5 Essential Ion Worksheet Answer Keys Revealed
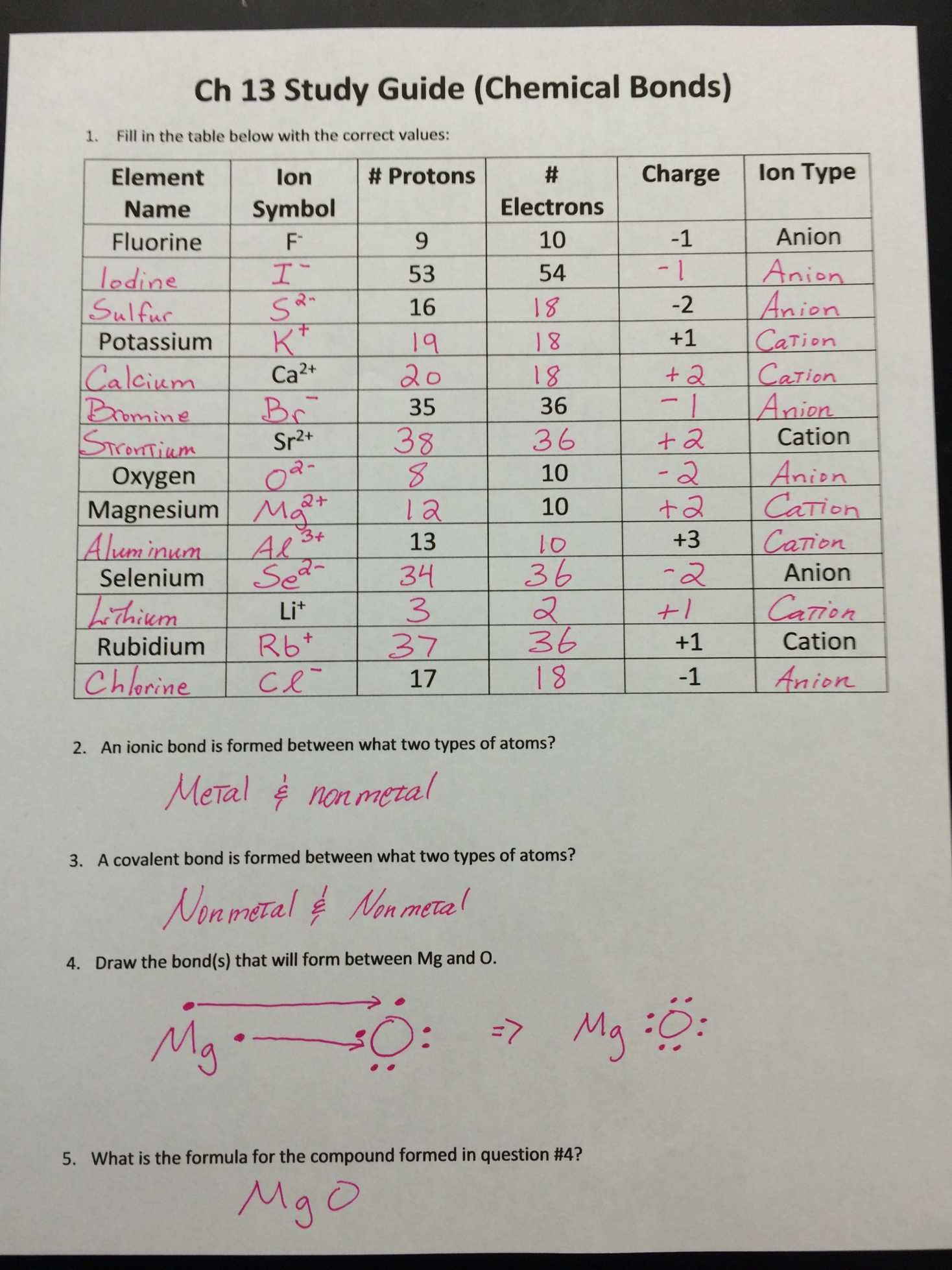
Embarking on a journey through chemistry, understanding ions and their behavior is fundamental for students and educators alike. Whether you're learning for an upcoming test, preparing lesson plans, or simply brushing up on your chemistry knowledge, ion worksheets serve as an invaluable tool. This comprehensive blog post will unveil five essential ion worksheet answer keys that can streamline the learning