5 Key Answers to Isotopes, Ions, and Atoms Worksheet

Understanding the nuances of atoms, isotopes, and ions is foundational for any student of chemistry. These concepts are not only crucial for grasping more advanced topics but also integral to understanding the world at an atomic level. Today, we'll address some of the common questions encountered by students while tackling worksheets on these topics. Let's dive in.
1. What's the Difference Between Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes?
Before we proceed further, let's establish what distinguishes atoms, ions, and isotopes:
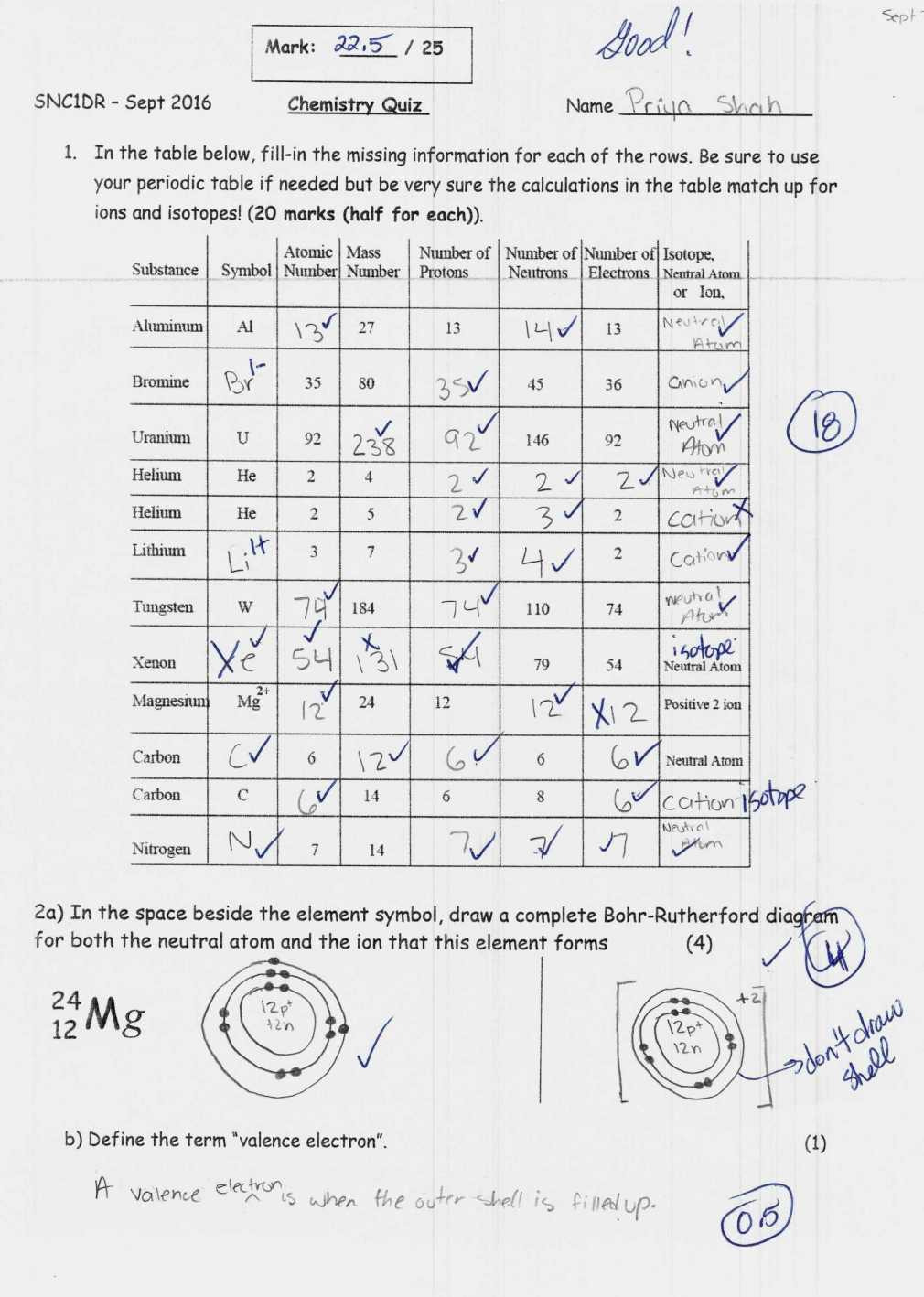
- Atoms: The basic building blocks of matter. An atom consists of protons, electrons, and neutrons. The number of protons defines the element, while the number of neutrons can vary.
- Ions: Atoms that have gained or lost electrons, thereby acquiring a net electrical charge. Cations are positively charged (lost electrons), while anions are negatively charged (gained electrons).
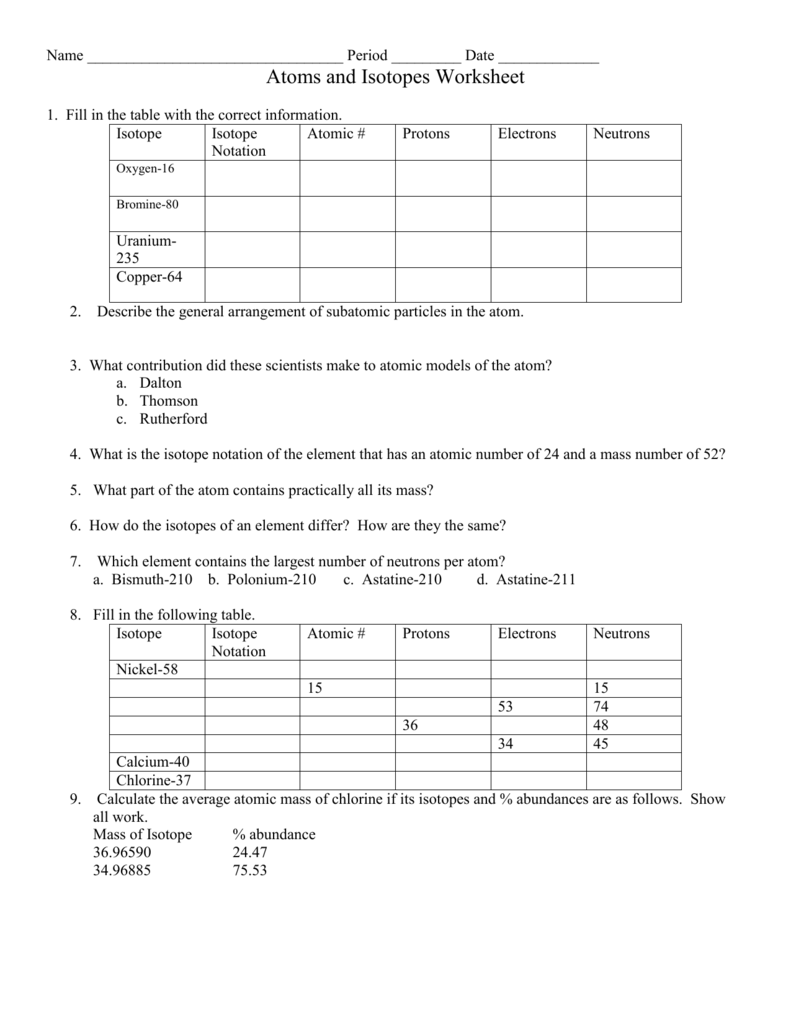
- Isotopes: Variants of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses due to these neutron variations.
📝 Note: The mass of an ion or an isotope can significantly affect its behavior in chemical reactions.
2. How Do You Determine the Charge of an Ion?

