5 Ways Force Affects Time
Introduction to Force and Time

The relationship between force and time is a fundamental concept in physics, and understanding this relationship is crucial for understanding various phenomena in the universe. Force is a push or pull that causes an object to change its state of motion, while time is a measure of the duration of events. In this article, we will explore how force affects time in different contexts.
1. Time Dilation due to Gravitational Force

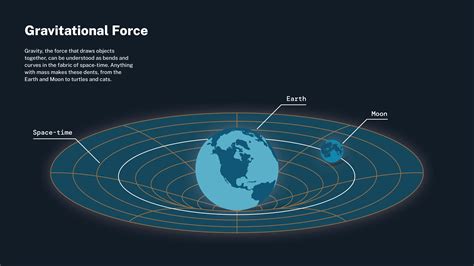
According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, the presence of a massive object such as a star or a black hole warps the fabric of spacetime, causing time dilation. Time dilation occurs when time appears to pass slower near a massive object due to its strong gravitational force. For example, time passes slower on the surface of the Earth than in space due to the Earth’s gravitational force. This effect, although small, has been experimentally confirmed and is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of gravity and time.
2. Time and the Electromagnetic Force

The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature and is responsible for interactions between charged particles. The electromagnetic force can also affect time, particularly in the context of special relativity. According to special relativity, time appears to pass slower for an observer in motion relative to a stationary observer. This effect, known as time dilation due to motion, is a consequence of the electromagnetic force and has been experimentally confirmed.
3. The Strong Nuclear Force and Time

The strong nuclear force is responsible for holding quarks together inside protons and neutrons, and for holding these particles together inside atomic nuclei. The strong nuclear force also plays a role in the decay of unstable particles, which is a process that occurs over time. The lifetime of an unstable particle is a measure of the time it takes for the particle to decay, and this lifetime is influenced by the strong nuclear force.
4. The Weak Nuclear Force and Time

The weak nuclear force is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay, such as beta decay. The weak nuclear force is a short-range force that acts over very small distances, and it plays a crucial role in the decay of certain particles. The half-life of a radioactive substance is a measure of the time it takes for half of the substance to decay, and this half-life is influenced by the weak nuclear force.
5. Quantum Mechanics and Time

In quantum mechanics, time is not an absolute quantity, but rather a relative concept that depends on the observer’s frame of reference. The Schrödinger equation is a fundamental equation in quantum mechanics that describes the time-evolution of a quantum system. The Schrödinger equation shows that time is a dimension that is intimately connected with the other dimensions of space, and that the evolution of a quantum system over time is governed by the forces that act upon it.
📝 Note: The relationship between force and time is complex and multifaceted, and a complete understanding of this relationship requires a deep understanding of physics and mathematics.
In summary, force affects time in various ways, including time dilation due to gravitational force, time dilation due to motion, the strong nuclear force, the weak nuclear force, and quantum mechanics. Understanding these relationships is essential for understanding the behavior of objects and particles in the universe.
To further illustrate the relationship between force and time, consider the following table:
| Force | Effect on Time |
|---|---|
| Gravitational Force | Time Dilation |
| Electromagnetic Force | Time Dilation due to Motion |
| Strong Nuclear Force | Lifetime of Unstable Particles |
| Weak Nuclear Force | Half-life of Radioactive Substances |
| Quantum Mechanics | Relative Time and Time-evolution of Quantum Systems |
Some key points to take away from this discussion include: * The relationship between force and time is complex and multifaceted. * Different forces affect time in different ways. * Understanding the relationship between force and time is essential for understanding the behavior of objects and particles in the universe.
As we continue to explore the universe and the laws of physics, our understanding of the relationship between force and time will continue to evolve and deepen. By studying the effects of force on time, we can gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental nature of reality and the behavior of objects and particles in the universe.
In final thoughts, the concept of force and time is intricate and has various implications in the field of physics. The relationship between these two concepts has been a subject of interest for many physicists and researchers, and understanding this relationship can help us better comprehend the workings of the universe.
What is the relationship between force and time?

+
The relationship between force and time is complex and multifaceted. Different forces, such as gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces, affect time in different ways.
How does the gravitational force affect time?

+
The gravitational force causes time dilation, which is the phenomenon of time passing slower near a massive object due to its strong gravitational force.
What is the role of the electromagnetic force in affecting time?

+
The electromagnetic force causes time dilation due to motion, which is the phenomenon of time passing slower for an observer in motion relative to a stationary observer.
How do the strong and weak nuclear forces affect time?

+
The strong nuclear force affects the lifetime of unstable particles, while the weak nuclear force affects the half-life of radioactive substances.
What is the role of quantum mechanics in affecting time?

+
Quantum mechanics shows that time is a relative concept that depends on the observer’s frame of reference, and that the evolution of a quantum system over time is governed by the forces that act upon it.