JROTC Army Ranks: 9 Key Positions Explained
Understanding the Hierarchy: A Comprehensive Guide to JROTC Army Ranks
The Junior Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (JROTC) program is a unique blend of academic and extracurricular activities designed to equip high school students with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in life. One of the critical aspects of the JROTC program is its rank structure, which mirrors the hierarchy of the United States Army. Understanding the various JROTC Army ranks is essential for students, instructors, and parents to appreciate the program’s goals and objectives. In this article, we will delve into the 9 key positions that comprise the JROTC Army rank structure, explaining the responsibilities, expectations, and requirements for each rank.
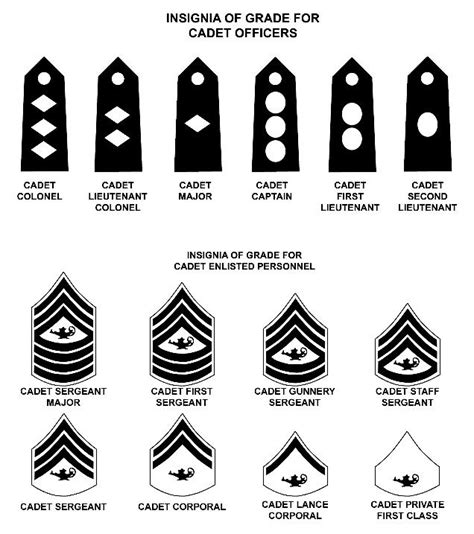
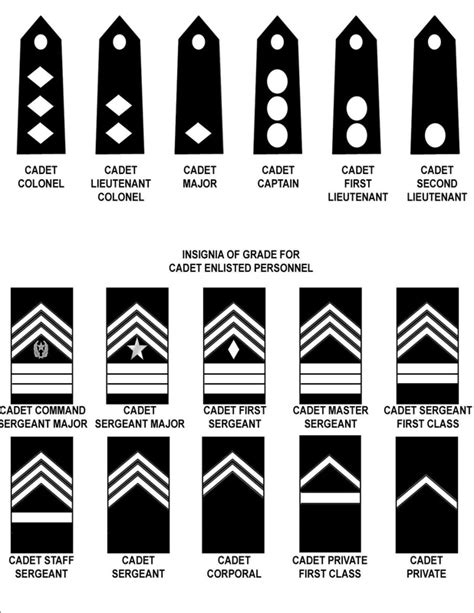
Cadet Private (PVT)

The Cadet Private is the entry-level rank for all new JROTC cadets. As a PVT, cadets are expected to learn the basics of the JROTC program, including uniform wear, drill and ceremony, and core values. To advance to the next rank, PVTs must demonstrate a satisfactory understanding of these fundamentals and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Private First Class (PFC)

The Cadet Private First Class rank is the first promotion for JROTC cadets. PFCs are expected to take on additional responsibilities, such as leading small groups and participating in community service events. To be eligible for promotion to PFC, cadets must demonstrate leadership potential, maintain good grades, and exhibit a positive attitude.
Cadet Corporal (CPL)

As a Cadet Corporal, individuals are expected to take on more significant leadership roles, such as squad leader or team leader. CPLs are responsible for mentoring lower-ranking cadets, leading drill teams, and participating in competitions. To advance to CPL, cadets must demonstrate strong leadership skills, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Sergeant (SGT)

The Cadet Sergeant rank is a significant milestone in the JROTC program. SGTs are responsible for leading larger groups, such as platoons, and are expected to demonstrate advanced leadership skills. To be eligible for promotion to SGT, cadets must have a strong record of leadership, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Staff Sergeant (SSG)
As a Cadet Staff Sergeant, individuals are expected to take on senior leadership roles, such as platoon sergeant or company first sergeant. SSGs are responsible for mentoring junior cadets, leading drill teams, and participating in competitions. To advance to SSG, cadets must demonstrate exceptional leadership skills, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Sergeant First Class (SFC)

The Cadet Sergeant First Class rank is a prestigious position in the JROTC program. SFCs are responsible for leading companies, battalions, or brigades and are expected to demonstrate advanced leadership skills. To be eligible for promotion to SFC, cadets must have a strong record of leadership, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Master Sergeant (MSG)

As a Cadet Master Sergeant, individuals are expected to take on senior leadership roles, such as battalion or brigade command sergeant major. MSGs are responsible for mentoring junior cadets, leading drill teams, and participating in competitions. To advance to MSG, cadets must demonstrate exceptional leadership skills, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Sergeant Major (SGM)

The Cadet Sergeant Major rank is the highest enlisted rank in the JROTC program. SGMs are responsible for leading battalions, brigades, or corps and are expected to demonstrate exceptional leadership skills. To be eligible for promotion to SGM, cadets must have a strong record of leadership, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
Cadet Command Sergeant Major (CSM)

The Cadet Command Sergeant Major rank is the highest rank in the JROTC program. CSMs are responsible for leading the entire JROTC corps and are expected to demonstrate exceptional leadership skills. To advance to CSM, cadets must demonstrate exceptional leadership skills, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
💡 Note: The promotion process and requirements may vary depending on the school and JROTC program.
| Rank | Responsibilities | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| PVT | Learn JROTC basics, uniform wear, drill and ceremony | Satisfactory understanding of fundamentals, commitment to the program |
| PFC | Lead small groups, participate in community service | Leadership potential, good grades, positive attitude |
| CPL | Lead squads, mentor lower-ranking cadets | Strong leadership skills, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| SGT | Lead platoons, demonstrate advanced leadership skills | Strong record of leadership, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| SSG | Lead platoons, mentor junior cadets | Exceptional leadership skills, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| SFC | Lead companies, battalions, or brigades | Strong record of leadership, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| MSG | Lead battalions or brigades, mentor junior cadets | Exceptional leadership skills, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| SGM | Lead battalions, brigades, or corps | Strong record of leadership, excellent grades, commitment to the program |
| CSM | Lead the entire JROTC corps | Exceptional leadership skills, excellent grades, commitment to the program |

In conclusion, understanding the JROTC Army rank structure is essential for success in the program. By knowing the responsibilities, expectations, and requirements for each rank, cadets can set goals and work towards achieving them. Remember, leadership is a key component of the JROTC program, and advancing through the ranks requires dedication, hard work, and a commitment to excellence.
What is the highest rank in the JROTC program?

+
The highest rank in the JROTC program is Cadet Command Sergeant Major (CSM).
What are the requirements for promoting to Cadet Sergeant (SGT)?
+To promote to Cadet Sergeant (SGT), cadets must have a strong record of leadership, maintain excellent grades, and show a commitment to the program.
What is the role of a Cadet Master Sergeant (MSG)?
+Cadet Master Sergeants (MSG) are responsible for leading battalions or brigades and mentoring junior cadets.