To determine the charge of an ion:
- If an atom loses electrons, the charge will be positive, equal to the number of electrons lost.
- If an atom gains electrons, the charge will be negative, equal to the number of electrons gained.
- Check the periodic table's group (column) numbers; elements in the same group often have similar charge states in ions.
📝 Note: Transition metals can have multiple ionic charges. For example, Iron (Fe) can form Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺.
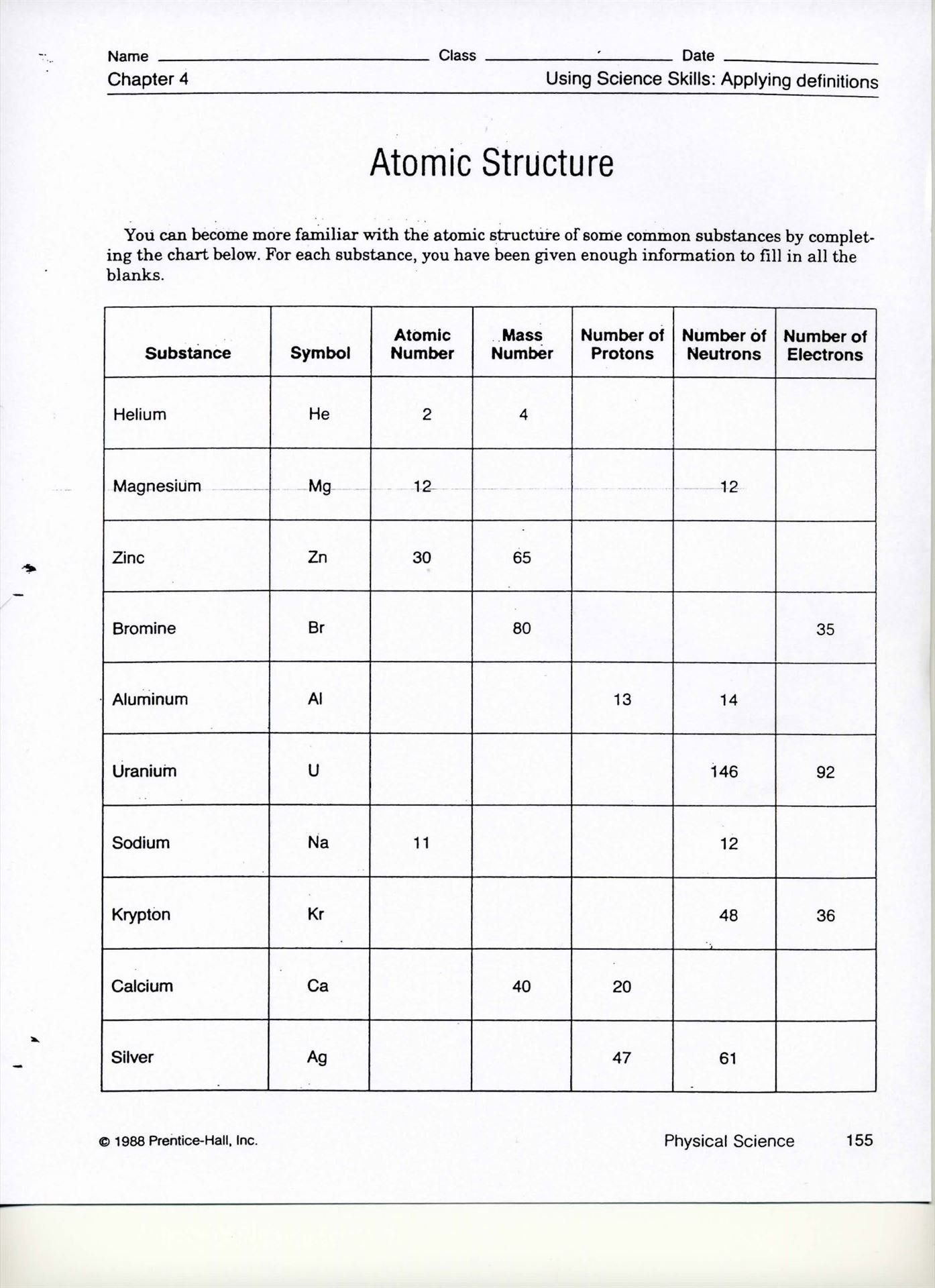
3. What's the Significance of Atomic Mass and Mass Number?

