Physical vs Chemical Changes: Worksheet Answers Unveiled
In the world of science, understanding the differences between physical and chemical changes is fundamental. Students often grapple with these concepts, and it's not just about memorizing definitions; it's about understanding the essence of these changes. This blog post aims to shed light on these key differences, offering insights into the physical vs chemical changes worksheet answers, and providing clarity to both students and teachers.
Exploring Physical Changes

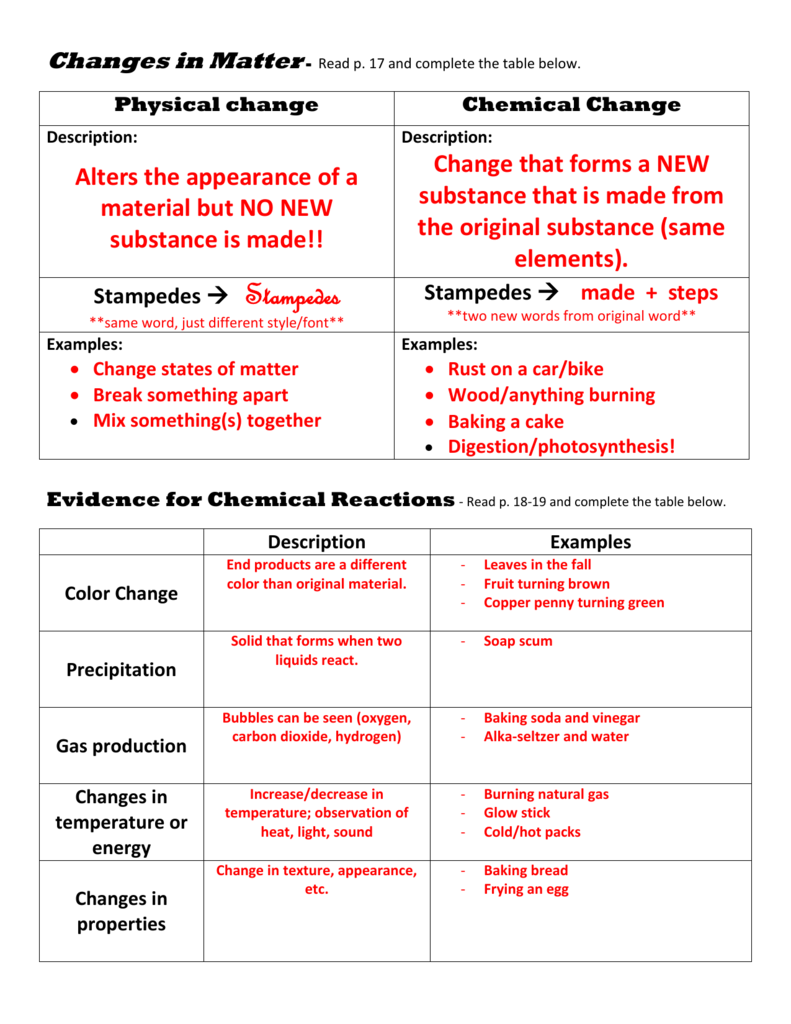
Physical changes involve alterations in the state or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical identity. Here are some key aspects:
- Changes in State: When you melt ice or boil water, you're observing a physical change. The water molecule (H2O) does not change; it just transitions from one state to another.
- Dissolution: Dissolving sugar in water is another example. The sugar doesn't become something else; it simply spreads out within the water.
- Physical Properties: These changes affect properties like density, volume, shape, and state but do not alter the substance at a molecular level.
One might remember this by understanding that in physical changes, energy might be absorbed or released, but the substances involved remain chemically the same.
Delving into Chemical Changes


Chemical changes, on the other hand, result in the formation of new substances with different properties. Here's how they differ:
- New Substances Formed: When iron rusts, for instance, the iron (Fe) combines with oxygen (O) to form iron oxide (Fe2O3), an entirely new compound.
- Energy Change: Chemical changes often involve significant energy changes, such as heat, light, or electricity. Burning wood is an example where energy is released in the form of heat and light.
- Irreversibility: Unlike physical changes, most chemical changes are not easily reversed. You can't simply put rust back to being iron and oxygen without an additional chemical reaction.
The Worksheet Decoded

Worksheets often present a challenge by asking students to classify various phenomena as physical or chemical changes. Here are some typical examples with their answers:
| Change Description | Type of Change |
|---|---|
| Melting chocolate | Physical Change |
| Wood burning in a fireplace | Chemical Change |
| Water freezing into ice | Physical Change |
| Rusting of iron | Chemical Change |
| Dissolving salt in water | Physical Change |

🔬 Note: When in doubt, ask yourself if a new substance has been created or if the substances are just changing form. This can help in distinguishing between the two types of changes.
It's crucial for students to understand the underlying principles rather than just memorizing examples. This conceptual understanding aids in accurately identifying changes when presented with new scenarios.
Importance of Knowing the Difference

- Environmental Impact: Understanding chemical changes helps in identifying pollution, like the rusting of cars or ships.
- Safety: Knowing what constitutes a chemical reaction can prevent accidents. For example, recognizing that combining certain household chemicals can produce harmful gases.
- Innovation: In industrial processes, knowing when a chemical change occurs is key to product development, like in pharmaceuticals where the reaction can lead to a new drug compound.
Engaging Experiments

Science is best learned through observation and experimentation. Here are some simple experiments that illustrate physical and chemical changes:
- Effervescence Experiment: Mix baking soda and vinegar to observe a chemical reaction where gas is released.
- Heat-Induced Changes: Heat sugar to show how it caramelizes (a chemical change) vs. melting wax (a physical change).
These experiments not only make the learning process enjoyable but also help students visualize and understand these changes at a practical level.
In closing, mastering the distinction between physical and chemical changes is not merely an academic exercise but a vital skill for understanding the world around us. Whether it's the rusting of a playground slide or the baking of a cake, these principles permeate our daily experiences. The key takeaway is to look beyond the obvious changes in appearance to understand if a substance's identity has been altered. This insight fosters a deeper appreciation for chemistry and its implications in life, from everyday occurrences to complex industrial processes.
Can a physical change be reversed?

+
Yes, most physical changes are reversible. For example, melted chocolate can be cooled and solidified again. However, some changes might require a process, like re-forming ice from water vapor, but the molecules remain the same.
How can I tell if a chemical change has occurred?

+
Indicators of a chemical change include the formation of a new substance, color change, energy release (like heat or light), gas production, or the creation of an insoluble solid (precipitate).
Why is it important to distinguish between physical and chemical changes?

+
Understanding these changes is fundamental in various fields like chemistry, engineering, medicine, and environmental science. It helps predict material behavior, manage industrial processes, and understand biological reactions.
Does a change in energy always indicate a chemical change?

+
No, while significant energy changes are often associated with chemical reactions, physical changes like freezing or melting can also involve energy absorption or release, though they do not result in new substances.