6 Ways to Master Histogram Worksheets for 6th Graders
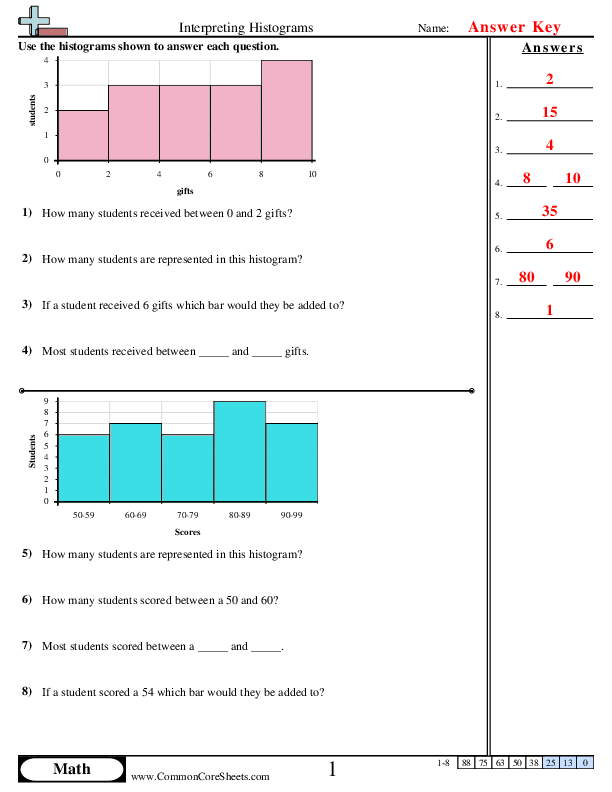
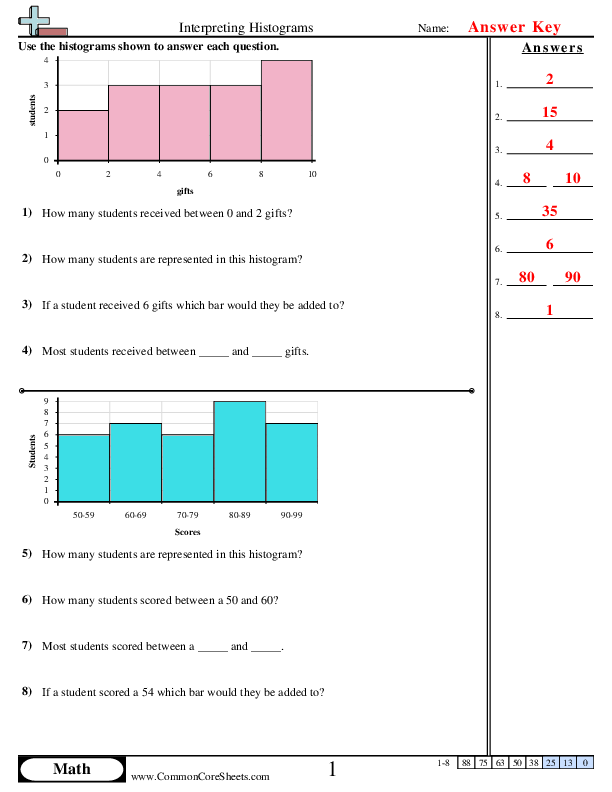
Learning to interpret histograms is a key skill for 6th graders, as it introduces them to basic data analysis and statistical representation, which are fundamental in math and science. Histograms, unlike bar graphs, show continuous data in intervals, or bins, making it crucial to understand how to read and use them effectively. Here are six engaging methods to help students master histogram worksheets:
1. Interactive Group Activities
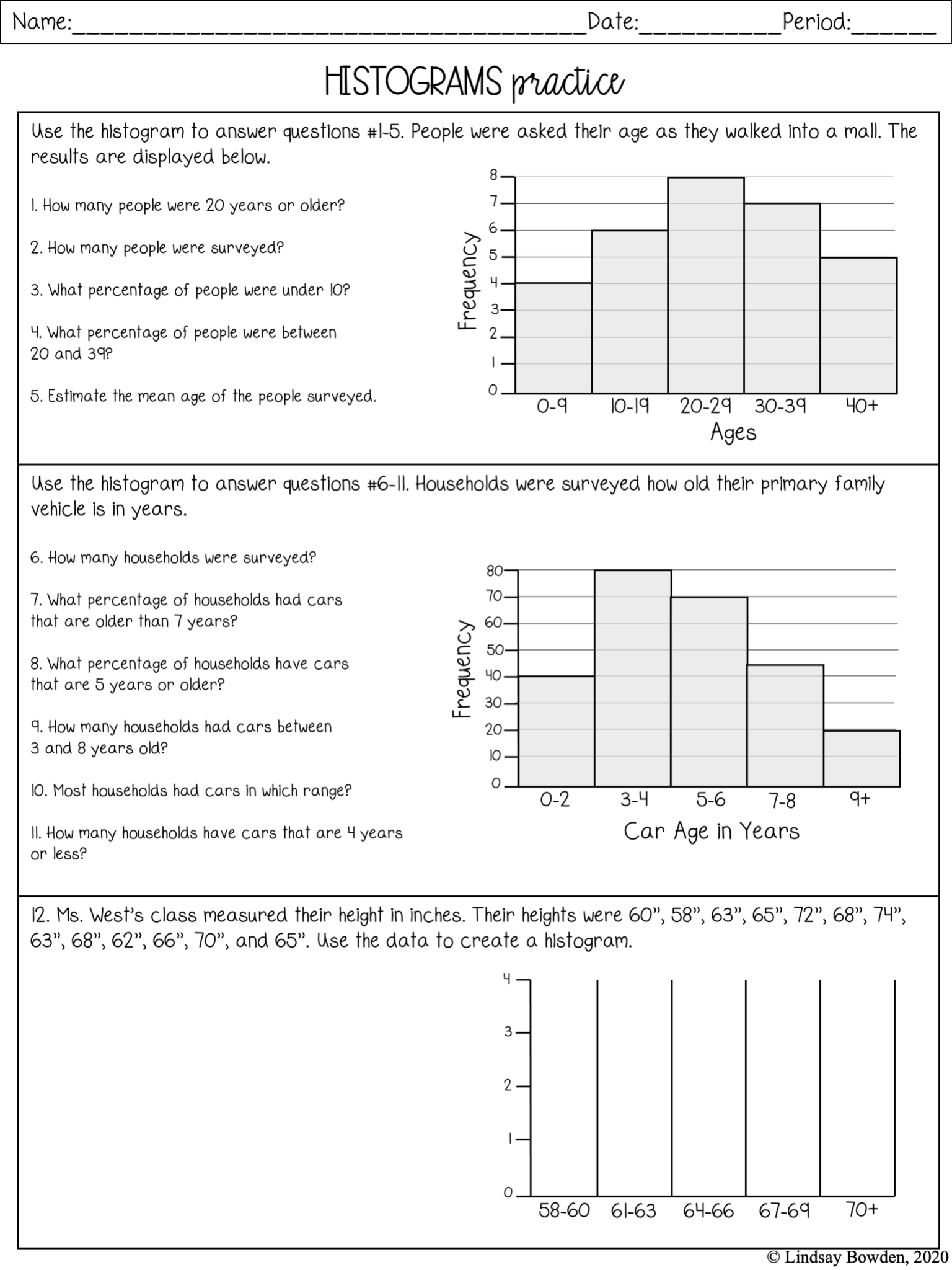
- Collaborative Histogram Building: Divide the class into small groups and provide each with a set of data. Ask the students to create their own histograms using physical objects or digital tools. This hands-on approach lets students decide on bin widths and discuss why they chose certain ranges.
- Histogram Competitions: Set up a friendly competition where groups create histograms based on given datasets. The group that produces the most accurate and clear representation wins.
💡 Note: Group activities not only make learning fun but also foster teamwork and communication skills.
2. Digital Histogram Tools

