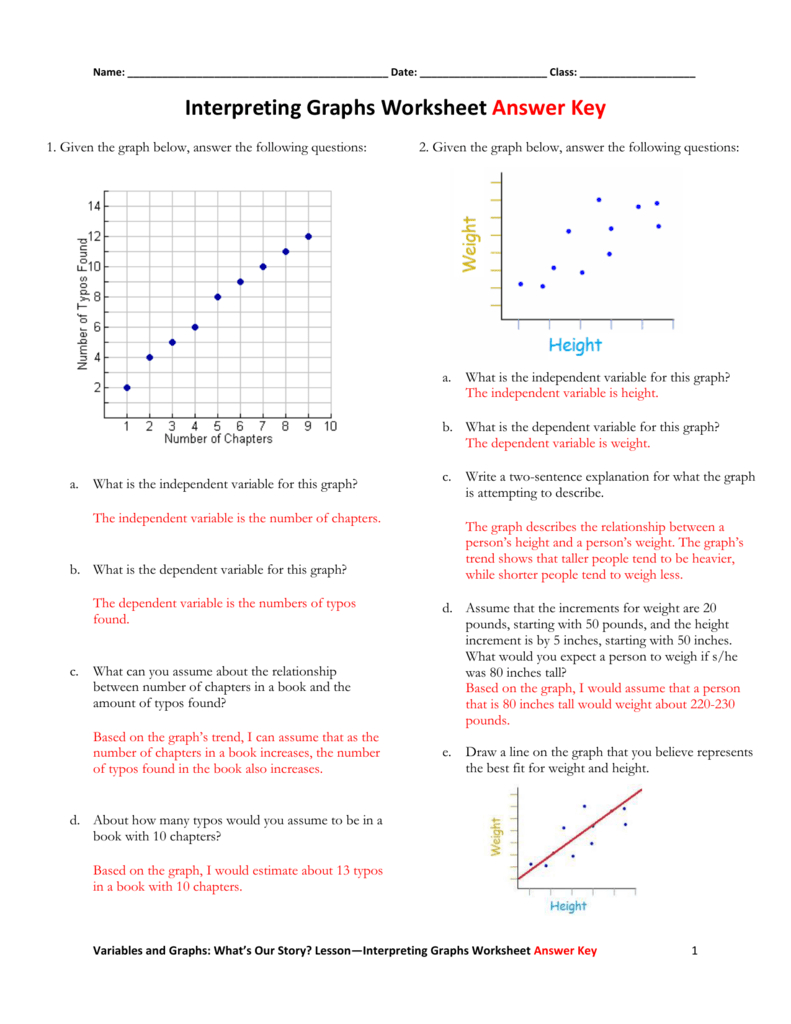
Unlocking Data Insights: Interpreting Graphics Worksheet Mastery

The Importance of Data Visualization
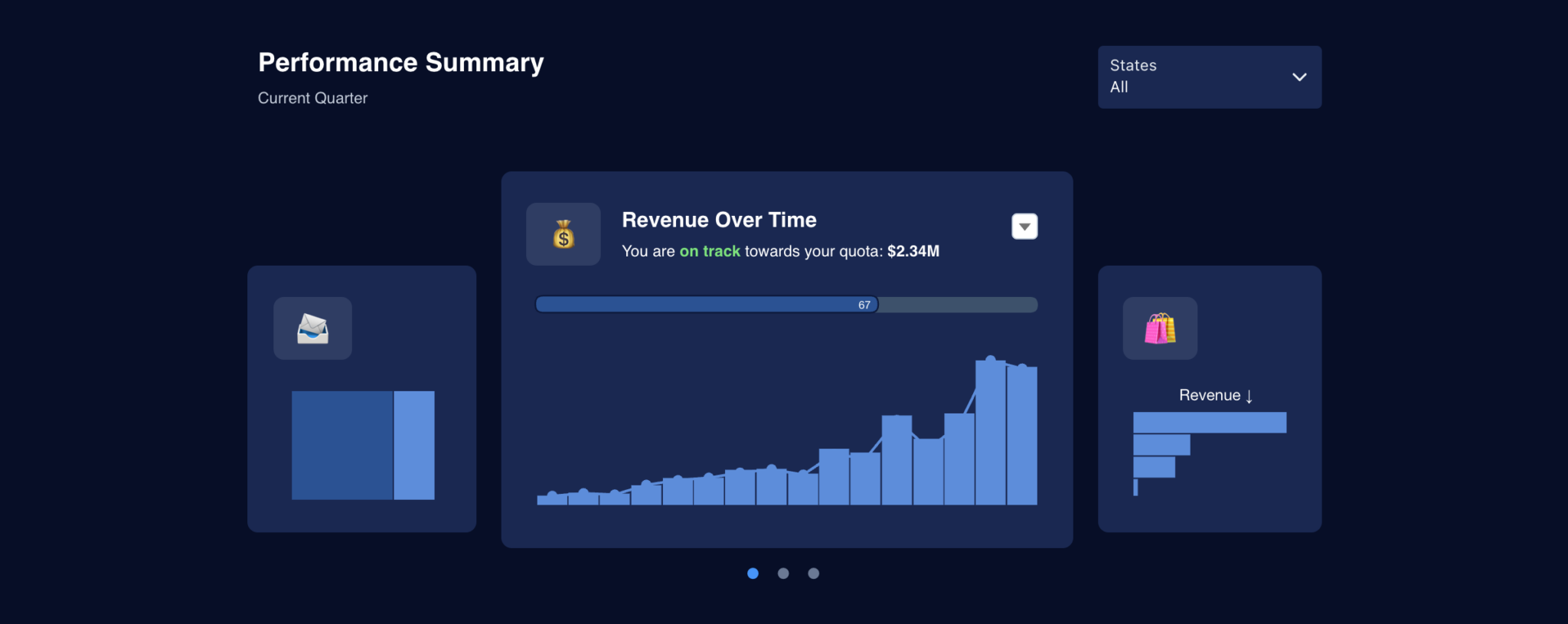
In the digital age, where data is abundant and decisions are increasingly data-driven, the ability to interpret and understand visual data representations is crucial. Data visualization is not just about making numbers look appealing; it’s a powerful tool for uncovering insights, identifying trends, and making informed decisions. Through this guide, we delve deep into the world of interpreting graphics worksheets to master the art of data analysis, ensuring that even complex information becomes accessible, understandable, and actionable.
Understanding Graphics Worksheets