Both atomic mass and mass number are crucial:
- Atomic Mass: This is the weighted average of the masses of an element's naturally occurring isotopes, considering their abundance. It's not a whole number because it accounts for the different isotopes.
- Mass Number: This is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. For an isotope, it reflects the number of each.
A common way to express an isotope is with its atomic symbol, mass number superscript, and charge, if applicable (e.g., ¹³C+2 for an isotope of carbon with 6 protons, 7 neutrons, and a +2 charge).
4. How Do Isotopes Affect Element Properties?

Here's how isotopes impact the properties:
- Nuclear Stability: The neutron to proton ratio affects an isotope's stability. Certain ratios lead to radioactive decay, changing the element itself.
- Physical Properties: Due to mass differences, isotopes can have slightly different melting points, boiling points, and diffusion rates.
- Chemical Properties: The chemical behavior of isotopes remains largely unchanged, but reaction rates can differ.
5. How Are Isotopes Useful?

Isotopes have various applications:
- Medicine: Radioactive isotopes are used in imaging techniques like PET scans to diagnose diseases or trace metabolic processes.
- Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating helps determine the age of organic materials.
- Industry: Isotopes help in tracking the movement of substances within manufacturing processes or for radiation safety testing.
- Environmental Studies: Stable isotopes are markers for understanding climate change or tracing water cycles.
In conclusion, understanding atoms, ions, and isotopes is not just about memorizing definitions. It's about recognizing how these fundamental concepts influence chemical behavior, biological processes, and even our environment. They provide a glimpse into the universe's complexity at a microscopic level, and mastering these concepts opens doors to deeper scientific understanding. The interplay between atomic structure and the physical world is both fascinating and essential for anyone exploring the sciences.
Why do we need to know about isotopes, ions, and atoms?

+
Knowledge about these particles allows us to understand how elements interact, form compounds, and react chemically. It’s vital in fields like chemistry, physics, biology, and materials science.
Can isotopes of the same element react differently?
+
While isotopes have the same chemical properties, their reaction kinetics might differ due to small differences in mass. However, the fundamental chemical behavior remains similar.
How can an element have both stable and unstable isotopes?

+
The stability of isotopes depends on the balance of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Stable isotopes have a ratio that allows for a balanced nuclear force, while unstable isotopes decay to achieve stability.
Are there any elements with no isotopes?
+
Every element has at least one isotope, but some, like hydrogen, have isotopes with significantly different properties (e.g., hydrogen, deuterium, and tritium).
How do ions form compounds?

+
Ions form compounds through electrostatic attraction, creating ionic bonds where positively and negatively charged ions arrange themselves into crystal lattices or molecular compounds.