Isotopes and Ions Worksheet: Simplified Answers

If you've ever found yourself puzzled by the intricacies of atoms, isotopes, and ions, you're in good company. Chemistry can be a complex field, but breaking it down into understandable parts can make a world of difference. This blog post serves as a comprehensive guide to navigating isotopes and ions worksheets, offering simplified answers to common questions, definitions, and how they fit into our understanding of the elemental world. Whether you're a student struggling with homework or someone simply curious about the science behind the atoms, this is your guide to mastering these fundamental concepts.
What Are Atoms?

Before we delve into isotopes and ions, it’s crucial to grasp what atoms are. An atom is the basic building block of matter, and everything around us is made up of atoms.
- Nucleus: The center of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: These negatively charged particles orbit around the nucleus.

Defining Isotopes

Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. Here’s how you can identify an isotope:
- Atomic Number: This indicates the number of protons, which is the same for all isotopes of an element.
- Mass Number: The sum of protons and neutrons, which differs among isotopes.
Let’s look at an example of isotopes of carbon:
| Isotope | Protons | Neutrons | Mass Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| Carbon-14 | 6 | 8 | 14 |

The World of Ions
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. There are two main types:
- Cations: Positively charged ions with more protons than electrons.
- Anions: Negatively charged ions with more electrons than protons.
Understanding how ions form is key to mastering chemistry:
- Ions form through processes like ionization or chemical reactions.
- The charge of an ion is determined by the number of electrons lost or gained.
Worksheet Guide: Isotopes and Ions

Here are some common questions you might encounter on an isotopes and ions worksheet along with simplified answers:
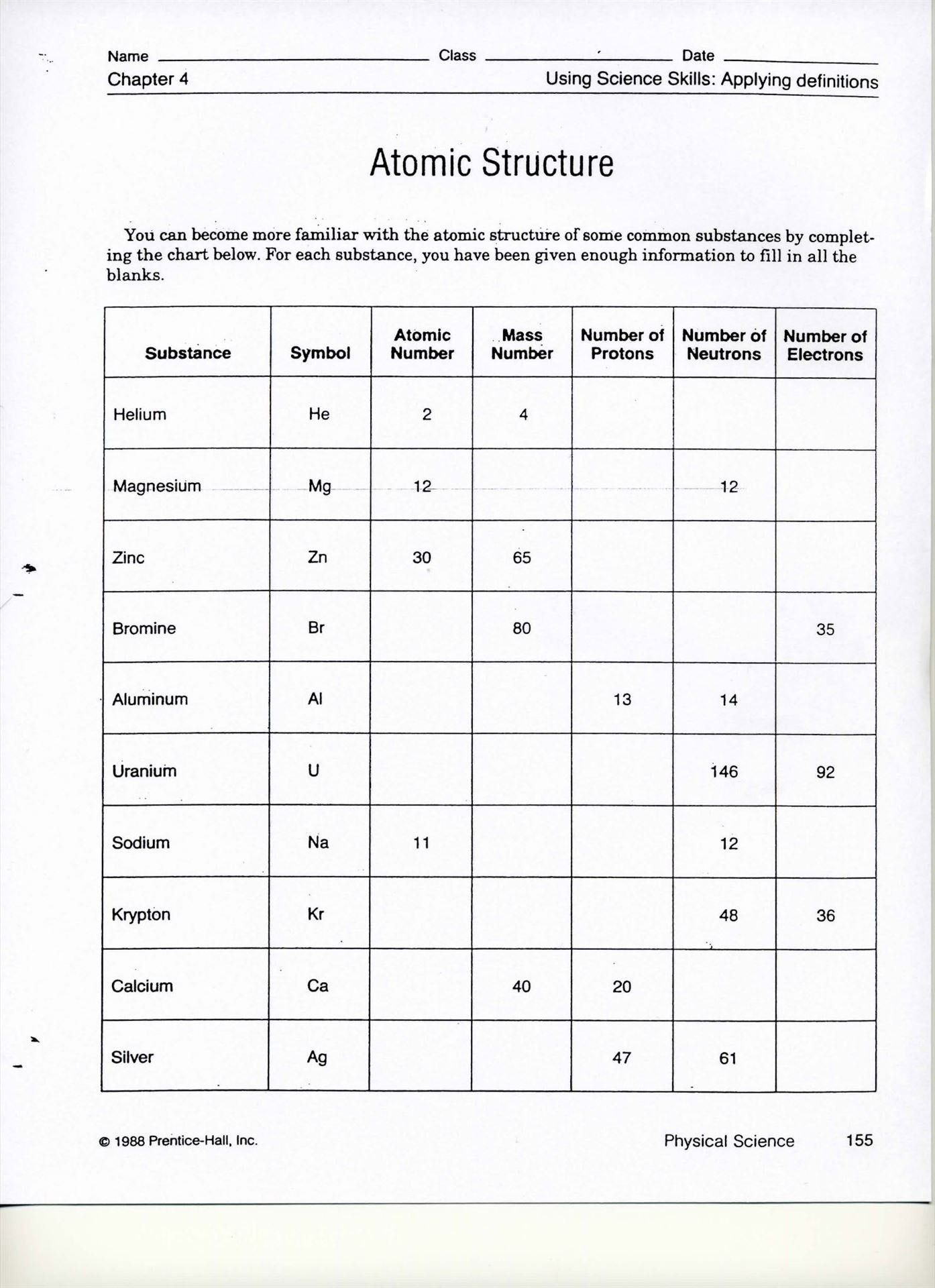
1. How Many Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Does Each Isotope Have?

