7 Must-Know Answers for Ions & Isotopes Worksheet
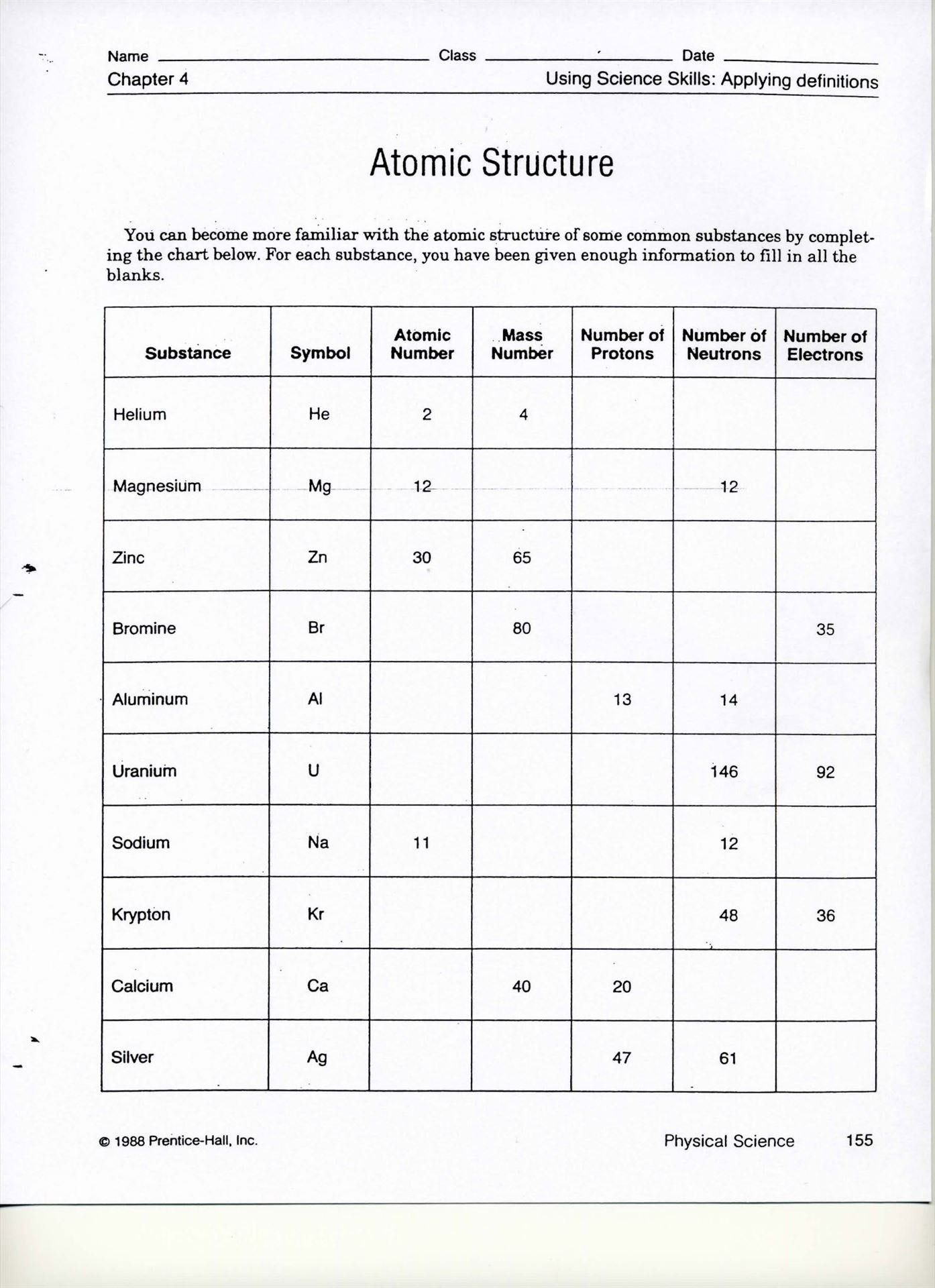
In the realm of chemistry, understanding ions and isotopes is fundamental for students and enthusiasts alike. These concepts might seem complex at first, but once you grasp them, they