process, enhance your understanding of ions, and boost your confidence in tackling related chemistry topics.
Ion Worksheet Answer Key #1: Ionic Charges
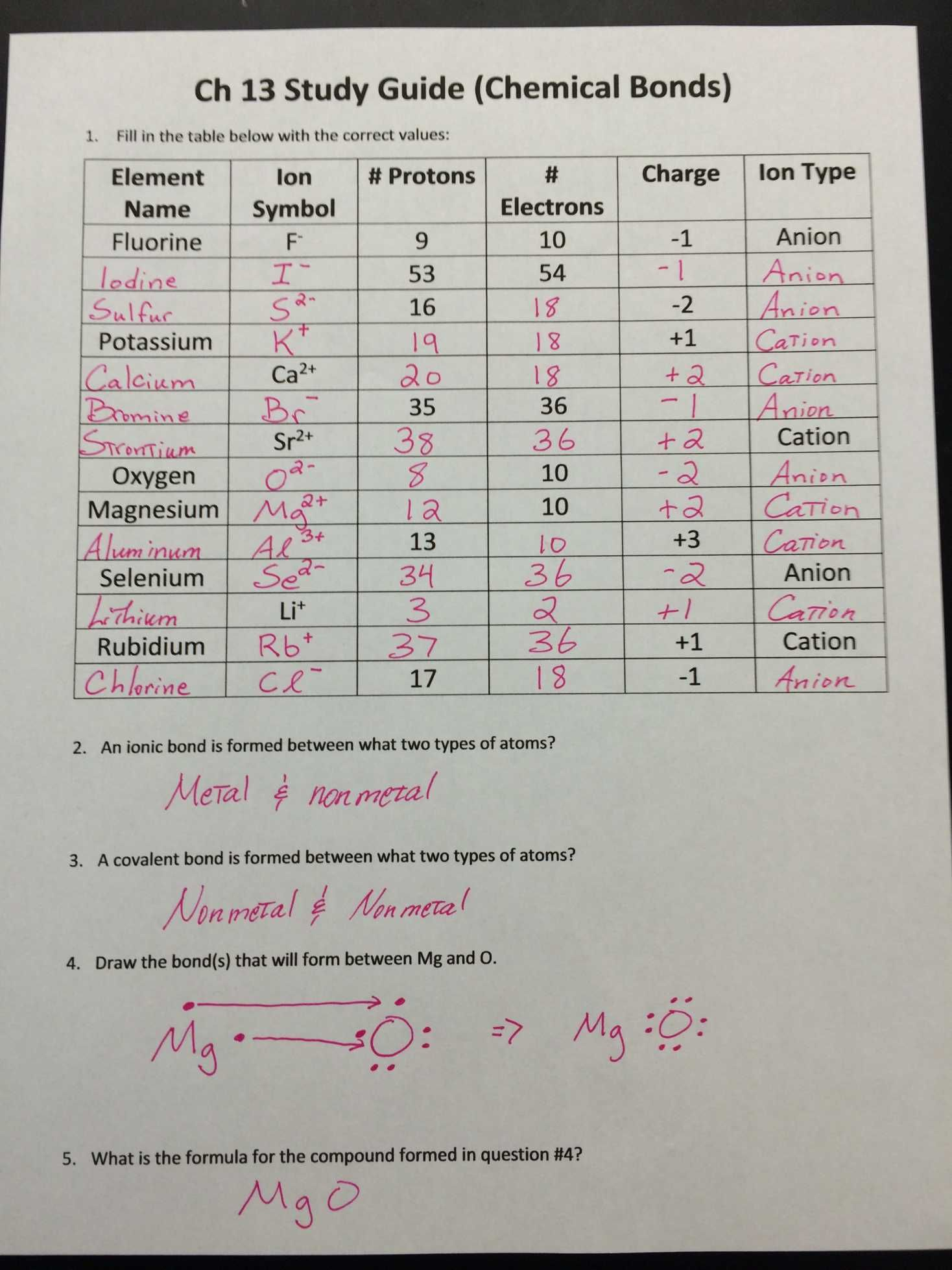
Ionic charges are pivotal in determining how elements bond and interact. Here’s a simple table that illustrates the common ionic charges:
| Element | Ionic Charge |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | +1 |
| Helium (He) | 0 |
| Lithium (Li) | +1 |
| Beryllium (Be) | +2 |
| Boron (B) | +3 |

