7 Steps Pilot Training

Introduction to Pilot Training
Pilot training is a comprehensive and structured program designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills, knowledge, and competencies to operate an aircraft safely and efficiently. The training process is rigorous, with a clear outline of steps that each aspiring pilot must follow to achieve their goal. In this article, we will delve into the 7 steps of pilot training, highlighting the key components and requirements of each stage.
Step 1: Meet the Basic Requirements

To begin pilot training, candidates must meet certain basic requirements. These include being at least 17 years old for a private pilot license, being able to read, speak, write, and understand English, and holding a valid medical certificate. The medical certificate is obtained by passing a medical examination by a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)-designated Aviation Medical Examiner (AME). This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the rest of the training process.
Step 2: Find a Flight School

The next step involves finding a suitable flight school. With numerous flight schools around the world, it’s essential to research and compare different institutions to find one that best fits your needs and budget. Consider factors such as location, cost, fleet, and instructor experience. Ensure that the school is certified by the relevant aviation authority, such as the FAA in the United States. A good flight school will provide the necessary resources and support for successful training.
Step 3: Ground School
Ground school is a critical component of pilot training, where students learn the theoretical aspects of aviation. This includes aircraft systems, weather, regulations, navigation, and aircraft performance. Students can attend a traditional ground school or opt for online courses. The ground school curriculum is designed to prepare students for the FAA knowledge test, which is a requirement for obtaining a pilot’s license. Understanding these concepts is vital for safe and competent flight operations.
Step 4: Flight Training
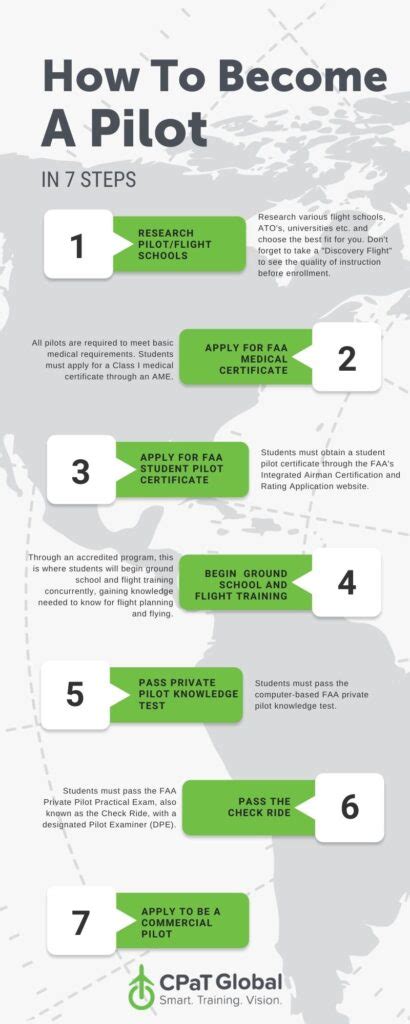
Flight training is the practical aspect of pilot training, where students apply the knowledge gained in ground school to real-world flight scenarios. Under the supervision of a certified flight instructor (CFI), students learn to operate the aircraft safely and efficiently. This includes takeoffs, landings, navigation, and emergency procedures. The flight training syllabus is structured to ensure that students achieve the necessary competencies to pass the practical test (checkride).
Step 5: Accumulate Flight Hours

To qualify for a private pilot license, students must accumulate a minimum of 40 hours of flight time, including 20 hours of flight training and 10 hours of solo flight time. Accumulating these hours provides students with the necessary experience to become proficient pilots. This step is crucial as it allows students to refine their skills and build confidence in their ability to operate an aircraft.
Step 6: Pass the Practical Test (Checkride)
The practical test, also known as the checkride, is the final step in obtaining a private pilot license. Conducted by an FAA inspector or designated examiner, the checkride assesses a student’s ability to safely and competently operate an aircraft. The test includes a pre-flight inspection, startup and taxi, takeoff, cruise, descent, and landing. Passing the checkride is a significant milestone, marking the completion of the pilot training program.
Step 7: Maintain and Improve Your Skills

Obtaining a private pilot license is just the beginning. To remain a safe and competent pilot, it’s essential to maintain and improve your skills through regular flight practice and ongoing training. This includes staying up-to-date with the latest regulations and procedures and expanding your flying skills and knowledge. Consider pursuing additional ratings, such as an instrument rating or multi-engine rating, to enhance your flying capabilities.
📝 Note: The cost of pilot training can vary significantly depending on the location, type of aircraft, and flight school. It's essential to research and budget accordingly to ensure a successful training experience.
In summary, becoming a pilot requires dedication, hard work, and a structured approach to training. By following these 7 steps, aspiring pilots can set themselves on the path to achieving their goal. Remember to stay focused, persistent, and always keep safety at the forefront of your training.
What is the minimum age requirement for a private pilot license?

+
The minimum age requirement for a private pilot license is 17 years old.
How many hours of flight time are required for a private pilot license?
+
A minimum of 40 hours of flight time is required, including 20 hours of flight training and 10 hours of solo flight time.
What is the purpose of the practical test (checkride)?

+
The practical test (checkride) assesses a student’s ability to safely and competently operate an aircraft.



