5 Ways To Find P Value

Introduction to P-Value

When conducting statistical tests, one of the key concepts you’ll encounter is the p-value. The p-value, or probability value, is a measure that helps you determine the significance of your results. It’s a crucial component in hypothesis testing, allowing you to decide whether to reject the null hypothesis or not. In this article, we’ll explore five ways to find the p-value, making it easier to interpret your statistical analysis results.
Understanding P-Value

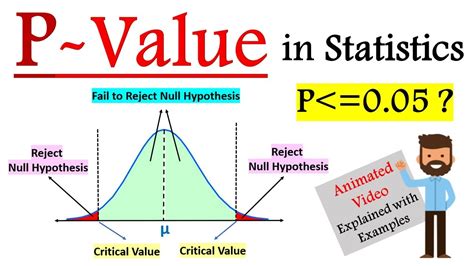
Before diving into the methods for finding the p-value, it’s essential to understand what it represents. The p-value is the probability of observing results at least as extreme as those you obtained, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that your results are statistically significant, meaning that the observed effect is unlikely to occur by chance. On the other hand, a large p-value suggests that the results might be due to chance, and you may not have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
Method 1: Using a Z-Table or T-Table

One of the most common methods for finding the p-value is by using a Z-table or T-table. These tables provide the critical values for the standard normal distribution (Z-table) or the t-distribution (T-table). To find the p-value using these tables, you’ll need to: * Calculate the test statistic (Z or t) from your sample data * Determine the degrees of freedom (for T-table) * Look up the critical value in the corresponding table * Find the p-value associated with that critical value
For example, if you’re conducting a one-sample Z-test and your calculated Z-score is 2.5, you can look up the corresponding p-value in the Z-table. The p-value will give you the probability of observing a Z-score at least as extreme as 2.5, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Method 2: Using Statistical Software
Another way to find the p-value is by using statistical software, such as R, Python, or SPSS. These programs often have built-in functions for conducting hypothesis tests and calculating p-values. For instance, in R, you can use the
t.test() function to perform a t-test and obtain the p-value.
Using statistical software can save you time and effort, especially when dealing with complex datasets or multiple tests. Additionally, these programs often provide more precise p-values than looking up critical values in tables.
Method 3: Using Online Calculators

If you don’t have access to statistical software or prefer a more straightforward approach, you can use online calculators to find the p-value. There are many online tools available, such as p-value calculators or statistical significance calculators. These calculators typically require you to input the test statistic, sample size, and other relevant information to calculate the p-value.
Online calculators can be a convenient option when you need to quickly determine the p-value for a specific test. However, be sure to choose a reputable calculator to ensure accuracy.
Method 4: Using Graphing Calculators

Some graphing calculators, such as the TI-83 or TI-84, have built-in functions for calculating p-values. These calculators can perform various statistical tests, including Z-tests and t-tests, and provide the corresponding p-values.
Using a graphing calculator can be a good option if you’re already familiar with the device and prefer a more hands-on approach. However, keep in mind that the calculators may have limitations in terms of the types of tests they can perform.
Method 5: Using Simulation Methods

The fifth method for finding the p-value involves using simulation techniques, such as Monte Carlo simulations. This approach involves generating random samples from a hypothetical population and calculating the test statistic for each sample. By repeating this process many times, you can estimate the p-value as the proportion of samples with test statistics at least as extreme as the one you observed.
Simulation methods can be useful when dealing with complex datasets or non-standard distributions. However, they may require more computational resources and expertise in programming.
💡 Note: It's essential to choose the correct method for finding the p-value based on your specific research question and data characteristics.
In summary, there are various ways to find the p-value, including using Z-tables or T-tables, statistical software, online calculators, graphing calculators, and simulation methods. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on your specific needs and preferences.
As we wrap up this discussion on finding p-values, it’s clear that understanding and correctly interpreting p-values is crucial in statistical analysis. By choosing the right method and following best practices, you can ensure that your results are reliable and meaningful.
What is the purpose of the p-value in statistical analysis?

+
The p-value helps determine the significance of the results, indicating whether the observed effect is unlikely to occur by chance.
Can I use online calculators to find the p-value for any type of test?

+
While online calculators can be convenient, they may not support all types of tests or complex datasets. Be sure to choose a reputable calculator and check its limitations before use.
How do I interpret a small p-value?

+
A small p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that the results are statistically significant, suggesting that the observed effect is unlikely to occur by chance.