To find out:
- Use the Atomic Number for protons.
- Subtract the atomic number from the mass number to get the number of neutrons.
- Assume the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons unless told otherwise.
⚠️ Note: In an ion, the number of electrons might be different due to electron loss or gain.
2. Determining the Charge of an Ion
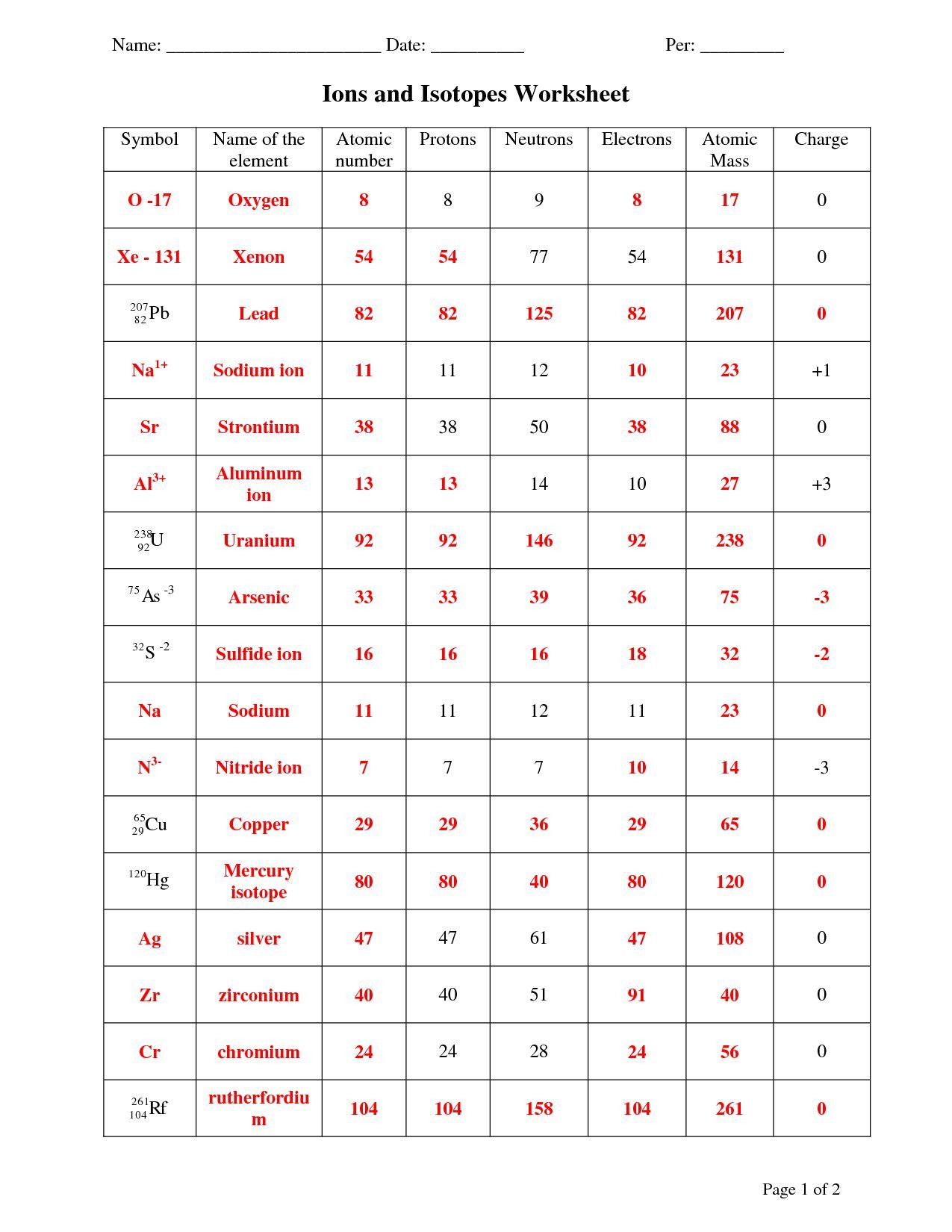
The charge is the difference between the number of protons and electrons:
- If protons are more, the ion is positively charged (cation).
- If electrons are more, the ion is negatively charged (anion).
3. Writing Chemical Symbols for Isotopes and Ions
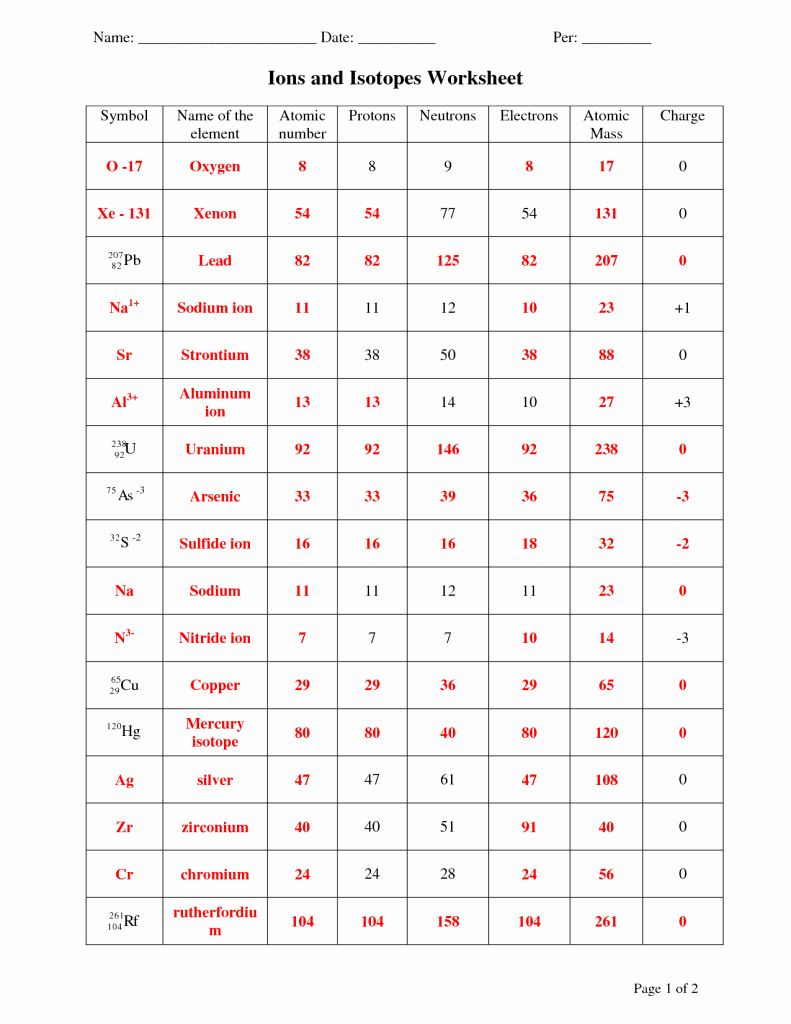
- Isotopes: Use the chemical symbol with the mass number as a superscript, e.g., Carbon-14 is written as 14C.
- Ions: Include the charge as a superscript following the symbol, e.g., Na+ for sodium ion.
When working through these worksheets, remember:
- Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to differing neutron counts.
- Ions have a charge due to a different number of electrons compared to protons.
- Be mindful of periodic table trends, which can help predict the number of valence electrons and likely charges of ions.
💡 Note: Understanding periodic table groups can make identifying ions easier.
By now, you should have a clearer picture of what isotopes and ions are, how to distinguish them, and how to answer common worksheet questions. This fundamental knowledge not only simplifies the world of chemistry but also opens doors to understanding various natural phenomena, from radioactive decay to the functioning of our own bodies.
What are the differences between isotopes and ions?

+
Isotopes differ in the number of neutrons, which affects the mass number. Ions differ by the number of electrons, leading to a charge difference but not affecting the mass number or atomic number.
How do isotopes affect the chemical properties of an element?

+
Since isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons, their chemical behavior is identical. However, differences in mass can influence physical properties like density or rate of chemical reactions.
Can ions be isotopes?

+
Yes, ions can be isotopes. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it can become an ion regardless of the number of neutrons it has.
What are some applications of isotopes?

+
Isotopes are used in various fields: in medicine for imaging techniques like PET scans, in dating archaeological finds through radiocarbon dating, in geology for age determination, and in nuclear energy.
Why is it important to know about ions?

+
Ions play crucial roles in biological systems, including nerve signaling, muscle function, and maintaining pH balance. They are also fundamental in industries like electrochemistry, water purification, and corrosion prevention.