Create Double Bar Graph In Excel
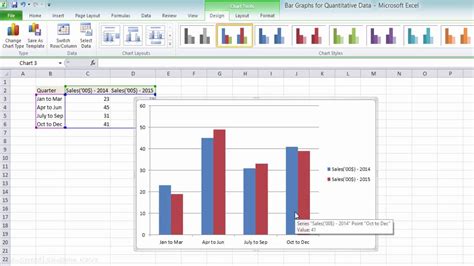
Introduction to Creating a Double Bar Graph in Excel

Creating a double bar graph in Excel is a useful way to compare two sets of data side by side. This type of graph is particularly helpful when you want to visualize the differences or similarities between two categories of data over the same period or across different groups. In this guide, we will walk through the steps to create a double bar graph in Excel, highlighting the process with examples and tips for customization.
Preparing Your Data

Before you start creating your double bar graph, it’s essential to have your data organized in a suitable format. Typically, you would have two sets of data that you want to compare. For instance, if you’re comparing sales figures for two different products over several months, your data might look something like this:
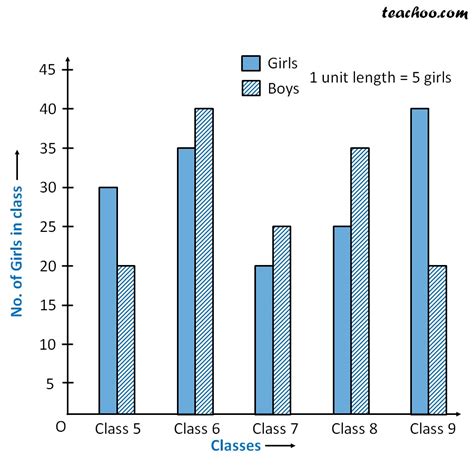
| Month | Product A Sales | Product B Sales |
|---|---|---|
| January | 100 | 120 |
| February | 110 | 130 |
| March | 130 | 140 |
Ensure that your data is in a table format with the categories (in this case, months) in the first column and the two sets of data you wish to compare in the subsequent columns.
Creating the Double Bar Graph

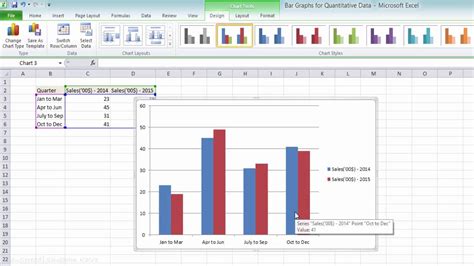
To create a double bar graph: 1. Select the entire data range, including headers. 2. Go to the “Insert” tab on the Excel ribbon. 3. Click on the “Bar Chart” button in the “Illustrations” group. 4. Select “2-D Clustered Bar Chart” from the dropdown menu. This will create a basic double bar graph where each category has two bars representing the two sets of data.
Customizing Your Double Bar Graph
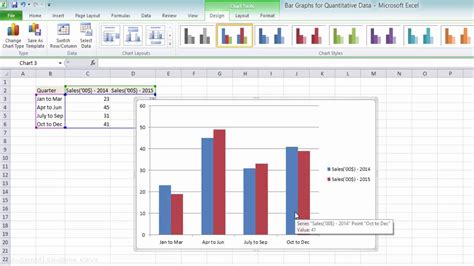
After creating the graph, you can customize it to better suit your needs: - Change Chart Title: Click on the chart title, and you can edit it directly to give your graph a meaningful name. - Legend: You can adjust the legend’s position by clicking on it and then using the “Legend” options in the “Chart Elements” menu that appears when you click on the “+” icon next to the graph. - Axis Labels: To add or edit axis labels, click on the axes and use the “Axis Options” in the “Format Axis” pane. - Colors and Effects: You can change the colors of the bars and add effects by selecting the series (one set of bars) and using the “Fill & Line” options in the “Format Data Series” pane.
Tips for Effective Double Bar Graphs
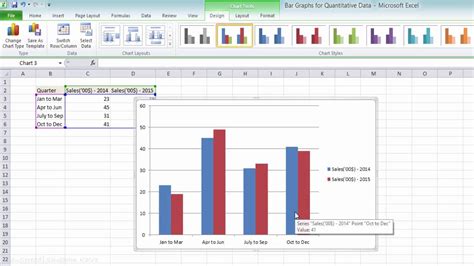
- Keep It Simple: Ensure that your graph is easy to understand. Avoid clutter and focus on the key message. - Use Appropriate Colors: Choose colors that are visually appealing and distinguishable, especially if you’re presenting to an audience that may include individuals with color vision deficiency. - Label Correctly: Make sure all elements of the graph are clearly labeled, including the title, axes, and legend.
📊 Note: When creating graphs for presentations or reports, consider the audience and the message you want to convey. Ensure the graph is clear, concise, and supports your narrative effectively.
To summarize, creating a double bar graph in Excel is a straightforward process that can be customized to meet your specific needs. By organizing your data correctly and following the steps outlined above, you can create effective visualizations to compare two sets of data. Remember, the key to a good graph is that it should be easy to understand and provide clear insights into the data it represents. Whether you’re analyzing sales trends, website traffic, or any other kind of data, a well-crafted double bar graph can be a powerful tool in your data analysis arsenal.
What is the primary use of a double bar graph?
+
A double bar graph is primarily used to compare two sets of data side by side, making it easier to visualize the differences or similarities between them.
How do I ensure my double bar graph is effective?
+
To ensure your double bar graph is effective, keep it simple, use appropriate colors, and label all elements clearly. The goal is to make the graph easy to understand and to support your narrative effectively.
Can I customize the appearance of my double bar graph in Excel?
+
Yes, Excel provides various options to customize the appearance of your double bar graph, including changing colors, adding effects, adjusting the legend, and modifying axis labels.