5 Ways to Identify a Right Triangle
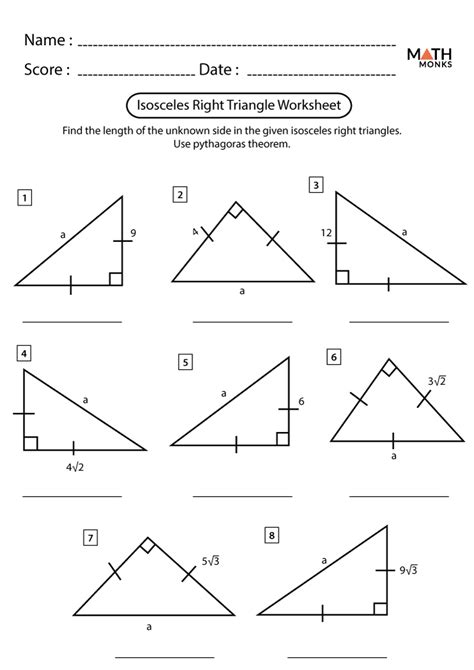
Understanding Right Triangles

Right triangles are a fundamental concept in geometry and trigonometry. A right triangle is a triangle with one right angle (90 degrees). Identifying right triangles is crucial in various mathematical and real-world applications, such as calculating distances, heights, and angles. In this article, we will explore five ways to identify a right triangle.
Method 1: Checking for a Right Angle

The most straightforward way to identify a right triangle is to check if it has a right angle. A right angle is denoted by a square or a small box at the vertex of the angle. If you see a right angle, you can be sure that the triangle is a right triangle.
📝 Note: A right angle is not the same as an acute angle or an obtuse angle. An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees.
Method 2: Using the Pythagorean Theorem
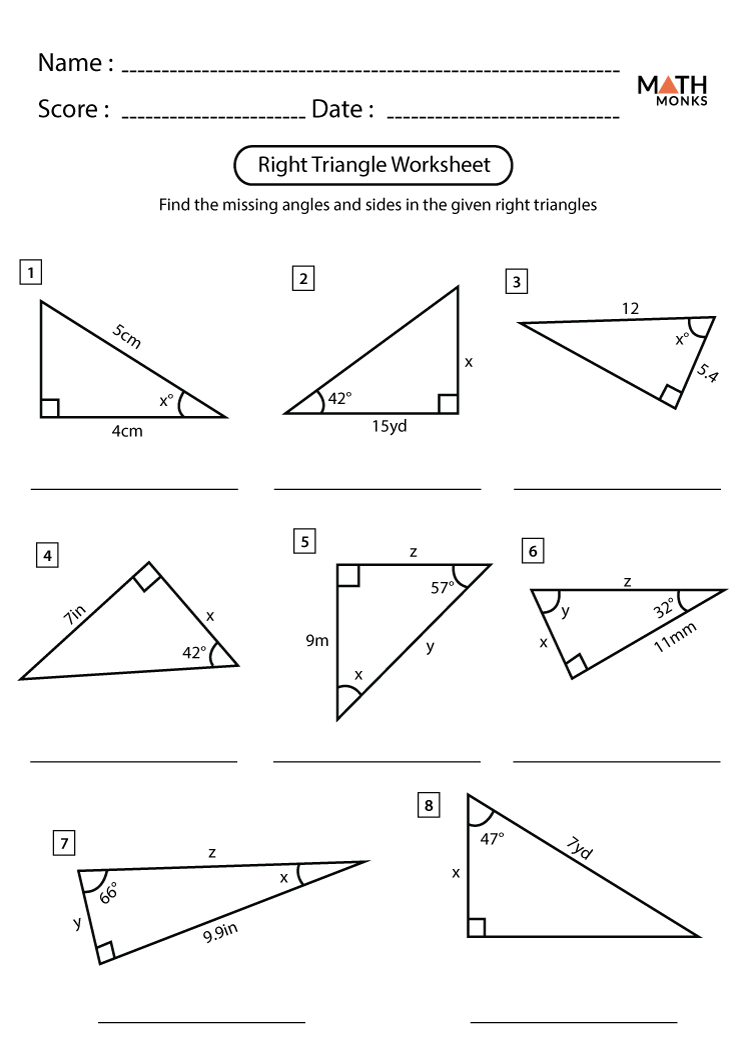
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry that states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. The theorem is often expressed as:
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
where a and b are the lengths of the two sides, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.
If the Pythagorean Theorem holds true for a triangle, you can be sure that it is a right triangle.
Method 3: Checking for Congruent Sides

In a right triangle, the two sides that form the right angle are called the legs of the triangle. If the two legs are congruent (i.e., they have the same length), the triangle is an isosceles right triangle. If the two legs are not congruent, the triangle is a scalene right triangle.
| Type of Right Triangle | Description |
|---|---|
| Isosceles Right Triangle | Two congruent sides (legs) |
| Scalene Right Triangle | Two non-congruent sides (legs) |

Method 4: Using Trigonometric Ratios
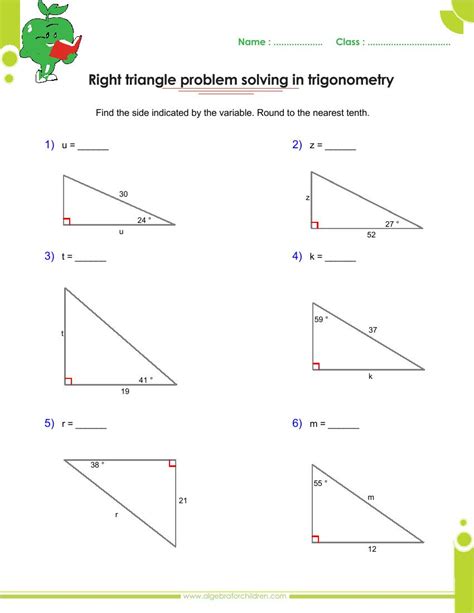
Trigonometric ratios, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, can also be used to identify right triangles. In a right triangle, the sine of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse, the cosine is equal to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse, and the tangent is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
If the trigonometric ratios hold true for a triangle, you can be sure that it is a right triangle.
Method 5: Checking for a Hypotenuse

Finally, you can identify a right triangle by checking if it has a hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle, and it is always opposite the right angle. If a triangle has a hypotenuse, it is likely to be a right triangle.
In conclusion, identifying right triangles is a crucial skill in mathematics and real-world applications. By using these five methods, you can easily identify right triangles and apply the concepts to solve problems.
As we wrap up this discussion, let’s summarize the key points:
- Check for a right angle
- Use the Pythagorean Theorem
- Check for congruent sides
- Use trigonometric ratios
- Check for a hypotenuse
By mastering these methods, you’ll become proficient in identifying right triangles and tackling complex mathematical problems with ease.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
+
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry that states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
What is the difference between an acute angle and a right angle?

+
An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while a right angle is exactly 90 degrees.
What is the longest side of a right triangle called?

+
The longest side of a right triangle is called the hypotenuse.
Related Terms:
- calculating area of triangle worksheet
- right triangle worksheets with answers
- solve right triangles worksheet
- special right triangles worksheets
- right triangle missing side worksheet
- right triangles worksheet pdf