Master Independent and Dependent Events: Worksheet Guide

In the vast and intricate world of mathematics, understanding the nature of events, particularly when they are interconnected, is essential for probability calculations, statistical analysis, and decision-making. Whether you are a student struggling with your homework or a teacher preparing educational materials, this guide will demystify independent and dependent events through detailed explanations and practical examples.
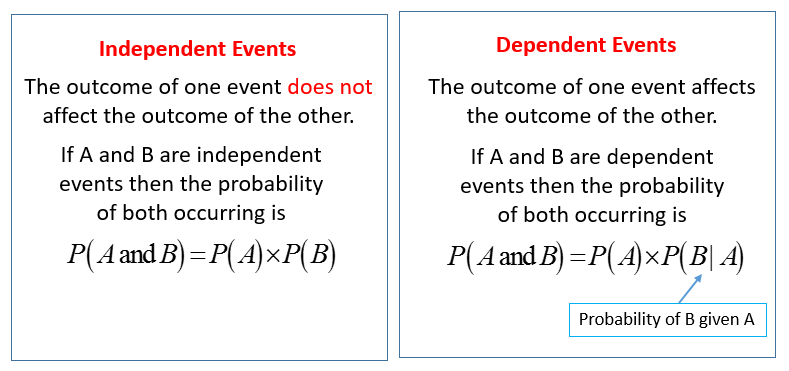
Understanding Independent Events

Independent Events are occurrences where the outcome of one event does not affect the probability of another event happening. In such cases, the events are said to be independent of each other. Here’s how to identify independent events:
- Probability formula: If A and B are independent events, then P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B).
- Examples: Flipping a coin and rolling a die, drawing two cards from a deck with replacement, etc.
Example Problem:

Let’s consider an example where you flip a coin twice. Determine the probability of getting heads on the first flip and tails on the second flip.
- P(First Flip Heads) = 0.5
- P(Second Flip Tails) = 0.5
- Since the flips are independent, P(Heads and then Tails) = 0.5 × 0.5 = 0.25 or 25%.
Dependent Events Explained

In contrast, Dependent Events are events where the outcome of one event affects the probability of another. For instance, drawing cards from a deck without replacement changes the probabilities because each draw modifies the pool of available cards:
- Conditional Probability: If event A happens, it changes the probability of event B. This can be represented as P(B | A).
- Examples: Drawing two cards from a deck without replacement, selecting balls from a bag where items are not replaced, etc.
Example Problem:
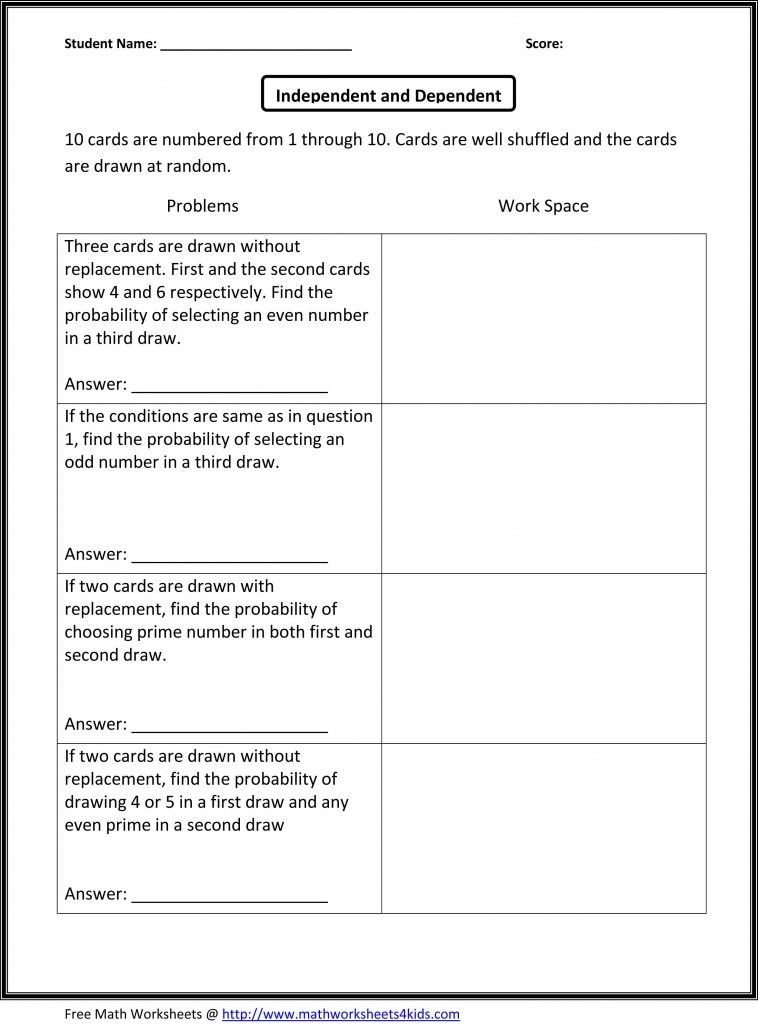
Suppose you are drawing two cards from a deck without replacement. Find the probability of drawing an Ace first and then a King of Hearts.
- P(Ace on the first draw) = 4⁄52 (There are 4 Aces in 52 cards).
- After drawing an Ace, the deck has 51 cards, with only one King of Hearts remaining.
- P(King of Hearts on the second draw | Ace on first) = 1⁄51.
- So, P(Ace and King of Hearts) = 4⁄52 × 1⁄51 = 1⁄663.
Using Worksheets to Master These Concepts

