Discover Isotopes Worksheet Answers Easily!
Understanding Isotopes: A Comprehensive Guide
The study of isotopes represents a fascinating journey into the heart of matter, revealing the diversity and complexity within the atoms that compose our universe. Isotopes, as they are known, are variants of chemical elements distinguished by their differing neutron counts in the nucleus. Understanding isotopes is not just crucial for chemists and physicists but also has practical applications across various fields such as medicine, archaeology, and even everyday consumer products.
In this long-form blog post, we will delve into the world of isotopes:
- What are isotopes?
- How isotopes are identified and represented.
- Worksheet examples with explanations.
- Practical applications and significance.
What Are Isotopes?

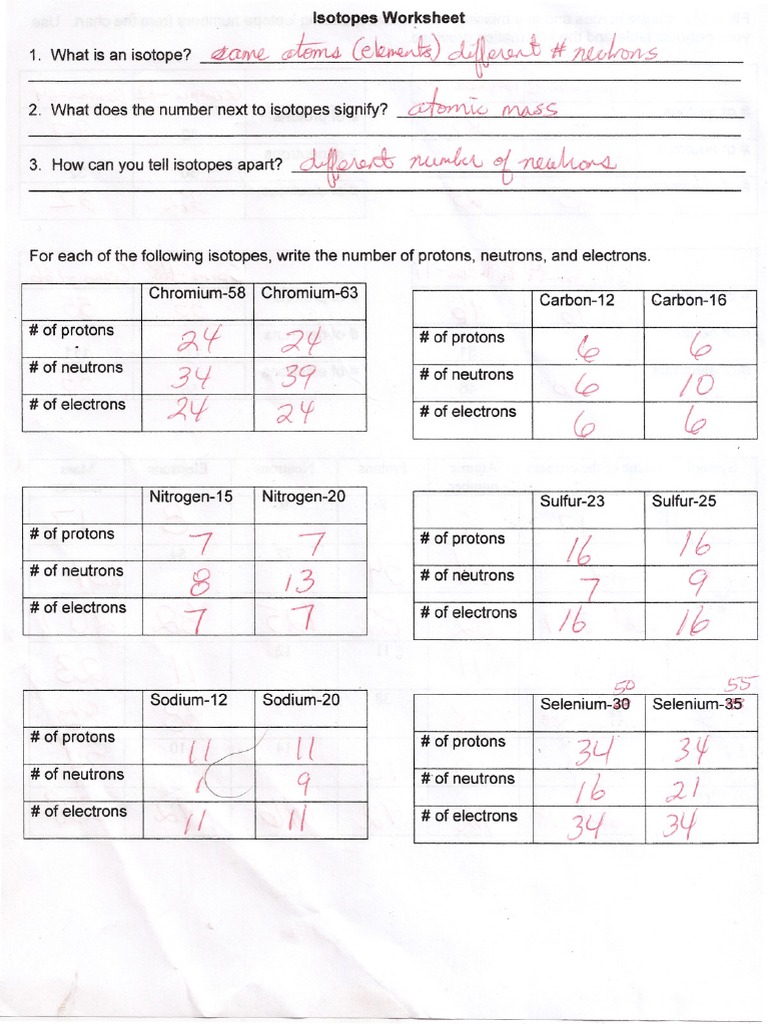
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. While all isotopes of an element share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of electrons, their physical properties, and behaviors in nuclear reactions can be markedly different. Here's a basic overview:
- Protons: These define the element, and their number is known as the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Adding or removing these changes the isotope, affecting its mass.
- Electrons: While not directly involved in defining an isotope, the electron configuration determines the chemical properties.

