7 Steps To Become Gynecologist
Introduction to Becoming a Gynecologist

To become a gynecologist, one must undertake a long and challenging journey that requires dedication, perseverance, and a strong passion for women’s health. Gynecologists are medical doctors who specialize in the care of women’s reproductive health, playing a crucial role in preventing, diagnosing, and treating conditions related to the female reproductive system. The path to becoming a gynecologist involves several steps, each designed to equip aspiring gynecologists with the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to provide high-quality patient care.
Step 1: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree

The first step towards becoming a gynecologist is to earn a bachelor’s degree from an accredited undergraduate institution. Most aspiring gynecologists choose to major in biology, chemistry, or pre-med, as these majors provide a solid foundation in the sciences and prepare students for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT). Coursework should include classes in anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology. Maintaining a strong grade point average (GPA) is essential, as it is a critical factor in medical school admissions.
Step 2: Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)

After completing the undergraduate degree, the next step is to take the MCAT. The MCAT is a standardized exam that measures a student’s knowledge in areas like biology, chemistry, physics, and critical thinking. Preparation for the MCAT typically involves several months of study, and many students enroll in prep courses to help them prepare. Performing well on the MCAT is crucial for gaining admission into medical school.
Step 3: Attend Medical School

Attending medical school is the next significant step. Medical school typically lasts four years and provides students with both theoretical knowledge and practical clinical experience. The first two years focus on classroom instruction and laboratory work, covering subjects such as pathology, pharmacology, and microbiology. The last two years involve clinical rotations in various specialties, including obstetrics and gynecology, where students gain hands-on experience in patient care under the supervision of licensed physicians.
Step 4: Complete a Residency Program

Following medical school, aspiring gynecologists must apply for and complete a residency program in obstetrics and gynecology. These programs, which typically last four years, provide intensive training in the clinical and surgical aspects of women’s health. Residents work under the supervision of experienced gynecologists, honing their skills in diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions, from routine check-ups and prenatal care to complex surgeries and high-risk pregnancies.
Step 5: Obtain Licensure
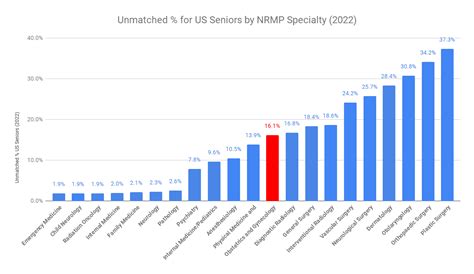
To practice as a gynecologist, one must obtain medical licensure. In the United States, this involves passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX) series. Licensure requirements may vary by state, so it’s essential to check with the state medical board for specific requirements.
Step 6: Pursue Certification

While not mandatory, becoming board certified is highly recommended for gynecologists. The American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG) offers certification for obstetricians and gynecologists who meet certain educational, training, and professional standards. To become certified, one must pass a written and practical exam. Certification demonstrates expertise and commitment to the field, enhancing a gynecologist’s credibility and career prospects.
Step 7: Maintain Certification and Stay Updated

Finally, gynecologists must commit to ongoing education and professional development. The field of gynecology is constantly evolving, with new technologies, treatments, and research findings emerging regularly. To maintain board certification, gynecologists must complete continuing medical education (CME) courses and adhere to the ABOG’s recertification requirements. Staying updated ensures that gynecologists provide the most current and effective care to their patients.
💡 Note: The journey to becoming a gynecologist is long and demanding, requiring significant time, effort, and financial investment. However, for those passionate about women's health, the rewards of this career path can be incredibly fulfilling.
The process of becoming a gynecologist is intricate and involves multiple steps, each designed to prepare individuals for the challenges and responsibilities of this critical role in healthcare. Through dedication, hard work, and a genuine commitment to women’s well-being, aspiring gynecologists can embark on a rewarding career that makes a tangible difference in the lives of their patients.
What is the average salary of a gynecologist?

+
The average salary of a gynecologist can vary widely depending on factors such as location, experience, and type of practice. However, gynecologists are generally among the higher-paid medical specialties, with median salaries ranging from 200,000 to over 400,000 per year.
How long does it take to become a gynecologist?

+
Becoming a gynecologist typically takes a minimum of 11-12 years after high school, including 4 years of undergraduate studies, 4 years of medical school, and 3-4 years of residency training. Additional time may be required for fellowship programs or to achieve board certification.
What are the most common specialties within gynecology?

+
Gynecology encompasses several subspecialties, including reproductive endocrinology and infertility, gynecologic oncology, maternal-fetal medicine, and urogynecology, among others. These specialties allow gynecologists to focus on specific areas of interest and expertise, providing specialized care to patients with unique needs.



