5 Key Answers for Catalase Activity Worksheet

Understanding the catalase activity worksheet can be a vital part of grasping the fundamentals of enzyme kinetics and biochemical reactions. Enzymes, like catalase, are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required. Here, we will explore five key answers that are commonly sought when analyzing the activity of catalase, an enzyme known for its role in breaking down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen:
1. What is Catalase?
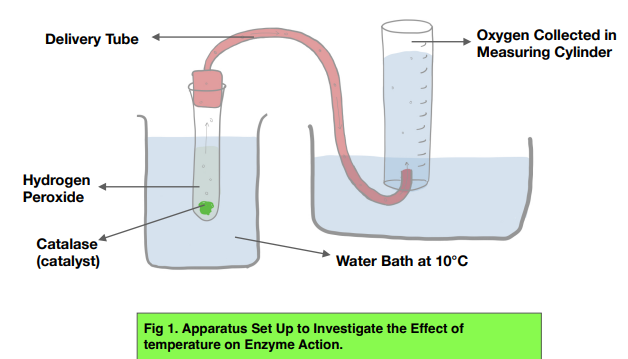

Catalase is an enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen. Its main function is to catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) into harmless substances like water and oxygen:
| Substance | Formula |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Peroxide | H₂O₂ |
| Water | H₂O |
| Oxygen | O₂ |

This reaction is crucial because hydrogen peroxide, a by-product of various metabolic processes, can be toxic if not managed:
- Protects cells: Catalase protects cellular components from oxidative damage caused by hydrogen peroxide.
- Efficient catalyst: It can turn millions of molecules of H₂O₂ into water and oxygen every second.
- Present in multiple locations: It’s found in high concentrations in the liver, kidney, and red blood cells, but also in various other tissues.
Understanding catalase’s function aids in exploring enzyme behavior in biological systems.
2. How Does Catalase Activity Work?


The catalase activity worksheet usually involves studying how:
- Substrate concentration affects reaction rates: With increasing H₂O₂ concentration, the rate of reaction increases until it plateaus due to enzyme saturation.
- Temperature influences catalase efficiency: An optimal temperature range where the reaction rate peaks before the enzyme denatures.
- pH impacts enzyme functionality: Catalase has an optimal pH, generally neutral, where it is most active.
- Enzyme concentration plays a role: More enzyme means a higher initial reaction rate until the substrate concentration becomes limiting.
Here, students often measure the oxygen released to quantify catalase activity, employing visual observation or measuring the rate of oxygen gas production.
3. What Factors Affect Catalase Activity?

