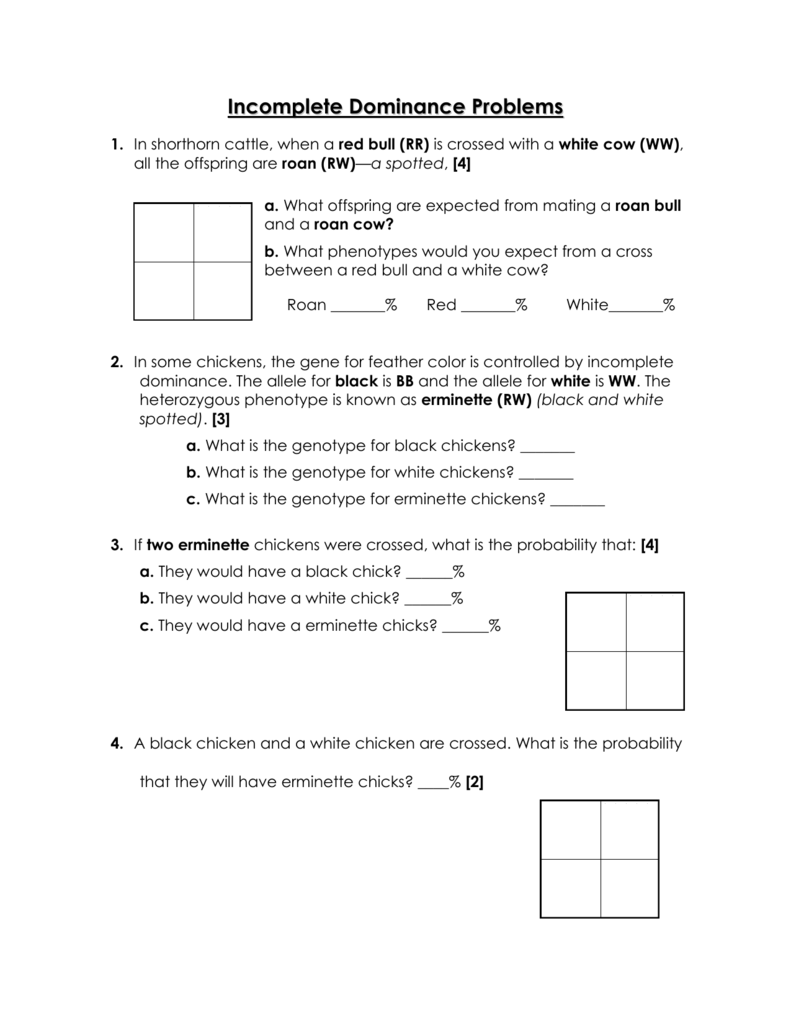
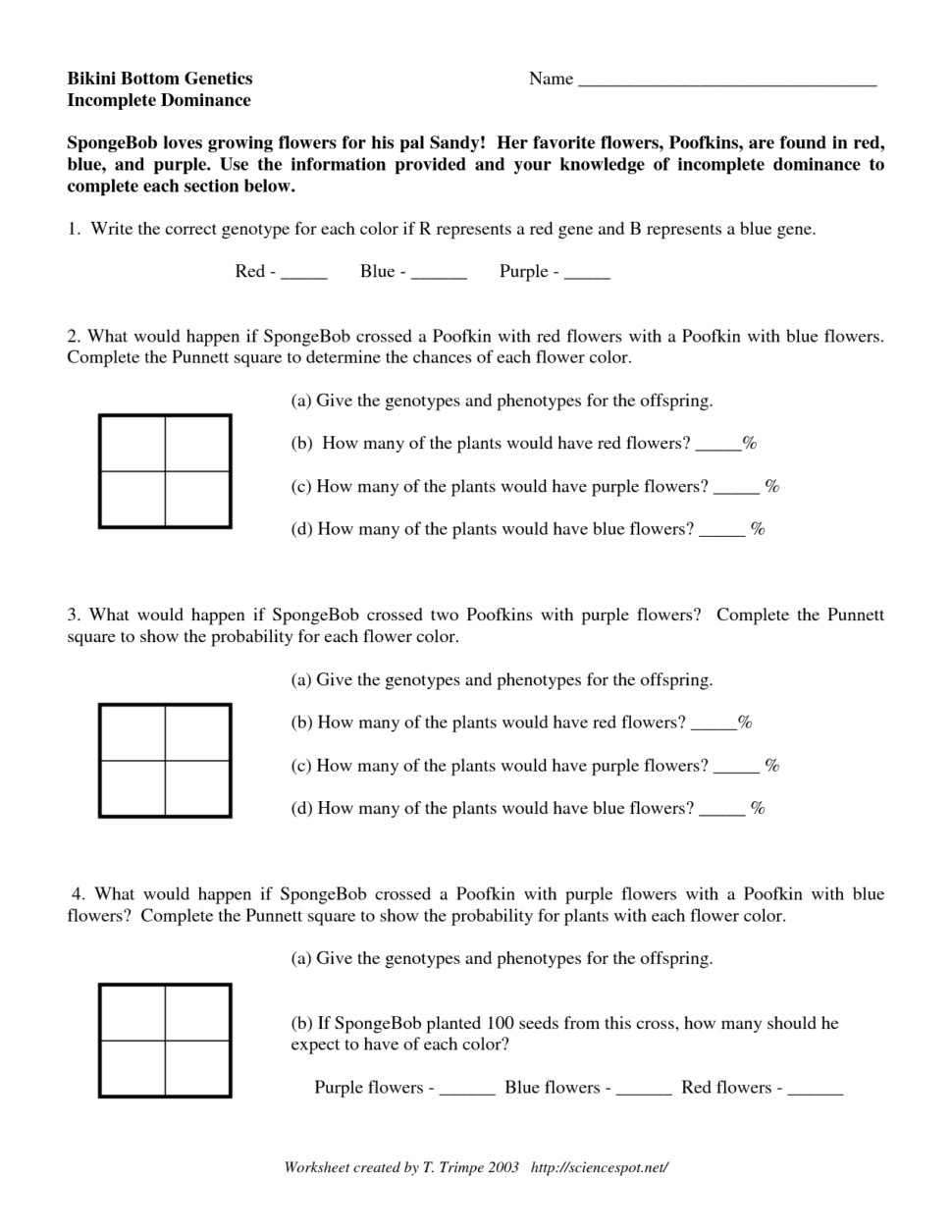
5 Key Answers for Incomplete Dominance Worksheet

