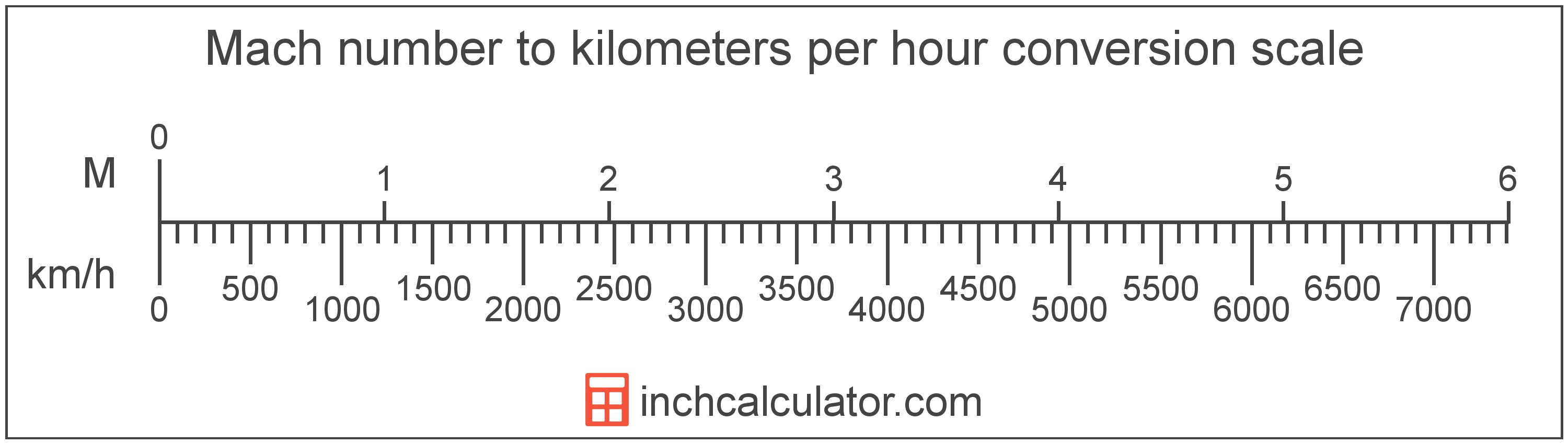
7 Steps to Become Surgeon
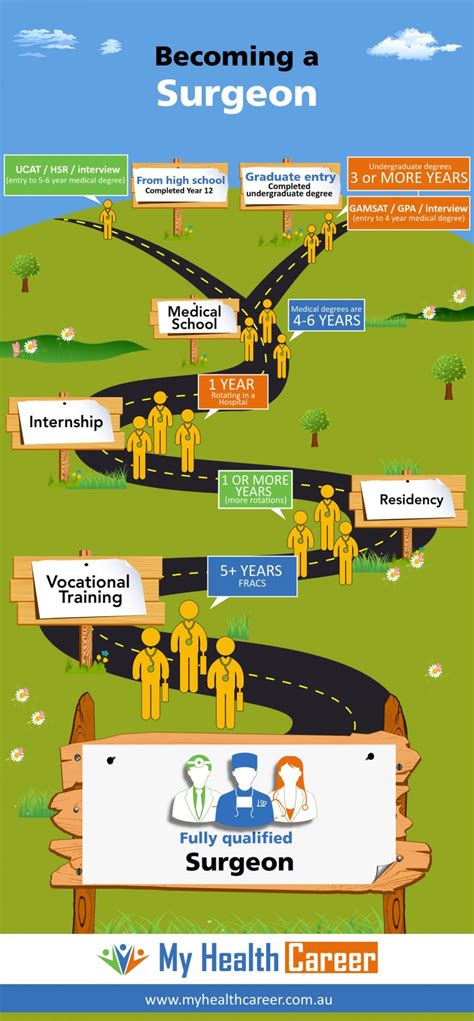
Introduction to Becoming a Surgeon