- Utilize Software: Introduce students to software like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel where they can input data and create histograms. This teaches them both the concept and practical application.
- Online Simulations: Websites like GeoGebra or PhET offer simulations where students can drag data points into bins and see the histogram update in real-time.
3. Real-Life Applications
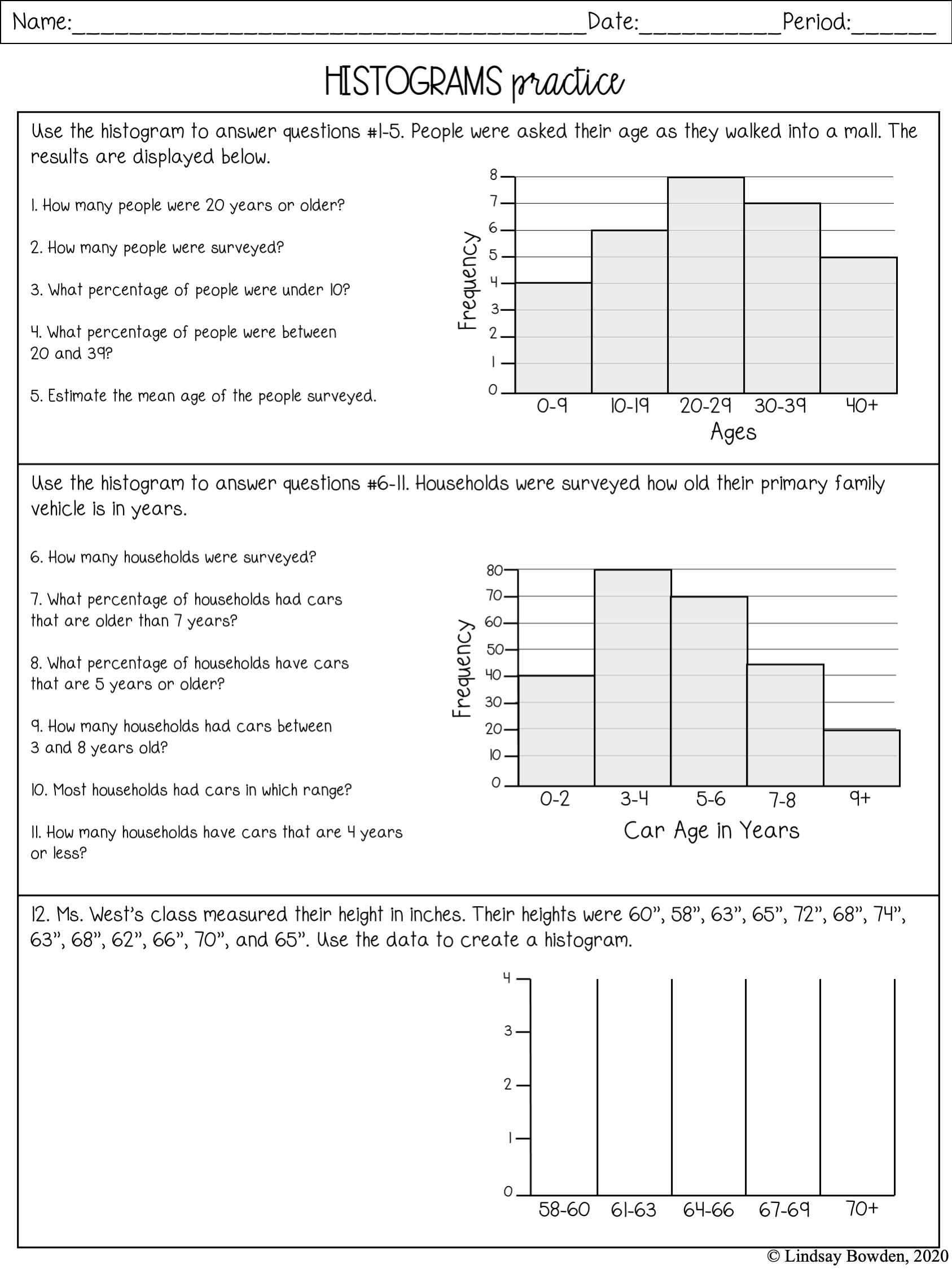
- Data from Sports: Use statistics from sports like basketball or baseball to show how histograms can depict player performances. For example, create histograms to represent the frequency of points scored or goals made.
- Environmental Data: Collect data on local weather conditions (like temperature or rainfall) and have students construct histograms to analyze climate patterns.
📊 Note: Connecting histograms to real-life scenarios helps in retaining the information as it becomes relevant and applicable.
4. Customized Practice Sheets