Graphics worksheets, or data visualizations, come in various forms, each suited for different types of data and purposes:
- Bar Charts: Ideal for comparing quantities across different categories.
- Line Graphs: Best for showing trends over time or continuous data.
- Pie Charts: Useful for demonstrating proportions or percentage distributions within a whole.
- Scatter Plots: Great for spotting relationships and patterns between variables.
- Heat Maps: Effective for showing magnitude or density through color gradients.
- Box Plots: Offer insights into statistical distributions, central tendency, and variability.
📌 Note: Choosing the right type of chart or graph is vital for effectively conveying your message. Each graphic tool has its strengths and is best used in specific contexts.
Mastering the Interpretation of Data Visualization
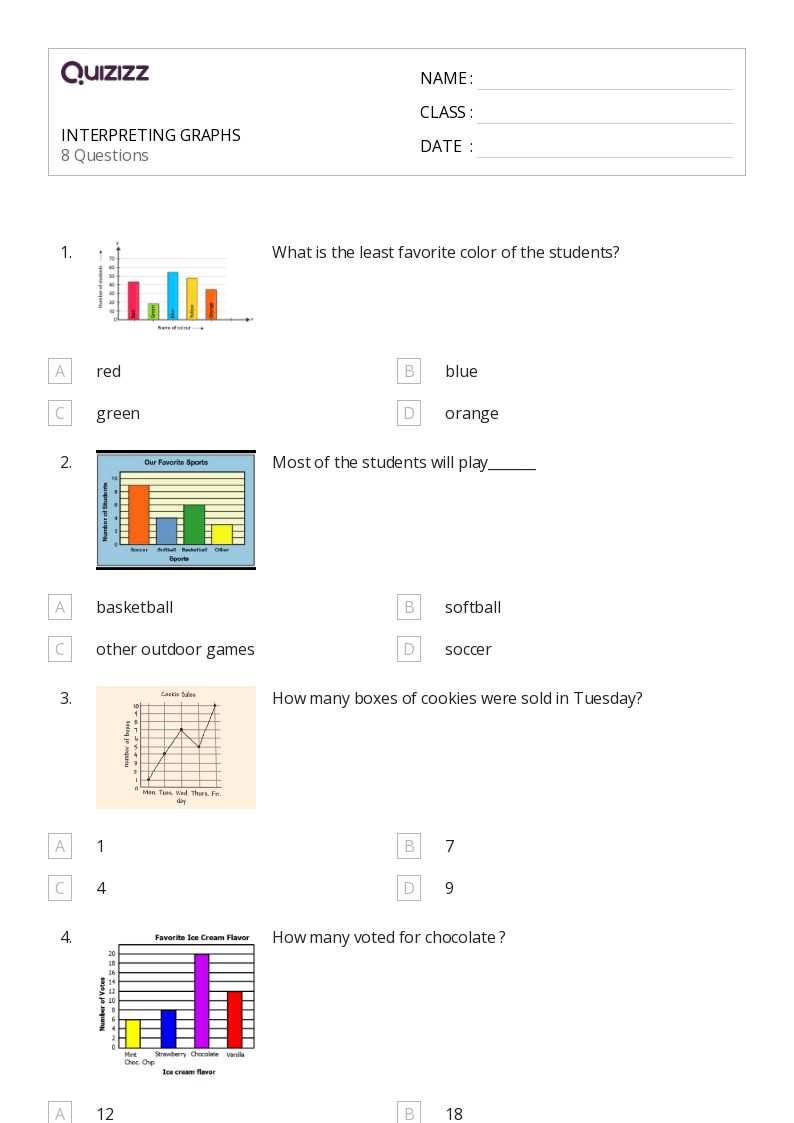
To unlock the full potential of data visualization, here are several steps and considerations:
1. Identify the Purpose of the Visualization

