7 Ways to Master Identifying Tone and Mood
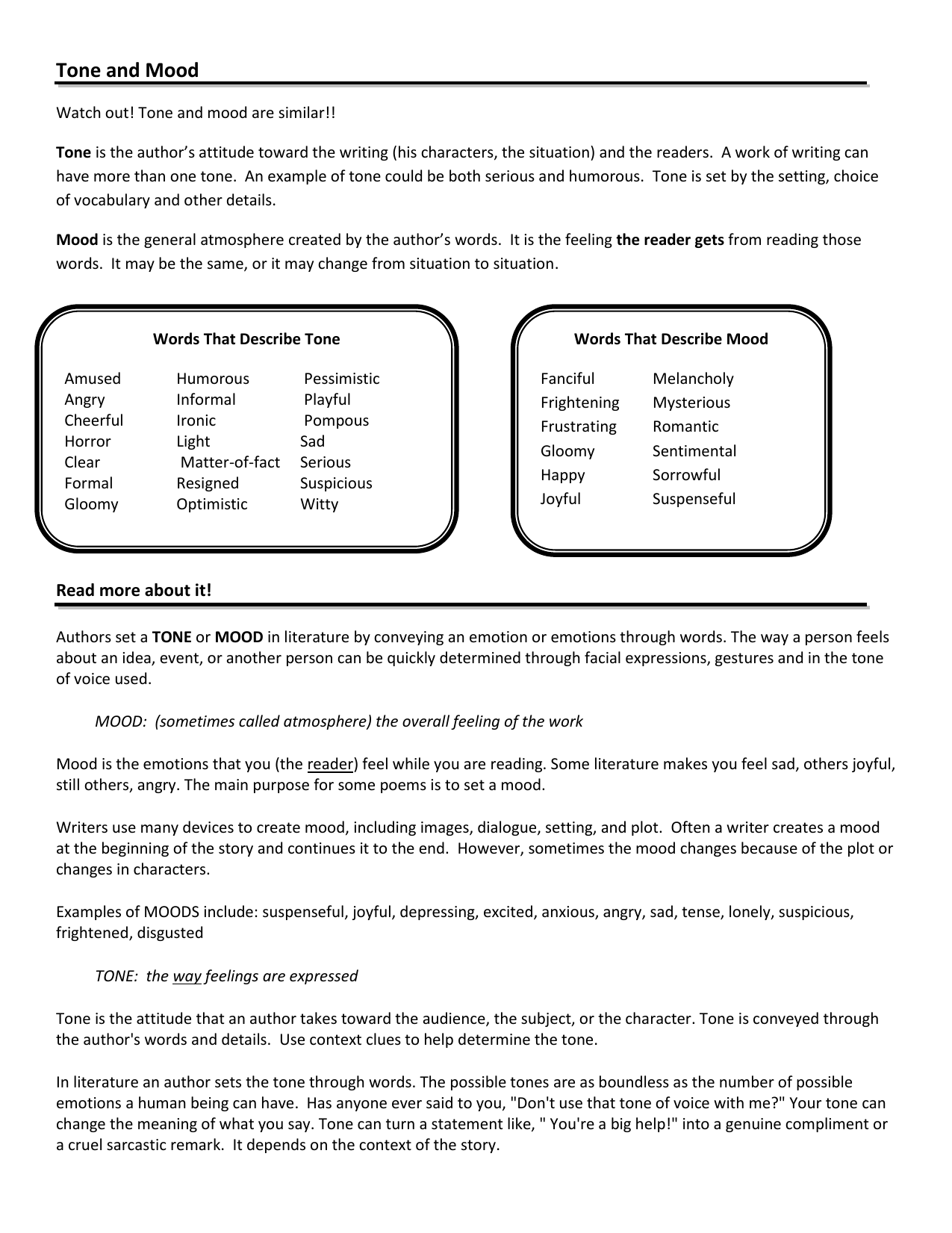
Understanding tone and mood is essential for readers and writers alike. These literary elements not only enhance the depth of narrative but also guide our emotional responses to texts. This comprehensive guide will explore seven ways you can master the identification of tone and mood in literature, providing you with tools to enrich your reading experience and improve your writing.
1. Contextual Clues

