Ions Worksheet Answers: Simplified Guide for Easy Learning

In the vast landscape of chemistry, understanding ions and their behavior is pivotal for both students and professionals. This blog will serve as an ions worksheet answers guide, aiming to clarify the principles surrounding ions, their charges, and their reactions through a straightforward and engaging approach.
The Basics of Ions
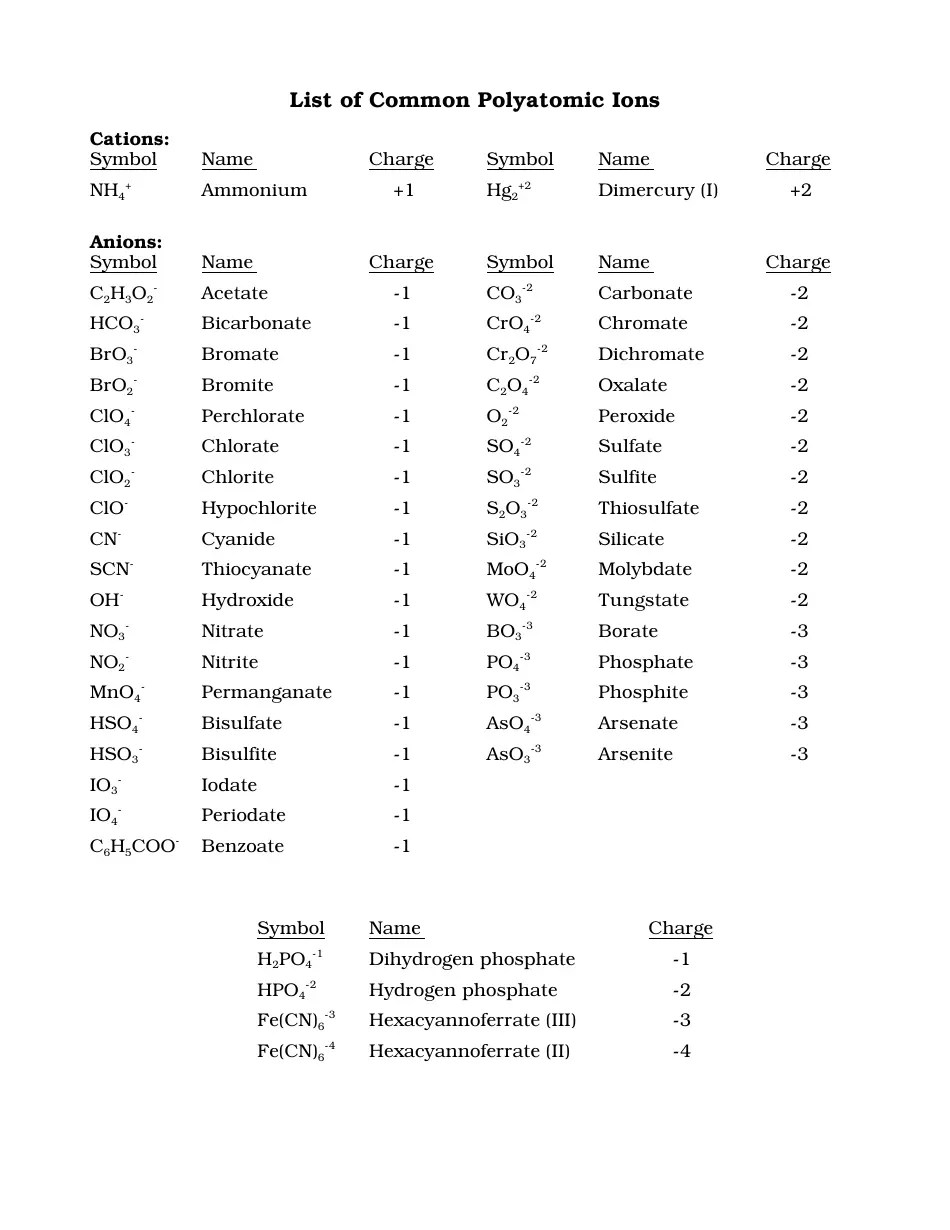

Before diving into the specifics, let's revisit the concept of an ion:
- Cations: Positively charged ions that result from losing electrons.
- Anions: Negatively charged ions formed by gaining electrons.
Ions worksheet answers often require a solid understanding of these fundamental definitions. They play a crucial role in:
- Electrolyte solutions
- Acid-base reactions
- Electrochemistry
Types of Ions and Their Charges

Ions can be categorized by the number of charges they carry. Here's a simplified table for common ions:
| Ion | Symbol | Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | Na+ | +1 |
| Chloride | Cl- | -1 |
| Magnesium | Mg2+ | +2 |
| Oxide | O2- | -2 |

🔬 Note: Some elements can form ions with different charges, known as multiple oxidation states.
Writing Ion Formulas

Constructing ion formulas requires attention to charge balance. Here's how to approach it:
- Determine the charges of the ions involved.
- Use the crisscross method to balance the charges:
- Place the numerical value of each ion's charge as the subscript to the other element's symbol.
- Reduce subscripts to their lowest common denominator.
For instance, if you're combining Aluminum and Sulfate:
Al3+ + SO42- → Al2(SO4)3
Ions Worksheet Answers: Examples and Common Misconceptions

Ions worksheets often include exercises where students must:
- Identify ions in a compound
- Write the formula of an ionic compound
- Determine the charge on a polyatomic ion
Let's work through some examples:
- What is the formula for calcium phosphate?
- Calcium ion: Ca2+
- Phosphate ion: PO43-
- Balancing charges: 3Ca2+ + 2PO43- → Ca3(PO4)2
- Identify the ions in sodium carbonate.
- Sodium ion: Na+
- Carbonate ion: CO32-
📝 Note: Remember that in the case of polyatomic ions, parentheses may be needed to indicate the number of ions within the formula.
Advanced Concepts in Ionic Compounds

Beyond the basics, here are some more intricate concepts:
- Hydration of Ions: When ions dissolve in water, they become surrounded by water molecules, altering their reactivity.
- Ion Solubility: Not all ionic compounds dissolve in water, leading to rules of solubility which predict whether a compound will form a solution or a precipitate.
- Ion Pair Formation: Oppositely charged ions can form ion pairs in solution, affecting the compound's behavior.
The study of ions extends into electrochemistry, where understanding redox reactions and electrochemical cells requires knowledge of ion movement.
Summing Up Key Takeaways

Mastering the world of ions and their reactions is essential for a comprehensive grasp of chemistry. We've explored the basics, types of ions, writing formulas, and tackled common worksheet questions. Understanding ions not only aids in chemical understanding but also in practical applications like electroplating, battery design, and even biological processes.
What’s the difference between an ion and a neutral atom?

+
Neutral atoms have an equal number of protons and electrons, thus having no net charge. Ions, however, gain or lose electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge, respectively.
How do I identify whether a compound will dissociate into ions in water?

+
Solubility rules and the concept of ionic strength can help predict this. Generally, ionic compounds with highly ionic bonds (like sodium chloride) will dissociate, while those with covalent bonds might not. Also, check the solubility product (Ksp) values.
Can an element form more than one type of ion?

+
Yes, elements with multiple oxidation states can form different ions. For example, iron can form Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, known as iron(II) and iron(III).
What is an ion pair?

+
An ion pair is when two oppositely charged ions in solution are close enough to interact without fully dissociating, which can affect chemical reactions and ion movement.
Why is it important to balance charges in ionic formulas?

+
Balancing charges ensures that the compound is electrically neutral as a whole, reflecting the chemical stability required for the compound to exist in nature.