How Stirling Engines Work: Efficient Heat Conversion
Introduction to Stirling Engines

Stirling engines are a type of heat engine that converts thermal energy into mechanical work. They are known for their high efficiency, quiet operation, and ability to use various heat sources. The Stirling engine is a closed-cycle regenerative heat engine, which means it uses a working fluid that is sealed within the engine and transferred back and forth between two chambers. This process allows the engine to convert heat energy into mechanical energy with minimal loss.
Components of a Stirling Engine
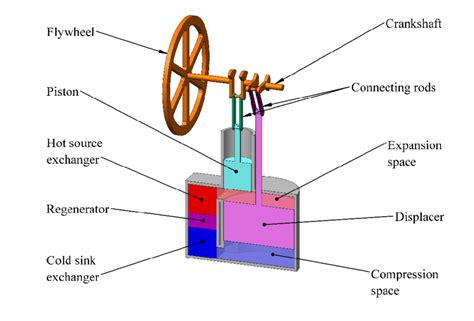
A typical Stirling engine consists of the following components:
- Displacer: A piston or a moving component that transfers the working fluid between the hot and cold chambers.
- Power Piston: A piston that converts the pressure difference between the hot and cold chambers into mechanical energy.
- Cylinder: The chamber where the displacer and power piston move.
- Heat Exchangers: Components that transfer heat from the external source to the working fluid and from the working fluid to the external sink.
- Regenerator: A component that stores heat energy from the working fluid during one cycle and releases it during the next cycle.
Working Principle of a Stirling Engine

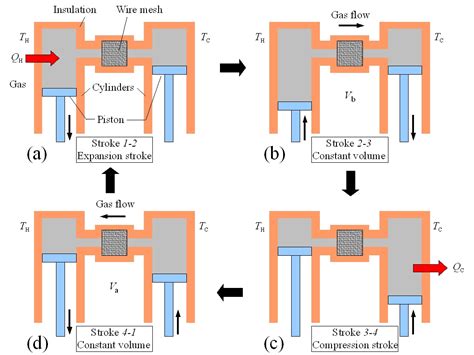
The Stirling engine works on the principle of closed-cycle regenerative heat transfer. The process involves four stages:
- Isothermal Expansion: The working fluid is heated in the hot chamber, causing it to expand and push the power piston down.
- Isochoric Heat Transfer: The displacer transfers the working fluid from the hot chamber to the cold chamber, where it releases its heat to the external sink.
- Isothermal Compression: The working fluid is cooled in the cold chamber, causing it to contract and pull the power piston up.
- Isochoric Heat Transfer: The displacer transfers the working fluid from the cold chamber back to the hot chamber, where it absorbs heat from the external source.
Advantages of Stirling Engines
Stirling engines offer several advantages over traditional internal combustion engines:
- High Efficiency: Stirling engines can achieve high efficiency, often above 40%, compared to traditional internal combustion engines, which typically have an efficiency of around 20-30%.
- Low Emissions: Stirling engines can operate on various fuels, including solar energy, biomass, and waste heat, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Quiet Operation: Stirling engines are known for their quiet operation, making them suitable for applications where noise is a concern.
- Long Lifespan: Stirling engines have a long lifespan due to their simple design and minimal moving parts.
Applications of Stirling Engines
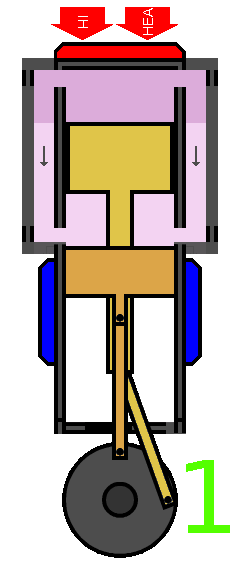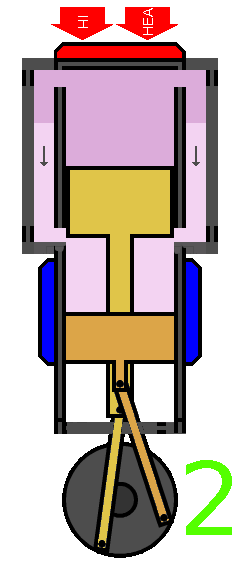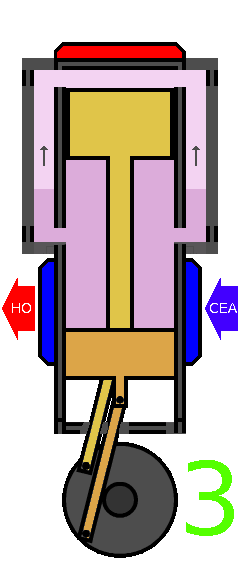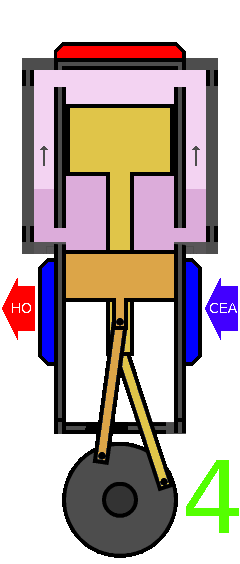
Stirling engines have various applications:
- Solar Power Systems: Stirling engines can be used to generate electricity from solar energy.
- Biogas Generation: Stirling engines can be used to generate electricity from biogas.
- Waste Heat Recovery: Stirling engines can be used to recover waste heat from industrial processes and convert it into electricity.
- Space Exploration: Stirling engines have been used in space exploration due to their high efficiency and reliability.
🔍 Note: Stirling engines are not widely used in commercial applications due to their high upfront costs and limited scalability.
Conclusion

Stirling engines are a promising technology for efficient heat conversion. Their high efficiency, low emissions, and quiet operation make them suitable for various applications. While they have limitations, Stirling engines have the potential to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing energy efficiency.
What is the main advantage of Stirling engines?

+
The main advantage of Stirling engines is their high efficiency, often above 40%, compared to traditional internal combustion engines.
What are the typical applications of Stirling engines?

+
Stirling engines have various applications, including solar power systems, biogas generation, waste heat recovery, and space exploration.
What is the main limitation of Stirling engines?

+
The main limitation of Stirling engines is their high upfront costs and limited scalability.
Related Terms:
- Stirling engine generator
- Who invented the Stirling engine
- Stirling engine PDF
- Gamma Stirling engine
- Fuel for Stirling engine
- Stirling diesel engine