To become a surgeon, one must undergo a long and challenging journey that requires dedication, hard work, and a strong passion for the medical field. The path to becoming a surgeon is not an easy one, but for those who are willing to put in the time and effort, it can be a highly rewarding career. In this article, we will outline the 7 steps to become a surgeon, highlighting the key requirements and challenges that aspiring surgeons will face.
Step 1: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree

The first step to becoming a surgeon is to earn a bachelor’s degree from an accredited undergraduate institution. Most aspiring surgeons choose to major in biology, chemistry, or physics, as these subjects provide a strong foundation in the sciences. It is also essential to take pre-medical courses, such as anatomy, biochemistry, and physiology, to prepare for medical school. GPA and MCAT scores are crucial in this step, as they will determine an individual’s competitiveness for medical school.
Step 2: Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)

The MCAT is a standardized exam that is required for admission to medical school. The exam tests a student’s knowledge in areas such as biology, chemistry, physics, and critical thinking. Preparation for the MCAT is essential, as it can significantly impact an individual’s chances of being accepted into medical school. Aspiring surgeons should prepare thoroughly for the exam, using study materials and practice tests to ensure they are well-prepared.
Step 3: Attend Medical School

After completing their undergraduate degree and taking the MCAT, aspiring surgeons must apply to medical school. Medical school typically takes four years to complete and provides students with a comprehensive education in the medical sciences. Clinical rotations are an essential part of medical school, as they provide students with hands-on experience in a variety of medical specialties, including surgery.
Step 4: Complete a Surgical Residency Program

After graduating from medical school, aspiring surgeons must complete a surgical residency program. These programs typically last from five to seven years and provide surgeons with the training and experience they need to become proficient in surgical procedures. Residency programs are highly competitive, and aspiring surgeons must be prepared to work long hours and make significant sacrifices in their personal lives.
Step 5: Obtain Licensure and Certification

To become a licensed surgeon, individuals must obtain a medical license and certification from a professional organization, such as the American Board of Surgery (ABS). The ABS offers certification in a variety of surgical specialties, including general surgery, surgical critical care, and pediatric surgery. To become certified, surgeons must meet certain education and training requirements and pass a written and practical exam.
Step 6: Pursue Additional Training and Education

Many surgeons choose to pursue additional training and education in a specialized area of surgery, such as cardiothoracic surgery or neurosurgery. This additional training can be completed through fellowship programs, which typically last one to two years. Fellowship programs provide surgeons with advanced training and experience in a specific area of surgery and can be highly competitive.
Step 7: Maintain Certification and Stay Current

Finally, surgeons must maintain their certification and stay current with the latest advances in surgical techniques and technologies. This can be achieved through continuing medical education (CME) courses, conferences, and workshops. Surgeons must also adhere to a code of ethics and maintain the highest standards of professionalism and patient care.
📝 Note: Becoming a surgeon requires a long-term commitment to education and training, as well as a strong passion for the medical field. Aspiring surgeons must be prepared to make significant sacrifices in their personal lives and be willing to continually update their knowledge and skills to provide the best possible care for their patients.
To summarize, becoming a surgeon requires a significant amount of education, training, and dedication. Aspiring surgeons must be prepared to complete a bachelor’s degree, attend medical school, complete a surgical residency program, obtain licensure and certification, pursue additional training and education, and maintain their certification and stay current with the latest advances in surgical techniques and technologies. By following these steps and staying committed to their goals, individuals can achieve their dream of becoming a surgeon and providing high-quality patient care.
What is the typical salary range for a surgeon?
+
The typical salary range for a surgeon can vary depending on factors such as location, experience, and specialty. However, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for surgeons is around $266,950.
How long does it take to become a surgeon?

+
Becoming a surgeon typically takes a minimum of 10-15 years of education and training after high school. This includes 4 years of undergraduate studies, 4 years of medical school, and 5-7 years of surgical residency training.
What are the most common specialties for surgeons?

+
Some of the most common specialties for surgeons include general surgery, orthopedic surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, neurosurgery, and plastic surgery. These specialties require additional training and education beyond general surgery.