unlock many doors in the world of chemical sciences. Here, we will delve into the 7 must-know answers for ions and isotopes worksheets, providing you with clarity and the knowledge needed to excel in chemistry.
What are Ions?
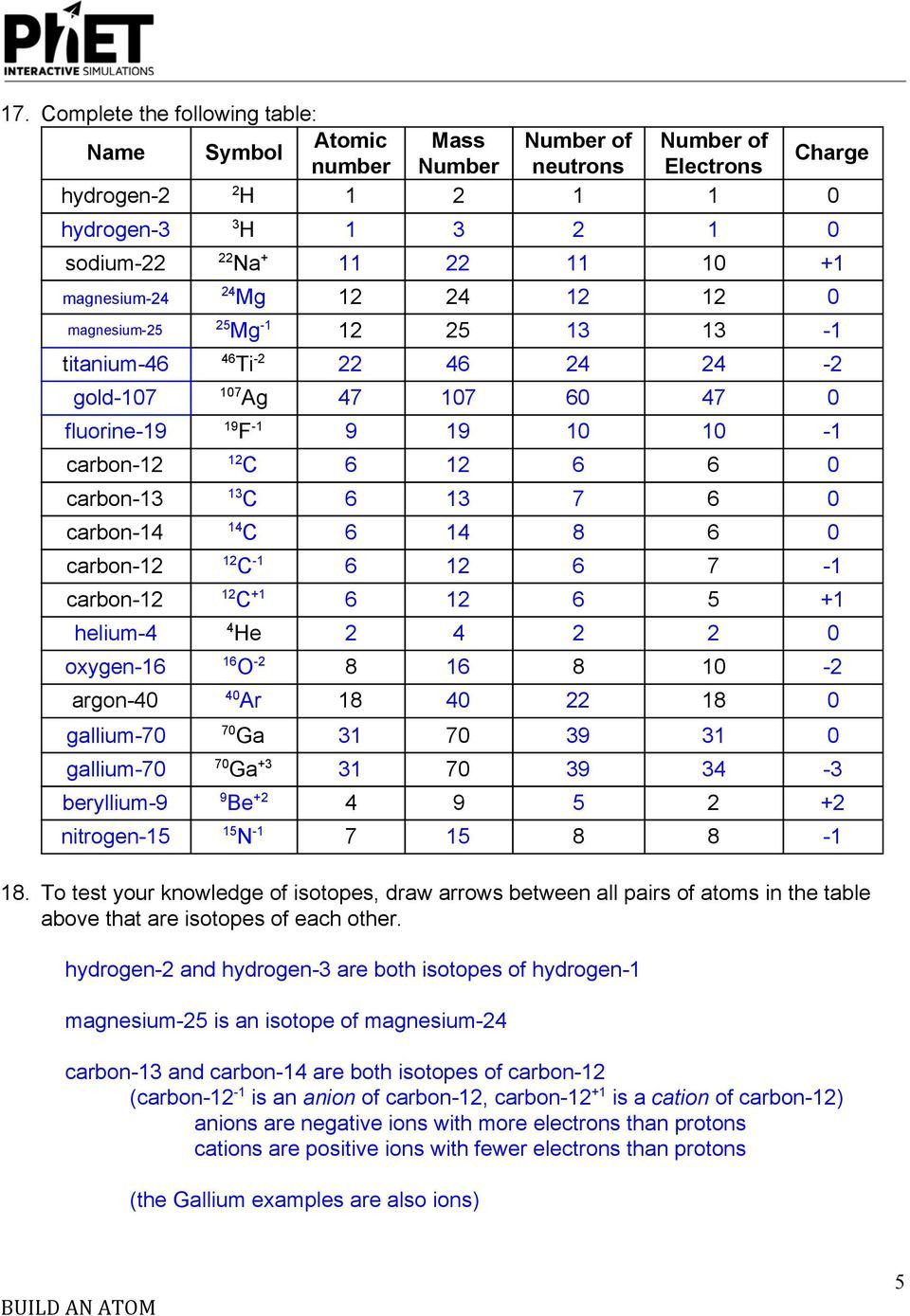

Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons, giving them a net electrical charge. Here’s a closer look:
- Cations: Positively charged ions created when an atom loses electron(s).
- Anions: Negatively charged ions formed when an atom gains electron(s).
Ions play crucial roles in chemical reactions, particularly in forming ionic compounds where oppositely charged ions attract one another.
How are Isotopes Different?


Isotopes, on the other hand, are variants of elements that differ in neutron numbers but share the same proton count:
- They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
- Chemical properties remain largely the same due to unchanged proton numbers.
- Physical properties like density and stability can differ.
Isotopes are essential for understanding why elements can have different masses and for applications in fields like medicine and nuclear energy.
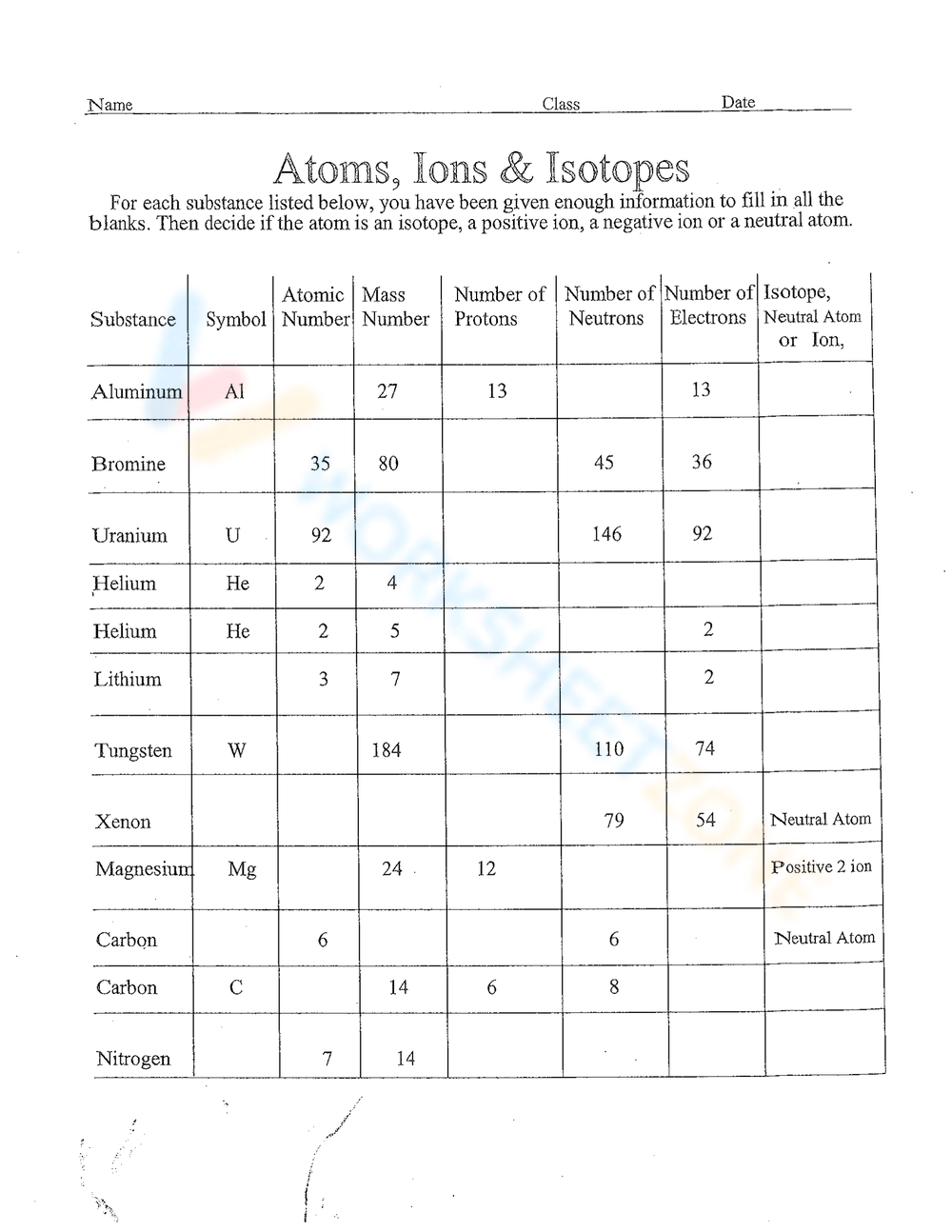
How to Identify Ions from Isotopes on a Worksheet

