout worksheets:
- Quality of Images: Poor image quality can lead to misinterpretations.
- Interpretation Errors: Incorrectly matching or pairing chromosomes.
- Software Limitations: Not all software provides the same level of accuracy or detail.
Future of Karyotyping
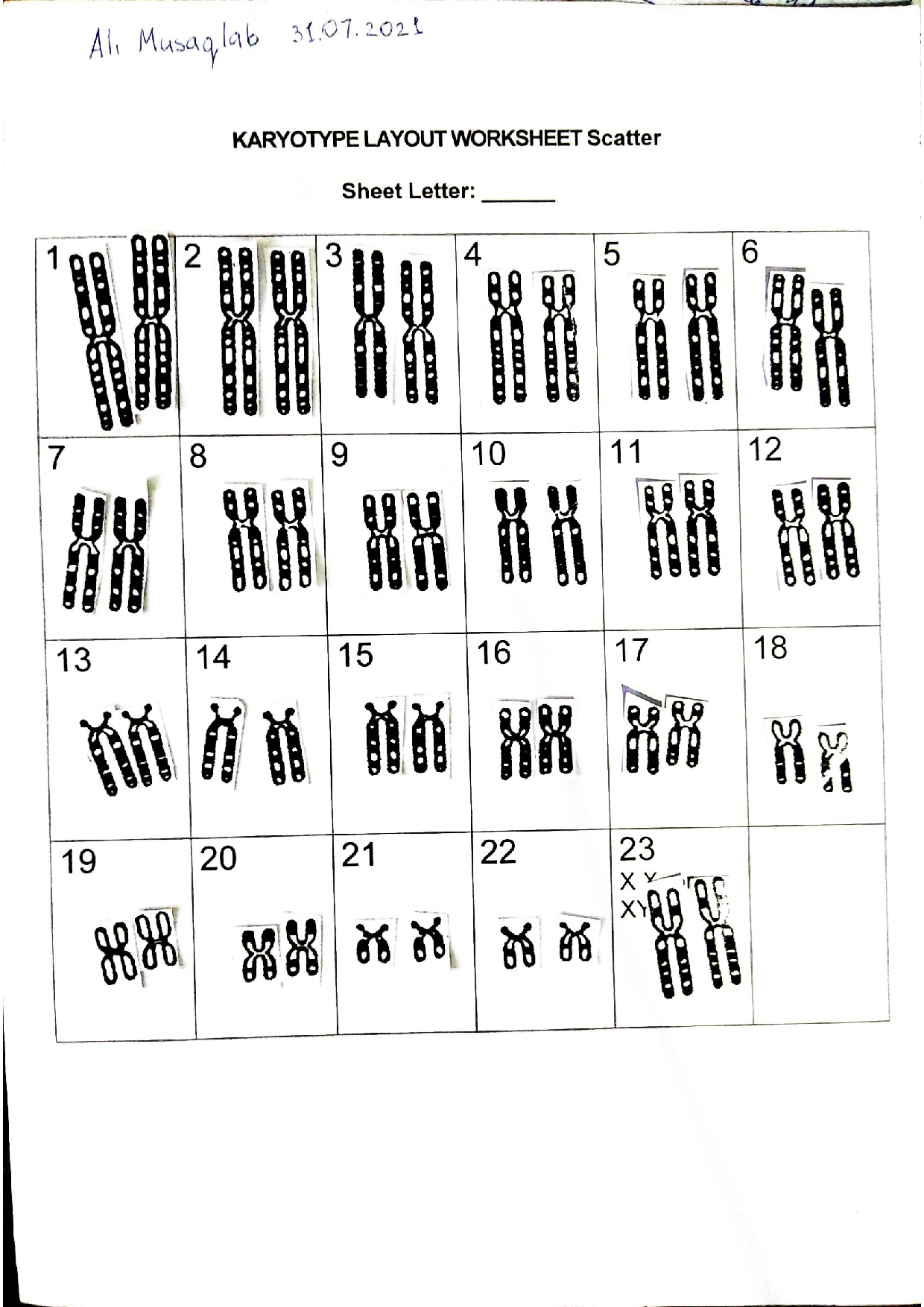
The field of karyotyping is constantly evolving:
- Molecular Techniques: New methods like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) provide more detailed information.
- Automation: Software is becoming more sophisticated, reducing manual labor and increasing accuracy.
- Integration with Other Genomic Techniques: Combining karyotyping with next-generation sequencing for comprehensive genetic analysis.
🔬 Note: Always cross-reference automated results with manual observations to ensure accuracy.
In the complex yet fascinating world of genetics, understanding chromosomes through karyotyping provides essential insights into inheritance patterns, abnormalities, and even evolution. By meticulously preparing and interpreting karyotype layout worksheets, students and researchers can unlock a wealth of genetic information. This guide has touched upon the steps for creating karyotypes, interpreting them, educational uses, common challenges, and the future of the field. As technology advances, the accessibility and precision of karyotyping will continue to improve, opening new doors in genetic research and diagnostics. The journey of learning genetics through karyotyping is not just educational but also deeply engaging, fostering a profound appreciation for life’s blueprint.
What is the purpose of banding in karyotyping?

+
Banding enhances the visibility of chromosomal features, allowing for easier identification of individual chromosomes, chromosomal abnormalities, and specific gene locations.
Can karyotyping detect all genetic disorders?

+
Karyotyping can identify large-scale chromosomal abnormalities like aneuploidies or structural changes. However, it might miss smaller mutations or microdeletions. Molecular techniques often complement karyotyping for a more complete genetic analysis.
Why is it important to study karyotypes in education?

+
Studying karyotypes teaches students about genetics, inheritance, and genetic disorders. It visually demonstrates the principles of chromosomes, DNA, and inheritance, providing a tangible learning tool.
