Master Ionic & Covalent Compounds with This Worksheet

Understanding the fundamental differences between ionic and covalent compounds is pivotal for any student of chemistry. This article will guide you through an engaging worksheet tailored to solidify your grasp on these two types of chemical bonding. Whether you're preparing for an upcoming exam or deepening your understanding of chemistry, this worksheet will offer practical exercises that illustrate key concepts and distinctions between ionic and covalent compounds.
What Are Ionic and Covalent Compounds?

Ionic and covalent compounds represent two major classes of chemical compounds, each with distinct properties:
- Ionic Compounds: These form when one atom loses an electron (cation) and another gains an electron (anion). The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions creates the bond. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
- Covalent Compounds: Here, atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Bonds within these compounds are generally less strong than ionic bonds but allow for complex molecular structures. Common examples are water (H₂O) and methane (CH₄).
Your Ionic and Covalent Worksheet
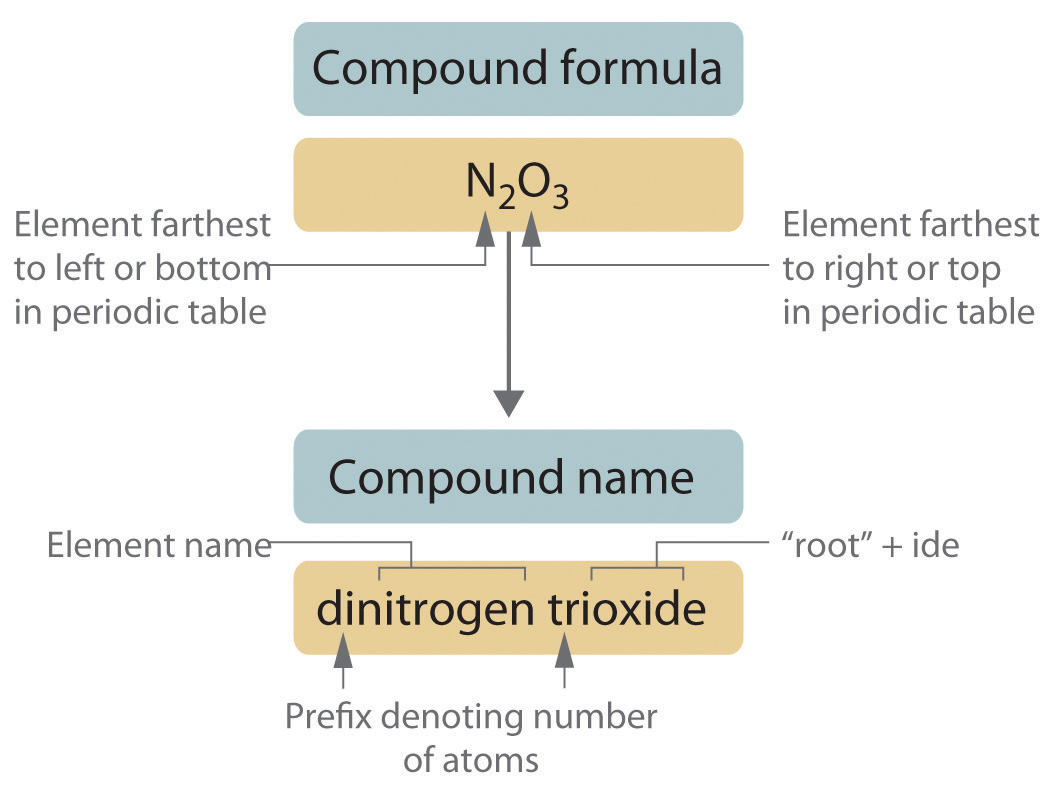
| Compound | Type (Ionic or Covalent) | Electronegativity Difference | Example Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Chloride | Ionic | >1.7 | MgCl₂ |
| Carbon Dioxide | Covalent | < 1.7 | CO₂ |
| Sodium Oxide | Ionic | >1.7 | Na₂O |
| Hydrogen Fluoride | Covalent | 1.9 (slightly polar) | HF |

Worksheet Instructions

This worksheet is designed to enhance your understanding of ionic and covalent bonds through practical applications:
- Identify the Type: Determine whether each compound listed in the table is ionic or covalent.
- Analyze Electronegativity: Use the electronegativity difference to confirm your selection. If the difference is greater than 1.7, classify the bond as ionic.
- Construct Molecules: Draw Lewis dot structures for covalent compounds and provide dot notation for ionic compounds.
⚠️ Note: The classification by electronegativity difference is not foolproof; there are exceptions, but it's a good starting point.
Practical Applications