Identification and Representation of Isotopes
The identification of isotopes involves several notations:
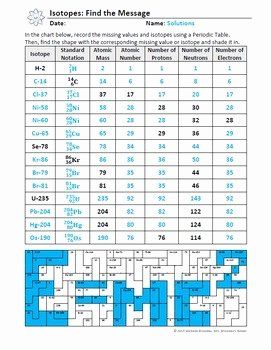
- Nuclide notation: A common way to represent isotopes is A_E^X where X is the chemical symbol of the element, A is the mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and E is the atomic number (number of protons).
- Isotope notation: A hyphen or the element's name followed by the mass number, e.g., carbon-12, C-12.
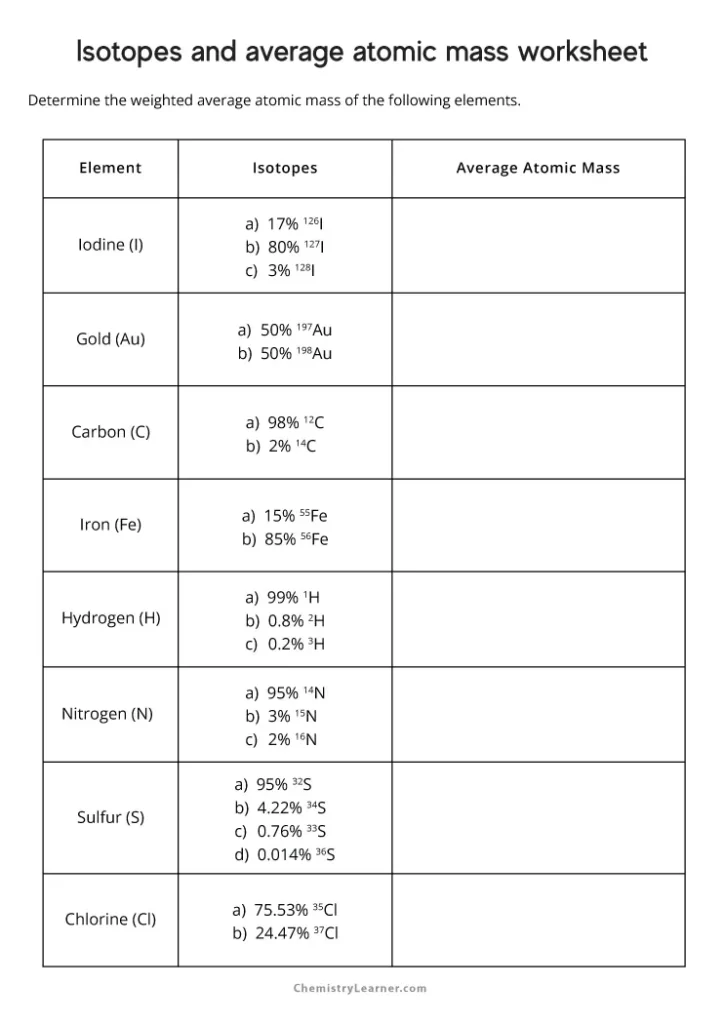
🔬 Note: Atomic mass is an average of all isotope masses, weighted by their natural abundance.
| Element | Mass Number | Atomic Number | Neutrons | Nuclide Notation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 | 0 | {}^{1}_{1}H |
| Hydrogen | 2 | 1 | 1 | {}^{2}_{1}H |
| Hydrogen | 3 | 1 | 2 | {}^{3}_{1}H |

Worksheet Example: Solving Isotope Problems

Let’s work through an example to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Determining Isotopic Composition

Problem: The element with atomic number 92 has a mass number of 238. Find its number of neutrons, the corresponding isotope notation, and its electron number in its neutral state.
Solution:
- Protons (Atomic Number): 92
- Mass Number: 238
- Number of Neutrons: (238 - 92 = 146)
- Isotope Notation: ({}^{238}U_{92}) or Uranium-238
- Number of Electrons: 92 (since it’s neutral, electrons equal protons)
👓 Note: While solving isotope problems, it's critical to recognize that while the number of protons defines the element, it's the neutron count that differentiates the isotopes.
Practical Applications of Isotopes

Isotopes play a pivotal role in numerous fields:
- Medicine:
- Radioactive isotopes like technetium-99m are used in medical imaging.
- Stable isotopes like deuterium are used in breath tests to diagnose medical conditions.
- Nuclear Power: Uranium-235 is used in nuclear reactors to produce energy.
- Archaeology:
- Carbon-14 dating helps determine the age of organic materials.
- Uranium series disequilibrium dating is used for geological samples.
- Industry:
- Tracing water flow in hydrology.
- Neutron activation analysis for material characterization.
Isotopes in Everyday Life

Isotopes are not just the province of scientists; they affect our daily lives in various ways:
- Food Safety:
- Irradiation with gamma rays from cobalt-60 or cesium-137 to sterilize food.
- Stable isotopes are used in food labeling to ensure the authenticity of products.
- Smog Tests:
- Isotopes can help analyze air pollution levels in automobiles.
- Water Quality:
- Stable isotopes are used to trace contaminants in water supplies.
To wrap up, isotopes are not just theoretical constructs but have tangible impacts on our lives. From the energy we use, the medicine we take, to the very atoms that compose us, isotopes are a fundamental part of our world. Understanding and utilizing these variants of elements can lead to advances in technology, health, and environmental protection.
What are isotopes and why do they matter?

+
Isotopes are different forms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They matter because their properties can be utilized in various applications like medicine, power generation, and dating ancient artifacts.
How can I differentiate between isotopes?

+
You can differentiate isotopes by their mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes of the same element will have different mass numbers due to varying neutron counts.
Why are some isotopes radioactive?

+
Some isotopes are radioactive because they have unstable nuclei. The neutron-proton ratio in their nucleus makes them prone to decay into a more stable state, releasing energy in the process.