A common challenge in chemistry worksheets is differentiating between ions and isotopes. Here are the key steps:
- Check the Charge: Ions will always have a charge written next to the symbol, whereas isotopes won’t.
- Mass Number: Look for different mass numbers in an element; these indicate isotopes.
- Atomic Number: Ensure both ions and isotopes have the same atomic number.
🔍 Note: Atomic number tells you about the element, while the charge or mass number provides information about ions and isotopes respectively.
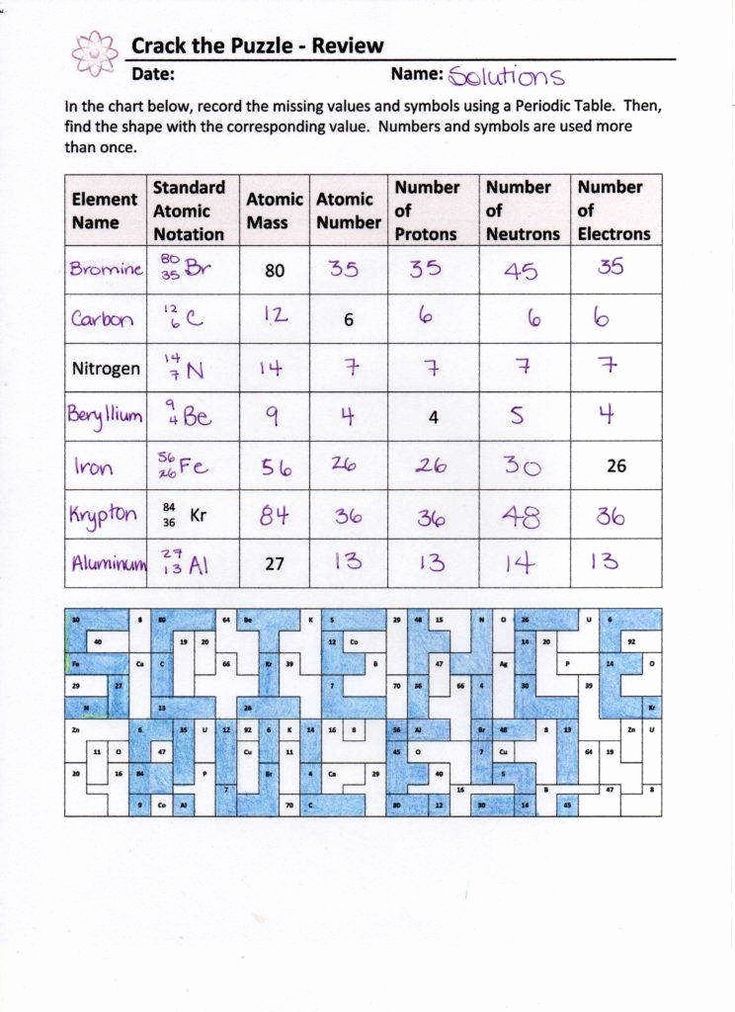
Common Calculations in Ions and Isotopes Worksheets

Worksheets often include calculations related to ions and isotopes:
- Finding Charge: Subtract the number of electrons from the number of protons. A positive result means a cation, and a negative result an anion.
- Isotope Abundance: Use relative abundance to calculate the average atomic mass of an element.
- Ionic Mass: When an atom ionizes, its mass remains the same since electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
| Element | Protons | Neutrons | Mass Number | Isotopes (Mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 0, 1 | 1, 2 | 1H, 2H (D), 3H (T) |
| Chlorine | 17 | 18, 20 | 35, 37 | 35Cl, 37Cl |

How do Ions and Isotopes Affect Chemical Behavior?

Both ions and isotopes influence chemical behavior, but in different ways:
- Ions: Ions determine the type of chemical bonds formed, like ionic bonds in compounds like sodium chloride.
- Isotopes: They affect the rate of chemical reactions due to the mass differences, but not the type of reactions or products formed.
Practical Applications of Ions and Isotopes