Before diving into the data:
- Understand what the data is supposed to communicate. Is it for comparison, trend analysis, or distribution?
2. Analyzing Components of Graphics

Every visual has components that need to be understood:
- Axes: Check what the axes represent, especially if non-linear scales are used.
- Legends: Decipher what different colors, symbols, or lines signify.
- Titles and Labels: These provide context and clarify what you’re looking at.
- Units of Measure: Ensure you know if you’re dealing with percentages, absolutes, or some other metric.
3. Extract Insights

Now, engage with the data to uncover:
- Trends: Look for patterns over time or changes in distribution.
- Outliers: Identify data points that don’t fit the overall trend.
- Correlations: Search for relationships between different variables.
4. Evaluate Data Integrity

It’s essential to ensure:
- The data is accurate and free from manipulation.
- The representation isn’t misleading due to graphical exaggeration or misrepresentation.
🧐 Note: Data visualizations can sometimes be misleading if not interpreted with care. Look for missing axes, truncated scales, or missing data points that could skew your understanding.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Let’s explore some practical scenarios where interpretation of graphics worksheets is key:
Example 1: Sales Data Visualization

| Quarter | Sales Volume |
|---|---|
| Q1 | 1000 |
| Q2 | 1200 |
| Q3 | 1500 |
| Q4 | 2000 |

Analyzing this bar chart, one can identify an upward trend in sales from Q1 to Q4. However, the data might not always reflect the entire picture:
- What were the contributing factors to this growth?
- Are there seasonal effects that could explain the variance?
Example 2: Market Segmentation

Here, a pie chart shows the market share of different segments:
- Segment A: 35%
- Segment B: 25%
- Segment C: 20%
- Others: 20%
This visualization highlights which segments are most significant for targeting marketing efforts.
Case Study: Traffic Patterns Analysis

A line graph illustrating traffic patterns over several months can reveal trends like seasonal patterns, peak traffic hours, or impacts of events or construction. By understanding this, city planners or business owners can make strategic decisions:
- Where to invest in infrastructure.
- When to schedule deliveries or promotional activities.
Tools and Techniques for Creating Graphics Worksheets

To create compelling and accurate data visualizations, consider these tools and techniques:
1. Data Visualization Software
- Microsoft Excel: Widely used, with robust graphing capabilities.
- Tableau: Offers advanced interactive visualizations.
- Power BI: Great for connecting to various data sources and creating dashboards.
- Python with libraries like Matplotlib or Seaborn: For those with coding proficiency.
2. Best Practices in Data Visualization

- Simplicity: Avoid cluttering with too many data points or decorations.
- Accurate Scaling: Use the correct scale to represent data faithfully.
- Accessibility: Ensure visuals are readable to people with visual impairments.
✍ Note: Always design with the audience in mind. What might be clear to you might not be to your audience, so test your visuals with others.
Final Thoughts on Data Visualization Mastery

Mastering the interpretation of graphics worksheets is not just about knowing how to create charts; it’s about understanding the stories data can tell, the insights they can reveal, and the decisions they can influence. Through this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored how to approach different types of data visualizations, analyze their components, extract meaningful insights, and even create your own visual representations. Data literacy, particularly the ability to interpret visual data, is a key competency in today’s data-centric world, enabling better strategic decisions across various sectors and industries.
Why is it important to choose the right type of chart?
+
Selecting the appropriate chart type ensures that the data is presented in the most effective manner to convey the intended message or highlight specific aspects of the data like trends, proportions, or relationships.
Can misleading data visualization affect decision making?
+Yes, misleading visualizations can lead to incorrect interpretations of data, influencing decisions in a potentially harmful or unproductive way. It’s important to critically analyze how data is presented.
What should I do if I notice a discrepancy in the data?
+If you detect an anomaly or inconsistency in the data, cross-reference with the data source, check for errors in data entry, and consider if there might be external factors influencing the data. Understanding the context is crucial.
How can I become better at interpreting data visualizations?
+Regular practice, understanding different types of charts and their purposes, as well as learning from case studies and real-world examples, can significantly enhance your ability to interpret data visualizations effectively.
Which tool is best for creating professional data visualizations?
+The choice of tool depends on your needs, familiarity, and the complexity of the data. For beginners, Excel is accessible. For more advanced users, Tableau, Power BI, or even coding with Python libraries like Matplotlib can offer superior capabilities.