5 Ways To Find P-Value
Introduction to P-Value
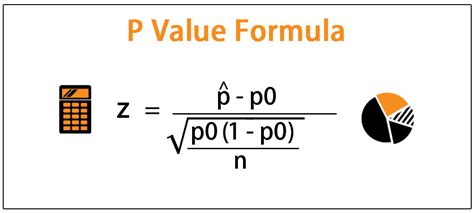
In statistical hypothesis testing, the p-value plays a crucial role in determining the significance of the results. It is defined as the probability of observing the results of the study, or more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. The p-value is a vital component in statistical analysis, and finding it is essential to understand the significance of the results. In this article, we will discuss five ways to find the p-value and their applications in different statistical tests.
Understanding P-Value
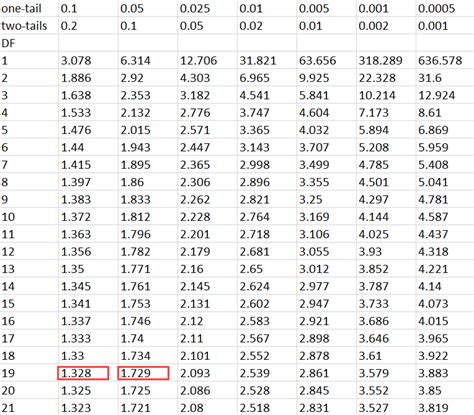
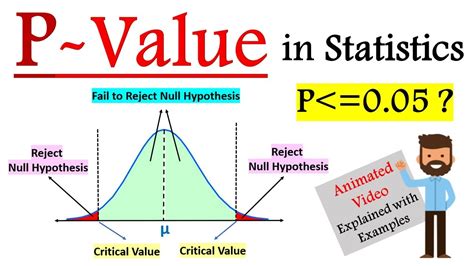
Before diving into the methods to find the p-value, it is essential to understand its concept. The p-value is a measure of the strength of evidence against a null hypothesis. A small p-value indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, while a large p-value indicates weak evidence. The p-value is typically compared to a significance level, usually set at 0.05, to determine whether the results are statistically significant.
5 Ways to Find P-Value
There are several methods to find the p-value, and the choice of method depends on the type of statistical test being performed. Here are five ways to find the p-value:
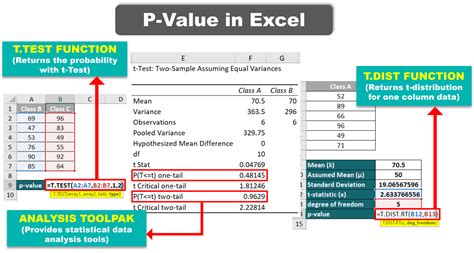
- Method 1: Using a Z-Table or T-Table: For z-tests and t-tests, the p-value can be found using a z-table or t-table. These tables provide the critical values of z or t for different significance levels. By looking up the critical value in the table, the p-value can be determined.
- Method 2: Using a Calculator or Software: Many calculators and software packages, such as R or Python, have built-in functions to calculate the p-value. These functions can be used to find the p-value for various statistical tests, including ANOVA and regression analysis.
- Method 3: Using a Statistical Package: Statistical packages, such as SPSS or SAS, provide an easy way to calculate the p-value. These packages have built-in procedures for various statistical tests and can produce the p-value as part of the output.
- Method 4: Using a P-Value Calculator: There are several online p-value calculators available that can be used to find the p-value for different statistical tests. These calculators are often easy to use and provide a quick way to determine the p-value.
- Method 5: Using a Simulation: For more complex statistical tests, such as permutation tests or bootstrap tests, the p-value can be estimated using a simulation. This involves generating a large number of random samples and calculating the test statistic for each sample. The p-value can then be estimated as the proportion of samples with a test statistic more extreme than the observed test statistic.
Example of Finding P-Value
Let’s consider an example of finding the p-value using a z-table. Suppose we want to test the hypothesis that the mean height of a population is equal to 175 cm, with a standard deviation of 5 cm. We collect a sample of 100 individuals and find that the mean height is 180 cm. We can use a z-test to determine whether the difference between the sample mean and the population mean is statistically significant.
| Sample Mean | Population Mean | Standard Deviation | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 180 | 175 | 5 | 100 |

Using a z-table, we can find the critical value of z for a significance level of 0.05. Let’s say the critical value is 1.96. We can then calculate the z-score as follows:
z = (180 - 175) / (5 / sqrt(100)) = 5 / 0.5 = 10
Since the z-score is greater than the critical value, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the difference between the sample mean and the population mean is statistically significant.
📝 Note: The p-value can be sensitive to the sample size and the significance level. It is essential to consider these factors when interpreting the results.
In conclusion, finding the p-value is a crucial step in statistical hypothesis testing. There are several methods to find the p-value, including using a z-table or t-table, a calculator or software, a statistical package, a p-value calculator, or a simulation. By understanding the concept of the p-value and how to find it, researchers can make informed decisions about the significance of their results.
What is the purpose of the p-value?
+
The purpose of the p-value is to determine the significance of the results in a statistical hypothesis test. It measures the strength of evidence against a null hypothesis.
How is the p-value calculated?
+
The p-value can be calculated using various methods, including using a z-table or t-table, a calculator or software, a statistical package, a p-value calculator, or a simulation.
What is the significance level, and how is it related to the p-value?

+
The significance level, usually set at 0.05, is the threshold for determining whether the results are statistically significant. If the p-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected, and the results are considered statistically significant.