Delving into the complex world of genetics can be both fascinating and challenging, particularly when we address the nuances of incomplete dominance. This genetic phenomenon, different from the typical dominant-recessive interaction, occurs when neither allele in a pair is fully dominant, resulting in an intermediate phenotype in the heterozygous state. Here, we'll explore five key answers that can help you understand and complete an incomplete dominance worksheet more effectively, enhancing your grasp of this intriguing genetic principle.
What is Incomplete Dominance?


Incomplete dominance occurs when the offspring inherit a combination of traits from both parents that blend together, rather than expressing one trait more dominantly over the other. A classic example is in flower color where a red flower (RR) crossbred with a white flower (WW) results in pink flowers (RW).
Key Answers for Common Worksheet Questions

1. Explanation of Phenotype and Genotype

- Genotype: This refers to the genetic constitution of an organism, which can be described using letters to represent alleles.
- Phenotype: The physical expression of the genotype, which in incomplete dominance scenarios, is an intermediate trait.
2. Predicting Offspring’s Appearance

Use the Punnett square to predict the phenotypes of offspring:
| R | W | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR (Red) | RW (Pink) |
| W | RW (Pink) | WW (White) |
This helps visualize the different combinations of alleles from the parents.
3. Determining the Probability of Specific Phenotypes

- If two pink flowers (RW) are crossed, the offspring will have:
- 25% chance of being red (RR)
- 50% chance of being pink (RW)
- 25% chance of being white (WW)
4. Applying Incomplete Dominance to Non-Flower Examples

Beyond flower color, incomplete dominance can be seen in various traits:
- Curly hair vs. straight hair in humans, leading to wavy hair.
- The height in some plant species where crossing tall and dwarf plants results in medium-sized offspring.
5. Understanding the Codominance vs. Incomplete Dominance

While codominance also shows both alleles affecting the phenotype, they do not blend; rather, both are fully expressed. For instance, in codominance, a cow could have both red and white hairs instead of a mixed pink color as in incomplete dominance.
🌟 Note: Remember, incomplete dominance is not about coexisting traits but rather the blending or combination of traits from both parents.
Understanding these key answers will not only help you complete incomplete dominance worksheets but also deepen your comprehension of genetics, shedding light on why certain traits appear in organisms and how they are inherited.
FAQ

Can incomplete dominance occur in animals?
+
Yes, incomplete dominance is observed in various animals. For example, the color of the fur in some rabbit breeds can show incomplete dominance where a mixture of the parents’ fur colors results in a unique shade in the offspring.
How does incomplete dominance affect evolution?

+
Incomplete dominance can influence evolution by providing a wider range of phenotypic variation within a population. This variation can sometimes lead to better adaptability to environmental changes, influencing survival rates and breeding strategies.
Is there a test to determine if a trait follows incomplete dominance?

+
To identify incomplete dominance, one would need to observe the phenotypes of the offspring from known parental genotypes. If the offspring show intermediate characteristics, this could suggest incomplete dominance. Genetic tests, like DNA sequencing or molecular biology techniques, can also help identify the presence of multiple alleles.