5 Ways to Master Incomplete Dominance Worksheets With Answers

Mastering incomplete dominance concepts in biology is an essential skill for students studying genetics. The complexity of inheritance patterns can be overwhelming, but by using effective strategies, students can confidently tackle incomplete dominance worksheets. Here are five detailed methods to help you excel in understanding and completing these worksheets:
1. Understand the Concept

Before diving into worksheets, it’s vital to have a solid grasp of what incomplete dominance entails. Unlike simple dominance where one allele masks the other, incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele is fully dominant, leading to a phenotype that is a blend of both. Here’s how to master this concept:
- Visualize: Use diagrams or illustrations to visualize how alleles blend in offspring. Think of mixing two paint colors.
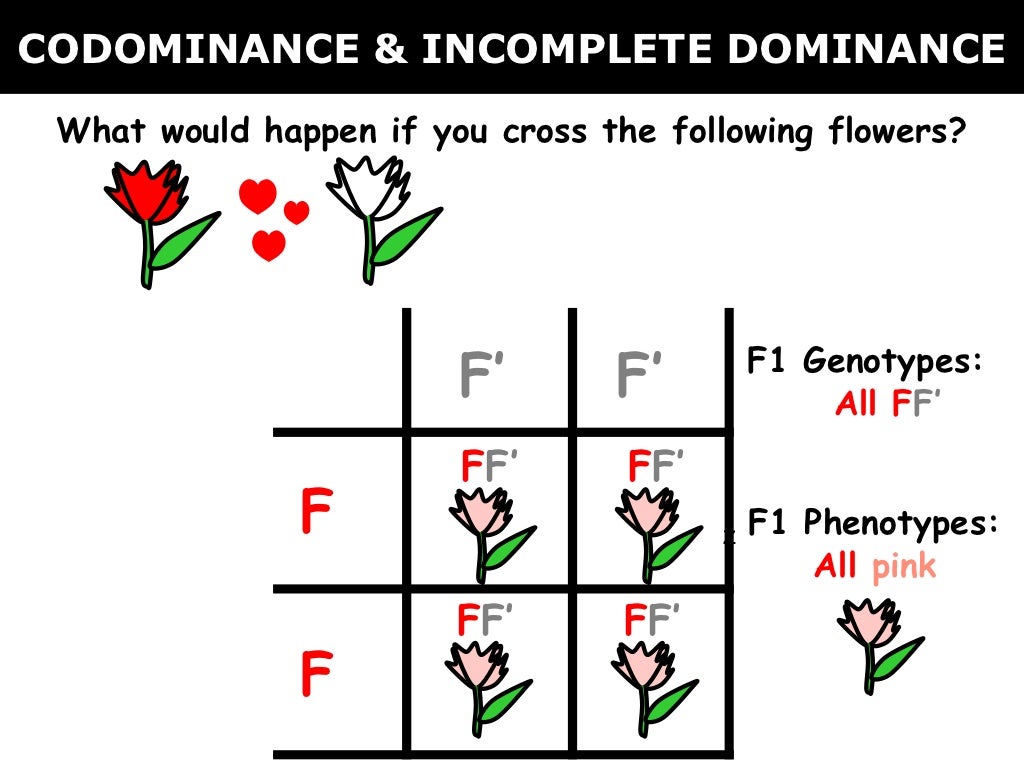
- Practice with Examples: Look for examples of plants or animals exhibiting incomplete dominance, such as pink flowers from red and white parents.
- Revise Basic Mendelian Genetics: Ensure you are comfortable with Mendelian inheritance as a foundation before tackling incomplete dominance.
2. Use Structured Approaches

Applying a systematic method to solve genetic problems can make working through incomplete dominance worksheets much easier:
- Punnett Squares: These are crucial for predicting the results of crossbreeding. For incomplete dominance, you’ll often find that both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous offspring.
- Analyze Ratios: Pay attention to the expected phenotypic ratios in the progeny. For incomplete dominance, expect a 1:2:1 ratio (one homozygous dominant, two heterozygous, one homozygous recessive).
- Break Down the Problem: If you’re given information about the parents, break down each allele to understand how they will mix in the offspring.
3. Work Through Example Problems

Example problems are not just practice; they are keys to understanding. Here’s how to make the most of them:
- Read the Problem Carefully: Understand what traits are being inherited, and how they are described (e.g., “Snapdragons have red, white, and pink flowers”).
- Identify Given Information: Mark down the known genotypes and phenotypes.
- Solve with Provided Answers: If answers are provided, use them to confirm your understanding.
- Create Your Own Problems: Test your grasp by creating scenarios where you have to determine the parent’s genotypes from the offspring’s traits.
4. Join or Form a Study Group

Studying genetics with peers can enhance learning through discussion and collaborative problem-solving:
- Peer Learning: Explain concepts to others. Teaching someone else often clarifies your own understanding.
- Sharing Work: Exchange worksheets and check each other’s solutions. Different perspectives can lead to better understanding.
- Discuss Mistakes: Go over any errors together to prevent common misunderstandings.
5. Review and Reflect
The final step in mastering incomplete dominance involves reflective learning:
- Identify Common Errors: Keep a log of mistakes and misunderstandings to prevent repeating them.
- Reflect on Your Learning Process: Consider which methods work best for you and refine your study techniques.
- Revisit Old Material: Go back to worksheets or notes you’ve previously worked on to reinforce your knowledge.
By following these methods, you're not just mastering incomplete dominance worksheets; you’re deepening your understanding of genetics overall. Use these approaches consistently, and you'll find the patterns and outcomes in genetic inheritance more predictable and manageable.
😄 Note: Remember, genetics is complex but logical. Persistence and practice will make these concepts second nature!
What is the key difference between incomplete dominance and codominance?

+
In incomplete dominance, the offspring phenotype is a blend of the parents’ traits, like a pink flower from red and white flowers. In codominance, both alleles are expressed equally; for example, a black and white cow having both black and white patches.
Why are Punnett squares important for solving genetic problems?

+
Punnett squares provide a visual way to determine the possible genetic outcomes when parents breed. They help predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring.
Can you provide a simple example of incomplete dominance?

+
One classic example is the snapdragon flower where red (RR) and white (WW) flowers are homozygous, producing pink flowers (RW) when crossed. Here, neither allele completely dominates, and the offspring have an intermediate phenotype.