Worksheets are an invaluable tool for both learning and teaching probability:
- They allow students to practice with various scenarios, reinforcing the theory with practical applications.
- Worksheets often provide a structured way to break down complex problems into manageable parts.
- Here’s a basic structure for a worksheet on independent and dependent events:
- Introductory Theory Explanation
- Questions for Independent Events
- Questions for Dependent Events
- Problem Solving Exercises
| Type of Event | Example | Probability Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Independent | Two coin flips | P(A) × P(B) |
| Dependent | Drawing cards without replacement | P(A) × P(B | A) |

Tips for Creating Effective Worksheets

- Vary Problem Difficulty: Start with simpler scenarios to warm up students and gradually increase complexity.
- Use Real-Life Scenarios: Incorporate everyday examples to make the math relatable.
- Provide Solution Steps: Showing how to solve problems can guide students towards independent learning.
Example Worksheet:
Here’s a sample question to illustrate the worksheet:
- Question: If you spin a spinner with 5 equal sections twice, what is the probability that the arrow lands on the same section both times?
- Answer:
- There are 5 possible outcomes for the first spin.
- Since spins are independent, the probability for the second spin remains 1⁄5 if we match the first spin.
- Therefore, P(Same section twice) = 1⁄5 × 1⁄5 = 1⁄25.
💡 Note: When creating worksheets, remember that real-world problems can often involve both types of events, necessitating a flexible approach to problem-solving.
In conclusion, mastering the distinction between independent and dependent events is not only a theoretical exercise but a skill necessary for making informed decisions in various fields. By utilizing structured worksheets and applying the concepts through example problems, students can deepen their understanding of probability. This practical knowledge can enhance their ability to handle both academic challenges and everyday decision-making with confidence and accuracy.
What’s the difference between independent and dependent events?

+
Independent events are those where the outcome of one event does not influence the probability of another. Dependent events, on the other hand, have outcomes where the occurrence of one affects the probability of the other.
Can you give an example of an independent event?

+
Yes, for example, rolling a die and flipping a coin. The result of the die roll doesn’t change the probability of the coin flip.
How do I solve a dependent events problem?

+
When solving dependent events, consider the effect of the first event on the second. Use the formula for conditional probability where necessary, adjusting the total number of outcomes based on the prior event’s result.
Why do we use conditional probability for dependent events?

+
Conditional probability takes into account the impact one event has on another. This allows for an accurate calculation of the probability of subsequent events given that a certain event has occurred.