7 Key Roles of Infantry Members

Understanding the Diverse Responsibilities of Infantry Members
Infantry members are the backbone of any military force, playing a crucial role in ground combat operations. Their responsibilities are diverse and demanding, requiring a unique blend of physical and mental toughness, technical skills, and strategic thinking. In this blog post, we will explore the 7 key roles of infantry members, highlighting their importance in modern military operations.
Role 1: Frontline Combat

Infantry members are trained to engage in frontline combat, using a range of weapons and tactics to defeat enemy forces. They must be able to operate in a variety of environments, from urban jungles to rural landscapes, and adapt to changing situations quickly. Frontline combat requires infantry members to be physically fit, mentally tough, and able to work effectively as part of a team.
Key Skills:

- Marksmanship and weapon handling
- Tactical maneuvering and formations
- First aid and medical evacuation
- Communication and coordination with other units
Role 2: Reconnaissance and Surveillance
Infantry members often conduct reconnaissance and surveillance missions to gather intelligence on enemy positions, movements, and strength. This involves using a range of skills and equipment, including observation posts, patrols, and specialized sensors. By gathering accurate and timely intelligence, infantry members can help inform command decisions and shape the outcome of battles.
Key Skills:
- Observation and reporting
- Map reading and navigation
- Surveillance and reconnaissance techniques
- Intelligence gathering and analysis
Role 3: Security and Defense

Infantry members are responsible for securing and defending key positions, such as military bases, checkpoints, and strategic locations. This involves establishing defensive positions, conducting patrols, and responding to potential threats. By securing and defending key positions, infantry members can help protect fellow soldiers and civilians, and maintain control over critical terrain.
Key Skills:

- Defensive tactics and techniques
- Security protocols and procedures
- Patrols and sentry duty
- Response to potential threats and emergencies
Role 4: Peacekeeping and Stability Operations
In addition to combat roles, infantry members often participate in peacekeeping and stability operations, working to maintain order and stability in conflict zones. This involves interacting with local populations, building relationships with community leaders, and providing humanitarian assistance. By engaging in peacekeeping and stability operations, infantry members can help promote peace and stability, and support the rebuilding of affected communities.
Key Skills:
- Cultural awareness and sensitivity
- Communication and negotiation
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster response
- Conflict resolution and mediation
Role 5: Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response

Infantry members may be called upon to provide humanitarian assistance and disaster response, supporting affected populations in the aftermath of natural disasters or conflicts. This involves providing aid, shelter, and medical care, as well as helping to rebuild infrastructure and restore basic services. By providing humanitarian assistance and disaster response, infantry members can help alleviate suffering and support the recovery of affected communities.
Key Skills:

- Humanitarian assistance and disaster response
- Medical care and first aid
- Shelter and infrastructure construction
- Logistics and supply chain management
Role 6: Training and Mentoring
Infantry members often serve as trainers and mentors, helping to develop the skills and capabilities of fellow soldiers and partner forces. This involves providing instruction, guidance, and feedback, as well as modeling best practices and standards. By training and mentoring others, infantry members can help build capacity and improve performance, supporting the overall effectiveness of military operations.
Key Skills:

- Instruction and teaching
- Mentoring and coaching
- Leadership and team management
- Assessment and evaluation
Role 7: Logistics and Support
Finally, infantry members play a critical role in logistics and support, helping to maintain the flow of supplies, equipment, and services that sustain military operations. This involves managing supply chains, maintaining equipment, and providing administrative support, among other tasks. By ensuring the smooth operation of logistics and support systems, infantry members can help maintain the effectiveness and efficiency of military operations.
Key Skills:
- Logistics and supply chain management
- Equipment maintenance and repair
- Administrative support and coordination
- Resource management and allocation
💡 Note: Infantry members must be adaptable and flexible, able to perform a range of tasks and respond to changing situations. By understanding the diverse responsibilities of infantry members, we can appreciate the complexity and demands of their role, and recognize the critical contributions they make to military operations.
As we reflect on the 7 key roles of infantry members, it is clear that their responsibilities are diverse, demanding, and critical to the success of military operations. From frontline combat to logistics and support, infantry members play a vital role in defending national interests, promoting peace and stability, and supporting humanitarian efforts.
In the fast-paced and dynamic environment of modern military operations, infantry members must be able to adapt, innovate, and overcome challenges, using their skills, experience, and teamwork to achieve their objectives. By recognizing the importance of infantry members and the diverse roles they play, we can better appreciate the complexity and demands of military service, and honor the sacrifices and contributions of these brave men and women.
What is the primary role of infantry members in military operations?

+
The primary role of infantry members is to engage in frontline combat, using a range of weapons and tactics to defeat enemy forces.
What skills are required for infantry members to perform their roles effectively?
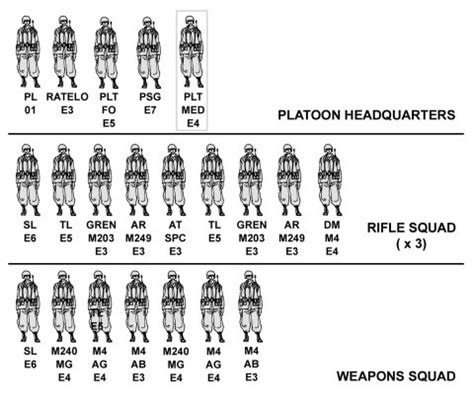
+
Infantry members require a range of skills, including marksmanship, tactical maneuvering, first aid, communication, and leadership, among others.
How do infantry members contribute to peacekeeping and stability operations?

+
Infantry members contribute to peacekeeping and stability operations by interacting with local populations, building relationships with community leaders, and providing humanitarian assistance.