Ions and isotopes have many practical applications:
- Medicine: Radioisotopes are used for diagnosing and treating various diseases, including cancer therapy through radiation.
- Environment: Isotopes help track pollution or water pathways in the environment.
- Industry: Ionic compounds like salts are used in a myriad of industrial processes.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
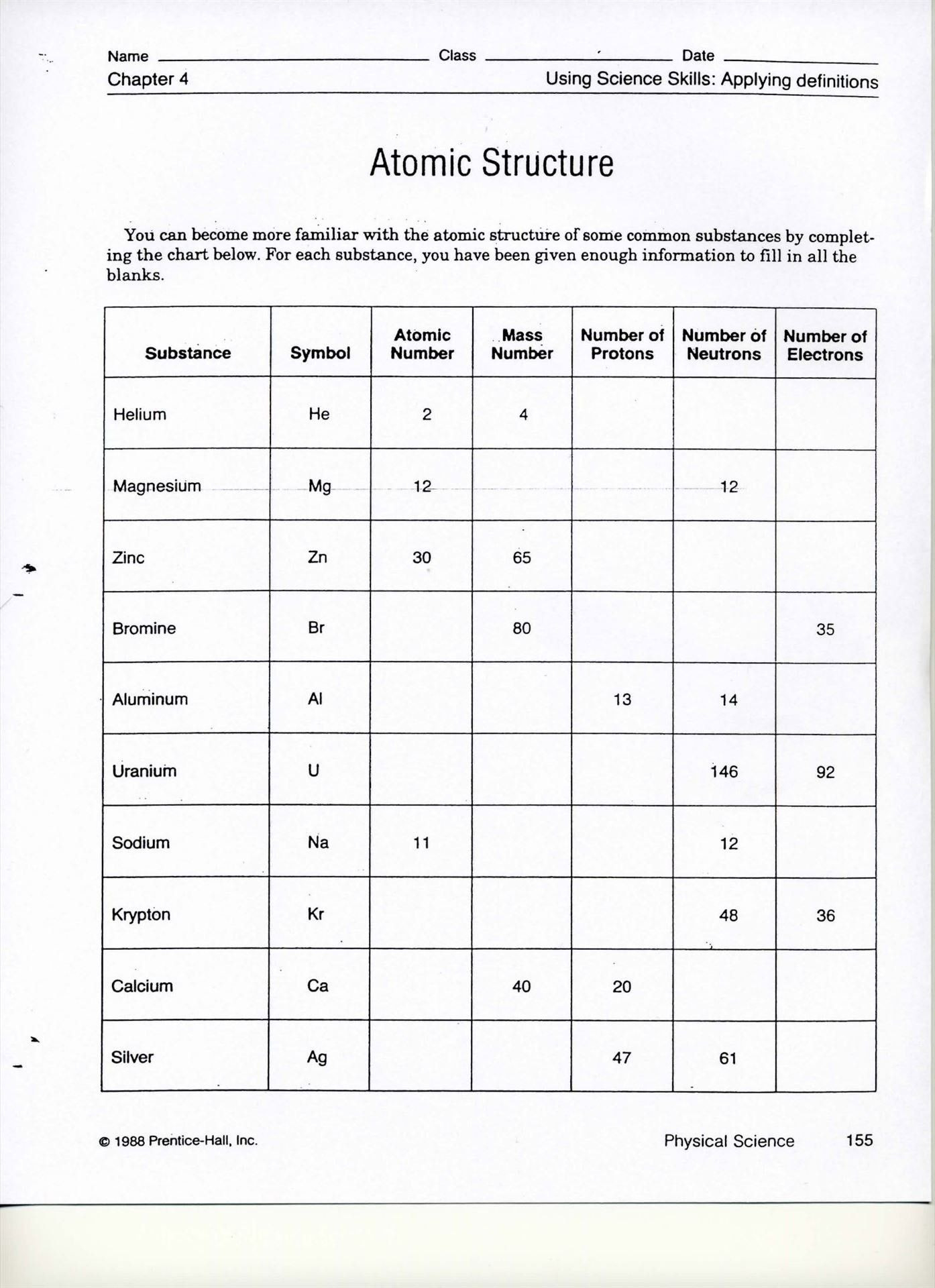
Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Mistaking isotopes for different elements.
- Confusing charge with mass when identifying ions.
- Thinking that isotopes change the element’s chemical identity.
💡 Note: Always remember that isotopes are different forms of the same element with the same number of protons but varying numbers of neutrons.
Mastering the differences between ions and isotopes is crucial for understanding chemistry at a deeper level. Through this detailed exploration, we have covered how ions and isotopes are identified, calculated, and applied in real-world scenarios. This knowledge not only clarifies their roles in chemistry but also enhances your ability to tackle chemistry problems and understand the fundamentals of matter.
What is the difference between an ion and an isotope?
+
An ion is an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. An isotope, however, refers to different forms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, hence differing in mass number but having the same atomic number.
How do ions form?

+
Ions form when atoms gain or lose electrons. This process can occur through various means, like in chemical reactions or through ionization in the gas phase by energy sources such as heat, light, or electrical discharge.
Why are isotopes important in medical science?

+
Isotopes, particularly radioisotopes, are crucial in medical science for diagnostic imaging (like PET scans) and for treating conditions such as cancer through targeted radiation therapy, where isotopes can selectively damage cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
Can an ion be an isotope, and vice versa?
+
Yes, an ion can be an isotope if it has gained or lost an electron from an isotope. Conversely, an isotope can become an ion if it loses or gains an electron. However, these are two separate properties: one is about charge, the other about nuclear composition.
How do you calculate the average atomic mass from isotopes?

+
To calculate the average atomic mass, you multiply the mass of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed as a fraction or percentage) and sum these products. The formula is:
(mass of isotope 1 × its abundance) + (mass of isotope 2 × its abundance) + …