Mach 3 Speed: What You Need to Know

Mach 3 Speed: What You Need to Know

The term “Mach 3” refers to an object moving at three times the speed of sound. In the realm of aerospace and aviation, Mach numbers are used to express the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound. While the concept of Mach 3 might seem straightforward, there are many fascinating aspects surrounding this speed.
Understanding Mach Numbers

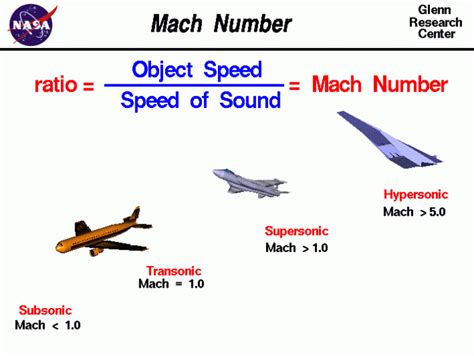
To grasp the concept of Mach 3, it’s essential to understand Mach numbers. The Mach number is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an object’s speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium, such as air. The speed of sound varies depending on factors like temperature, air pressure, and humidity.
In general, the speed of sound at sea level is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at room temperature. When an object moves at a speed greater than the speed of sound, it breaks the sound barrier, producing a sonic boom.
Reaching Mach 3 Speed

Reaching Mach 3 speed is an incredible feat, requiring an object to travel at an astonishing 2,300 mph (3,704 km/h) or more. To put this speed into perspective, consider the following:
- The fastest military aircraft, the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, has a top speed of around Mach 3.5 (approximately 2,400 mph or 3,862 km/h).
- The Space Shuttle, during its re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere, can reach speeds of up to Mach 25 (approximately 19,000 mph or 30,578 km/h).
- The Apollo 11 spacecraft, which carried astronauts to the Moon, reached a top speed of around Mach 25 (approximately 24,791 mph or 39,897 km/h) during its return to Earth.
Challenges of Mach 3 Flight

Reaching and sustaining Mach 3 speeds pose significant technical challenges. Some of the key difficulties include:
- Heat Generation: Friction with the air generates intense heat, which can cause damage to the aircraft’s structure and pose a risk to the occupants.
- Air Resistance: Air resistance increases exponentially with speed, making it difficult to achieve and maintain high speeds.
- Control and Stability: At high speeds, controlling the aircraft becomes increasingly complex, requiring sophisticated flight control systems.
Applications of Mach 3 Speed

While achieving Mach 3 speeds is a remarkable accomplishment, there are practical applications for such high velocities:
- Military Aviation: High-speed aircraft can quickly respond to threats, provide rapid deployment of troops, and conduct reconnaissance missions.
- Space Exploration: Reaching Mach 3 speeds is essential for spacecraft to escape the Earth’s atmosphere and travel to other planets.
- Scientific Research: High-speed flight enables scientists to study the behavior of materials and fluids at extreme conditions, advancing our understanding of physics and engineering.
Notable Examples of Mach 3 Capable Aircraft
Some notable aircraft capable of reaching Mach 3 speeds include:
- Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird: A supersonic reconnaissance plane developed by Lockheed Skunk Works.
- X-15: An experimental rocket-powered aircraft that reached speeds of up to Mach 6.72 (approximately 4,500 mph or 7,242 km/h).
- North American X-51 Waverider: An experimental scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) that aims to reach speeds of up to Mach 5 (approximately 3,800 mph or 6,116 km/h).
🚀 Note: The development of aircraft capable of reaching Mach 3 speeds requires significant investment, cutting-edge technology, and innovative design solutions.
Mach 3 speed represents an extraordinary achievement in aerospace engineering, pushing the boundaries of what is thought possible. The challenges of reaching and sustaining such high speeds are significant, but the rewards include enhanced military capabilities, scientific discoveries, and the potential for faster-than-sound travel.
What is the speed of sound at sea level?

+
The speed of sound at sea level is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at room temperature.
What is the fastest military aircraft?

+
The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird is the fastest military aircraft, with a top speed of around Mach 3.5 (approximately 2,400 mph or 3,862 km/h).
What are the challenges of reaching Mach 3 speeds?

+
Some of the key challenges include heat generation, air resistance, and control and stability issues.