Provide worksheets tailored to the students’ ability levels:
- Basic Questions: Start with worksheets where students only need to count the frequency of data points in different bins.
- Advanced Questions: Gradually introduce more complex histograms, including those with unequal bin sizes or skewed distributions.
5. Storytelling with Data

- Histogram Narratives: Ask students to create a story or scenario based on histogram data. This exercise promotes critical thinking and the ability to draw conclusions from data.
- Comparing Histograms: Give pairs of histograms and ask students to explain what differences in shapes might suggest about the data sets.
6. Feedback and Reflection

- Immediate Feedback: Use real-time quizzes or digital tools to provide instant feedback on histogram interpretation exercises.
- Reflection Journals: Encourage students to keep a journal where they write down what they learned about histograms each day, helping them reflect on their progress and challenges.
Incorporating these methods ensures a comprehensive understanding of histograms for 6th graders. Not only will students learn to read histograms, but they'll also understand the significance of data presentation in various contexts. By engaging in practical, real-world applications, using technology, and fostering collaborative learning environments, students will be well-equipped to handle more complex statistical analyses in higher grades. Their journey through histograms should be one of discovery and mastery, setting a foundation for statistical literacy that will serve them in their academic and future professional lives.
Why are histograms useful for students to learn?
+
Histograms are valuable because they help students understand data distribution, which is foundational for statistical analysis. This understanding is critical in subjects like mathematics, science, and even in real-world decision-making.
How can parents help their children with histograms at home?

+
Parents can help by creating simple histograms based on everyday activities or family data (e.g., number of hours spent watching TV). This practical approach helps to visualize abstract data and makes learning more relatable.
What are the differences between histograms and bar charts?
+
Histograms represent continuous data with bins and show frequency distribution, while bar charts show categorical data where each bar represents a separate category. The bars in histograms touch to indicate continuity, whereas in bar charts, they are usually separate.
Can histograms be used in real-world scenarios?

+
Absolutely! From analyzing customer purchasing habits, sports performance statistics, to understanding demographic distributions, histograms are widely used for making sense of large data sets in various fields.