HVAC Load Calculation Worksheet: Simplify Your System Design

Designing an efficient and effective HVAC system for a building isn't just about ensuring comfort; it's also about energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with building codes. Central to this process is the HVAC load calculation worksheet, a critical tool that engineers, architects, and HVAC professionals use to determine the heating and cooling requirements of a structure. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to simplify system design with this vital worksheet.
Understanding the Basics of HVAC Load Calculation

Before diving into the specifics of using the HVAC load calculation worksheet, it’s essential to grasp what load calculation entails. At its core, load calculation estimates the heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter for a building. This calculation informs the size and capacity of the HVAC system needed to maintain desired indoor conditions year-round.
Why It Matters?

- Energy Efficiency: Proper sizing prevents oversized systems that cycle on and off frequently, thus conserving energy.
- Comfort: Correct sizing ensures uniform temperatures and consistent air quality throughout the building.
- Cost Savings: Avoiding oversized equipment reduces initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Compliance: Adherence to energy codes and standards often requires accurate load calculations.
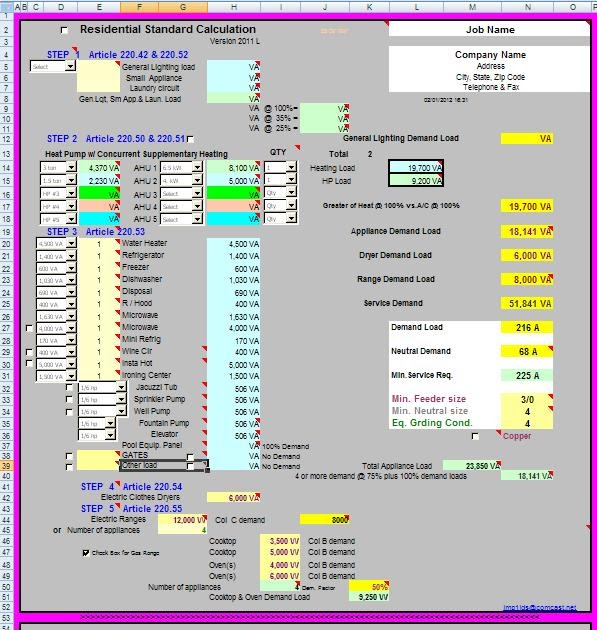
Components of an HVAC Load Calculation Worksheet
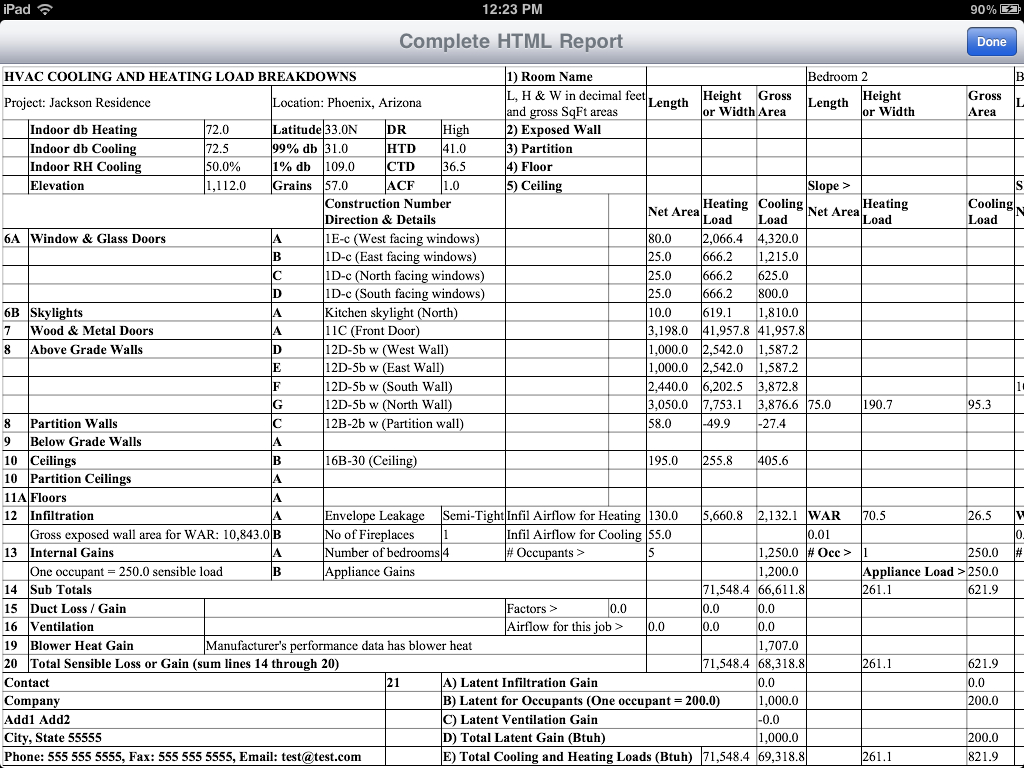
The load calculation worksheet comprises several key sections:
1. Project Information