This table highlights the usual ionic states of various elements in their simple ionic compounds. Knowing these charges helps in predicting the composition of ionic compounds and the charge balance between anions and cations.
🔬 Note: Always remember that an element can exhibit multiple charges based on its electron configuration and bonding context.
Ion Worksheet Answer Key #2: Writing Ion Formulas

Forming formulas from ions requires understanding the charge neutrality of compounds. Here are the steps to write ion formulas:
- Identify the Charges: Use the periodic table or the charge table above to identify the charges of the ions involved.
- Balance the Charges: Cross over the charges and reduce to their simplest ratio if possible. For example, for magnesium chloride (MgCl2), magnesium has a +2 charge, and chloride has a -1 charge, leading to MgCl2.
- Write the Formula: Place the symbols of elements together with the number of each atom indicated in the subscript.
Ion Worksheet Answer Key #3: Naming Ions and Ionic Compounds

Naming ions and ionic compounds follows these rules:
- Monatomic Ions:
- Cations from metals or hydrogen are named simply by the element name followed by the word ion, e.g., Sodium ion.
- Anions, typically from non-metals, take the root of the element name followed by the suffix -ide, e.g., Chloride ion.
- Polyatomic Ions: These are ions consisting of multiple atoms but acting as a single charged entity. Their names often indicate their composition, like sulfate (SO42-) for the sulfate ion.
- Transition Metal Ions: Roman numerals are used to indicate the charge when an element can have multiple valences, e.g., Copper(II) ion.
💡 Note: The use of Roman numerals is critical for metals with variable charges to differentiate between different oxidation states.
Ion Worksheet Answer Key #4: Predicting Ion Formation

By examining an element’s position on the periodic table, you can predict its likelihood to gain or lose electrons:
- Group 1: Elements like Sodium will readily lose one electron to achieve a noble gas configuration, forming a +1 cation.
- Group 16: Elements like Oxygen will tend to gain two electrons, forming a -2 anion.
- Transition Metals: Can lose electrons in different ways due to their complex electron configurations; e.g., Copper can form Cu+ or Cu2+.
Ion Worksheet Answer Key #5: Working with Ionic Compounds in Solutions

Solutions often contain ions as free charged particles, which can lead to various chemical reactions:
- Dissociation: Ionic compounds dissolve in water, dissociating into their constituent ions. For example, Sodium Chloride (NaCl) dissociates into Na+ and Cl- ions.
- Precipitation: When certain ions come into contact, they can form insoluble compounds. This process is used to confirm the presence of specific ions through precipitation reactions.
- Redox Reactions: Ions can participate in oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, changing oxidation states, e.g., Fe2+ to Fe3+.
In conclusion, mastering ions and their behavior opens up a world of understanding in chemistry. From predicting ion formation, writing formulas, and naming compounds to observing their interactions in solutions, the answers provided in these worksheet keys give you a strong foundation in ionic chemistry. Remember, practice with ion worksheets not only enhances your grasp of fundamental concepts but also sharpens your analytical and problem-solving skills in science.
Why are ions important in chemistry?

+
Ions are the building blocks of many compounds, crucial for understanding reactions, electricity conduction, and the behavior of substances in solutions.
What’s the difference between an anion and a cation?

+
Anions are negatively charged ions, typically formed by gaining electrons, while cations are positively charged ions, formed by losing electrons.
How do you determine an element’s likely ionic charge?

+
The position of an element in the periodic table gives clues to its likely ionic charge. For instance, elements in Group 1 tend to form +1 ions, while those in Group 17 form -1 ions.
What are some common mistakes when naming ions?

+
Not accounting for variable oxidation states of transition metals, misusing the -ide suffix for polyatomic ions, and neglecting the Roman numerals when necessary.
Can you use these ion worksheet keys for any curriculum?

+
These keys provide a general overview of ions, adaptable for most educational curriculums, though some adjustments might be needed to align with specific learning objectives or standards.