To understand catalase activity, one must consider the following factors:
- Substrate Concentration: If the concentration of H₂O₂ is low, the reaction rate is substrate-limited; if too high, the enzyme gets saturated.
- Enzyme Concentration: Higher catalase concentrations lead to higher initial rates of reaction.
- pH: Enzymes are sensitive to pH changes; catalase is most effective in neutral conditions.
- Temperature: Catalase functions best at an optimal temperature; beyond this point, the enzyme may start to denature, reducing activity.
- Inhibitors: Some substances can inhibit catalase activity either by binding to the enzyme or altering its structure.
🧬 Note: High concentrations of substrate can lead to a phenomenon known as substrate inhibition, where the enzyme is less effective at higher substrate concentrations.
4. Why is Studying Catalase Important?
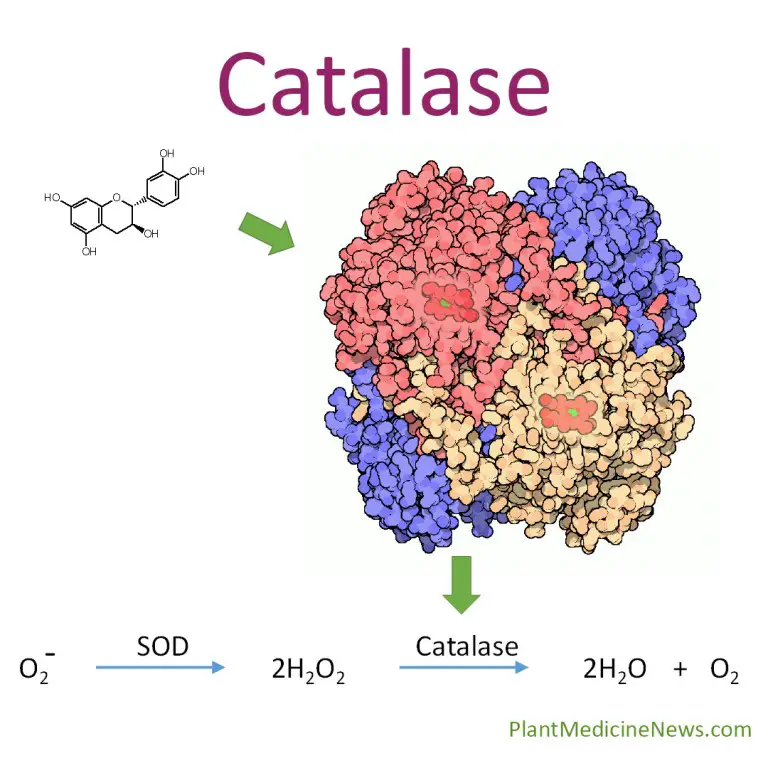
Studying catalase activity has several applications:
- Health Implications: Understanding enzyme kinetics can lead to insights into diseases involving oxidative stress or enzymatic dysfunction.
- Biotechnology: Enzymes like catalase are used in various industrial processes where their ability to detoxify is vital.
- Scientific Research: It’s a model for enzyme kinetics and can help in the development of new biochemical assays.
- Education: It provides a tangible example for teaching concepts like enzyme-substrate specificity, reaction rates, and factors affecting enzyme activity.
🔬 Note: Enzymes like catalase are also used in research to study reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play a role in cell signaling and various disease pathologies.
5. Practical Applications of Catalase Activity Experiments
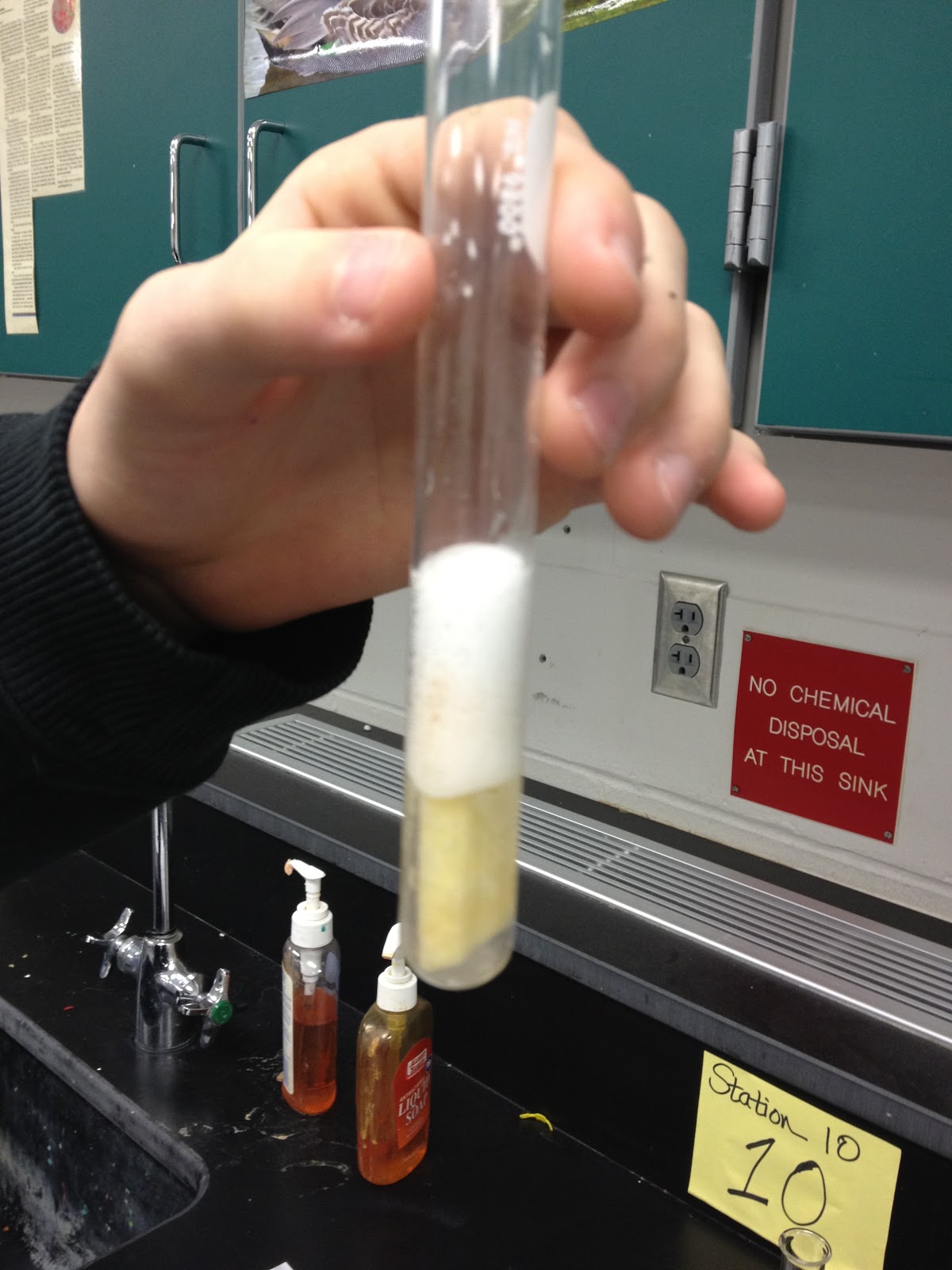
When conducting catalase activity experiments:
- Educational Demonstrations: Simple setups with potatoes or liver tissue can illustrate enzyme activity visually.
- Enzyme Assays: These experiments help quantify enzyme concentration in biological samples.
- Biotechnological Applications: Catalase’s ability to detoxify hydrogen peroxide makes it useful in medical, food, and textile industries.
- Environmental Control: Understanding catalase can help manage hydrogen peroxide levels in ecosystems.
- Research and Development: Insights from these experiments can be applied to drug development, particularly in therapies related to antioxidant systems.
The practical exploration of catalase activity can offer invaluable lessons in both the science and the practical application of enzyme kinetics.
Understanding and experimenting with catalase activity not only teaches fundamental biochemical concepts but also opens the door to practical applications across various fields. By exploring the kinetics of this enzyme, one gains insights into the balance of chemical reactions in living organisms, industrial processes, and even the potential for developing new therapies or improving existing ones. The study of catalase is thus not just an academic exercise but a step towards mastering the complexities of life at a molecular level.
What are the units used to measure catalase activity?