Here’s how you can apply these concepts:
- Understand why ionic compounds are often found in the solid state at room temperature, while covalent compounds can be gases, liquids, or solids.
- Recognize that ionic bonds typically result in high melting and boiling points due to the strong attraction between ions.
- Learn how covalent bonding allows for the creation of complex organic molecules, critical in biochemistry and materials science.
Exercises to Master the Concepts
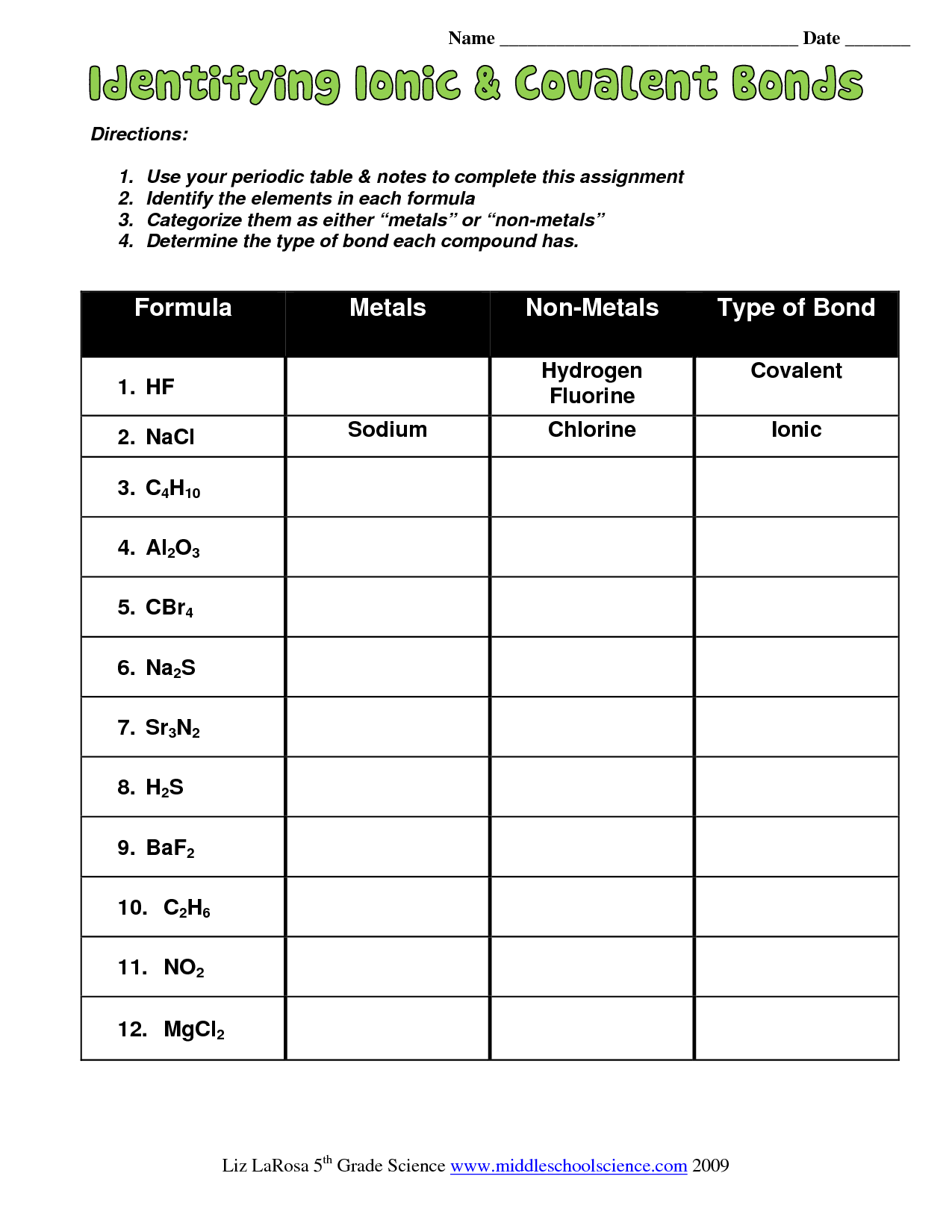
To reinforce your learning, here are some targeted exercises:
- Identify which elements would form an ionic bond if combined, and why.
- Practice drawing Lewis structures for simple covalent compounds like CO₂, H₂O, and NH₃.
- Analyze compounds from everyday life (e.g., sugar, salt) to determine their bonding type.
Deep Dive into the Differences

Let’s explore the nuances between ionic and covalent compounds:
- Solubility: Ionic compounds generally dissolve in polar solvents like water, whereas covalent compounds dissolve based on their polarity.
- Conductivity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved or molten, while covalent compounds do not.
- Reactivity: Covalent compounds often undergo chemical changes involving bond rearrangements, while ionic reactions often involve ion exchange or solubility differences.
By working through these differences, you'll develop a better appreciation for how different compounds behave under various conditions.
🔬 Note: The behavior of compounds is not just about bonding. Factors like molecular size, shape, and intermolecular forces also play significant roles.
Wrapping up this journey through the world of ionic and covalent compounds, we've seen how understanding the nature of chemical bonds can open up the complexities of chemical reactions, physical properties, and even the practical applications in daily life. The exercises and knowledge gained from this worksheet will not only prepare you for chemistry examinations but will also equip you with the ability to predict compound behaviors, aiding in both academic and practical applications.
What are the typical properties of ionic compounds?

+
Ionic compounds often have high melting and boiling points, are solid at room temperature, conduct electricity when dissolved or molten, and are usually brittle.
How do covalent compounds differ in physical properties?

+
Covalent compounds can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature, often have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds, and do not conduct electricity.
Can a compound exhibit both ionic and covalent bonds?

+
Yes, compounds like sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) exhibit both types of bonds. Sodium and bicarbonate ions form ionic bonds, while the bicarbonate ion internally has covalent bonds.