5 Ways Calculate Uncertainty
Introduction to Uncertainty Calculation

Calculating uncertainty is a crucial step in various fields, including science, engineering, and finance. Uncertainty refers to the degree of doubt or unpredictability associated with a measurement or prediction. It is essential to quantify uncertainty to make informed decisions and to understand the reliability of results. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate uncertainty, highlighting the importance of each method and providing examples of their applications.
1. Standard Deviation Method

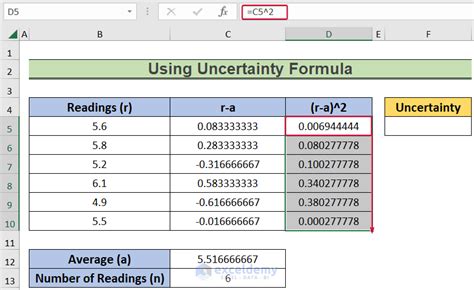
The standard deviation method is a widely used technique to calculate uncertainty. It involves calculating the standard deviation of a set of data points, which represents the spread or dispersion of the data from the mean value. The standard deviation (σ) is calculated using the formula: σ = √(Σ(xi - μ)² / (n - 1)), where xi is each data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points. The standard deviation is a measure of the uncertainty associated with a single measurement.
2. Propagation of Errors Method

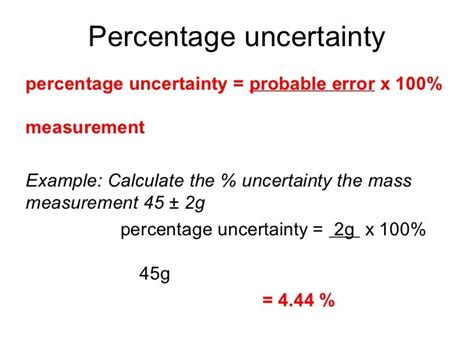
The propagation of errors method is used to calculate the uncertainty of a result that depends on multiple measurements. This method involves calculating the uncertainty of each individual measurement and then combining them to obtain the overall uncertainty. The propagation of errors formula is: Δy = √( (∂y/∂x1)²Δx1² + (∂y/∂x2)²Δx2² +… ), where Δy is the uncertainty of the result, and Δx1, Δx2, etc. are the uncertainties of the individual measurements.
3. Monte Carlo Method
The Monte Carlo method is a computational technique used to simulate complex systems and calculate uncertainty. This method involves generating random samples from a probability distribution and using these samples to estimate the uncertainty of a result. The Monte Carlo method is particularly useful for complex systems where analytical solutions are not possible.
4. Bayesian Method

The Bayesian method is a statistical approach used to calculate uncertainty based on prior knowledge and new data. This method involves updating the prior probability distribution with new data to obtain a posterior probability distribution, which represents the updated uncertainty. The Bayesian method is particularly useful for incorporating expert knowledge and prior information into the uncertainty calculation.
5. Fuzzy Logic Method
The fuzzy logic method is a technique used to calculate uncertainty in systems with uncertain or imprecise data. This method involves representing the uncertainty using fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic operators. The fuzzy logic method is particularly useful for systems with linguistic or qualitative data, such as expert opinions or survey responses.
📝 Note: The choice of method depends on the specific problem and the type of data available. It is essential to understand the limitations and assumptions of each method to ensure accurate and reliable results.
To illustrate the application of these methods, consider a simple example. Suppose we want to calculate the uncertainty of the average height of a population. We can use the standard deviation method to calculate the uncertainty of the average height based on a sample of data points. Alternatively, we can use the propagation of errors method to calculate the uncertainty of the average height based on the uncertainties of individual measurements.
In addition to these methods, there are other techniques available to calculate uncertainty, such as the bootstrapping method and the jackknifing method. These methods involve resampling the data to estimate the uncertainty of a result.
The following table summarizes the five methods discussed in this article:
| Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Deviation | Calculates uncertainty based on the spread of data | Single measurements |
| Propagation of Errors | Calculates uncertainty based on individual measurements | Multiple measurements |
| Monte Carlo | Simulates complex systems to estimate uncertainty | Complex systems |
| Bayesian | Updates prior knowledge with new data to estimate uncertainty | Prior knowledge and new data |
| Fuzzy Logic | Represents uncertainty using fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic operators | Uncertain or imprecise data |

In summary, calculating uncertainty is a critical step in various fields, and there are several methods available to do so. The choice of method depends on the specific problem and the type of data available. By understanding the limitations and assumptions of each method, we can ensure accurate and reliable results.
What is uncertainty in measurement?

+
Uncertainty in measurement refers to the degree of doubt or unpredictability associated with a measurement or prediction.
What is the standard deviation method?
+
The standard deviation method is a technique used to calculate uncertainty based on the spread of data.
What is the Bayesian method?

+
The Bayesian method is a statistical approach used to calculate uncertainty based on prior knowledge and new data.