+
The activity of catalase is often measured in units like katals (Kat), where 1 Katal is the amount of enzyme that converts 1 mole of substrate per second, or Units per milliliter (U/mL), where one unit of catalase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of 1 micromole of H₂O₂ per minute at 25°C and pH 7.0.
Can catalase activity be increased?
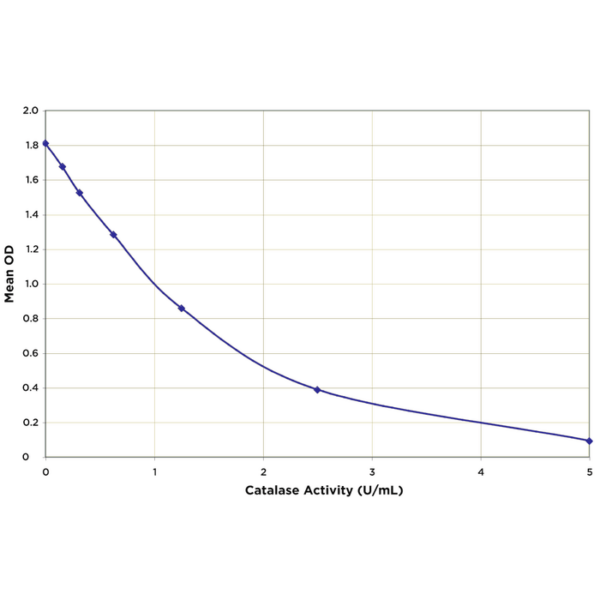
+
Yes, catalase activity can be enhanced by optimizing conditions like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. However, it can also be artificially increased by genetic engineering to produce more catalase or by using enzyme activators. But beyond certain limits, natural catalysts can denature, reducing their activity.
How does catalase benefit the food industry?

+
Catalase is used in the food industry for various purposes:
- Preservative: It helps to remove hydrogen peroxide used in food sterilization processes.
- Fermentation: It aids in the fermentation process by removing unwanted oxygen.
- Enzyme Modification: Catalase is added to modify the texture, flavor, and shelf-life of foods.
Can you use other substances besides potatoes for catalase experiments?

+
Absolutely! Apart from potatoes, you can use liver (both raw and cooked), yeast, and various fruits or vegetables with high catalase content like:
- Carrots
- Green beans
- Broccoli
These tissues contain catalase, allowing for visible reactions with hydrogen peroxide.
Is catalase harmful if ingested?

+
Catalase is not harmful when ingested in small amounts as it is present in various foods we consume daily. However, catalase supplements should be taken with caution, and as with any dietary supplement, consult a healthcare provider before starting any new regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.