The tone of a text is often revealed through the context. Here are some steps to identify tone using context:
- Observe the Setting: Setting can influence tone. A gloomy, foggy day setting typically indicates a melancholic or eerie tone.
- Analyze Dialogue: Characters’ dialogues can either reflect or contrast the mood of the narrative. Pay attention to choice of words, syntax, and length of speech.
- Read Between the Lines: Look for subtext, what is implied rather than stated outright, which often hints at the underlying tone.
🔍 Note: Setting and dialogue are pivotal in revealing the tone, but they can sometimes deceive; ensure to consider the broader narrative context.
2. Diction and Syntax

How authors choose words and structure sentences greatly affects the mood:
- Vocabulary: Positive, negative, or neutral words set the tone.
- Figurative Language: Metaphors, similes, and personification can alter mood rapidly.
- Sentence Length: Long, complex sentences might suggest formality or suspense, while short, choppy sentences could indicate urgency or tension.
3. Point of View

The narrative perspective can color the tone significantly:
- First Person: Creates a more intimate, subjective tone.
- Third Person: Can be either omniscient, providing a broader, potentially neutral tone, or limited, coloring the tone with the perspective character’s views.
- Second Person: Although less common, it gives an immediate, direct tone, often used in interactive or instructional texts.
4. Emotional Response of the Reader

Your emotional reaction while reading can be a guide:
- Reflect on how the text makes you feel - does it evoke happiness, sadness, fear, or anger?
- Consider the consistency of your emotions throughout the piece. Fluctuations might indicate changes in mood or tone.
💡 Note: Emotional responses are subjective; they can be influenced by your personal experiences and current mood, so balance them with other cues.
5. Literary Devices

Authors employ literary devices to convey mood and tone:
- Imagery: Vivid sensory descriptions can invoke specific emotional responses.
- Foreshadowing: Hints of future events can create tension or anticipation, shaping the tone.
- Irony: Whether verbal, situational, or dramatic, irony can add layers to the tone, often making it sardonic or humorous.
6. Theme and Message

The overarching theme or moral of the story often dictates the tone:
- Look for Recurring Motifs: Repetitive themes can signal a consistent tone.
- Author’s Intent: Consider what the author might be trying to communicate, as this can influence the overall mood.
7. Revision and Comparison

Reading the text multiple times and comparing it with other works can deepen your understanding of tone and mood:
- Read Aloud: Listening to the text can reveal nuances in tone.
- Compare and Contrast: Analyzing different texts by the same or different authors helps identify unique tone markers.
In our journey through mastering the identification of tone and mood, we've seen how integral these elements are to the overall experience of literature. Each of the seven methods provides a unique lens through which to view and interpret texts, enriching your analysis and appreciation. By becoming attuned to these subtleties, readers can engage more deeply with stories, and writers can craft narratives that resonate on emotional levels. Whether it's through the careful selection of words, understanding narrative perspectives, or considering the emotional landscape the text creates, these techniques empower you to explore the rich tapestry of human emotion and expression.
How can I improve my ability to detect subtle changes in tone?

+
Improve your reading skills by focusing on the nuances in language use, character interactions, and setting descriptions. Practice reading different genres and analyze how authors shift their tone throughout their works.
Is it possible to confuse tone with mood?

+
Yes, it’s common. Tone is the author’s attitude, while mood is the reader’s emotional response to the text. They are related but distinct; however, an author’s tone can certainly influence the mood of the piece.
How does understanding tone and mood enhance my writing?

+
By mastering tone and mood, you can better control the emotional impact of your writing. This allows you to create more compelling stories or arguments, engaging your readers emotionally as well as intellectually.
Can literary genres influence tone and mood?

+
Absolutely. Each genre tends to have conventional tones and moods. For instance, a mystery novel might lean towards suspenseful and dark tones, whereas romance novels often strive for an emotional or heartwarming mood.