This section includes details like project name, location, building dimensions, and use type. Accurate information here sets the foundation for subsequent calculations.
2. Weather Data

Local weather patterns play a significant role in HVAC design. The worksheet incorporates data like design temperatures, cooling degree days, and heating degree days to account for climatic variations.
3. Building Envelope
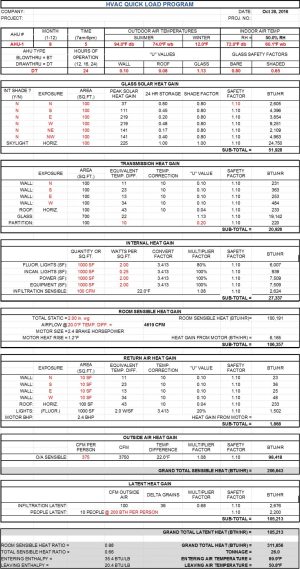
This part focuses on the physical structure of the building:
- Walls: Type of construction, insulation value, and fenestration details.
- Windows and Doors: Number, size, U-value, shading coefficients, etc.
- Roof: Insulation, materials, color, and orientation.
- Floor: Material, insulation, and exposure (e.g., slab-on-grade, basement).
4. Internal Gains
Heat generated from within the building due to occupants, lighting, equipment, and appliances impacts the load calculation. This includes:
- People: Occupancy load and activity levels.
- Lighting: Types of fixtures and their efficiency.
- Appliances/Equipment: Usage patterns and their heat output.
5. Ventilation
Ventilation requirements affect the HVAC load significantly, accounting for:
- Outdoor Air Requirements: Per building code or industry standards.
- Filtration: Efficiency of filters used.
- Humidity Control: Necessary adjustments for comfort and building preservation.
6. Heating and Cooling Load Summary

This section summarizes the calculated heating and cooling loads, breaking down the contributions from walls, windows, infiltration, ventilation, internal gains, etc. The summary aids in:
- Determining system size: Helps choose the right HVAC equipment.
- Identifying areas needing insulation or other energy-saving measures.
7. Notes and Observations

Room for additional notes, assumptions, or adjustments made during the calculation process.
How to Use the HVAC Load Calculation Worksheet

Using the worksheet efficiently requires following a structured approach:
- Gather Accurate Data: Start with precise measurements of the building's dimensions, materials, and existing conditions.
- Enter Project Details: Fill out the project information accurately to tailor calculations to your specific scenario.
- Input Weather Data: This helps in setting realistic load calculations based on local climate.
- Define Building Envelope: Carefully document the construction details for walls, roof, windows, and floors.
- Estimate Internal Gains: Use reasonable assumptions for occupancy, lighting, and equipment usage.
- Calculate Ventilation Needs: Ensure your estimates comply with industry standards and building codes.
- Perform the Calculations: Use either manual methods or load calculation software to compute the total heating and cooling loads.
- Review and Adjust: Cross-check calculations, consider any special conditions, and adjust as necessary.
💡 Note: Software tools can automate much of the calculation process, but human judgment is crucial for nuanced decisions like adjusting for unique building characteristics or specific comfort requirements.
Benefits of Accurate Load Calculations

Utilizing an HVAC load calculation worksheet provides several advantages:
- System Optimization: The right size ensures the system operates at peak efficiency.
- Energy Savings: Tailoring the system to actual needs reduces energy consumption.
- Comfort and Air Quality: Properly sized systems maintain consistent conditions, enhancing occupant comfort and health.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Oversized units cycle more frequently, leading to quicker degradation of components.
Wrapping Up

The HVAC load calculation worksheet is more than just a tool; it’s a roadmap for creating a perfectly tuned HVAC system. By following the outlined steps, HVAC professionals can ensure they’re not just installing equipment but are providing solutions that are cost-effective, energy-efficient, and tailored to the specific needs of each building. The key lies in the accuracy of data entry, understanding the nuances of the building’s characteristics, and using this worksheet as part of a broader design strategy to achieve the best possible HVAC performance.
Why is accurate load calculation important for HVAC system design?

+
Accurate load calculation ensures that the HVAC system is sized correctly to provide optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and longevity of equipment.
What happens if an HVAC system is oversized?

+
An oversized system leads to short-cycling, where the system turns on and off frequently. This not only increases energy consumption but also wears down the equipment faster due to excessive cycling.
Can you perform an HVAC load calculation manually?
+Yes, manual methods are still used by some, but they are more time-consuming and prone to human error. Software tools simplify the process and help in achieving more accurate results.
How does the building envelope impact HVAC load calculation?
+The building envelope, including walls, windows, and roofs, determines how much heat is lost or gained through conduction, convection, and radiation, significantly influencing the load calculations.