Heat With Phase Change Worksheet: Master Energy Calculations Now!

To understand the Heat with Phase Change, it's crucial to grasp how heat affects different substances in various forms - from melting ice to boiling water. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the intricate dynamics of energy during phase transitions, using a Heat with Phase Change Worksheet to calculate and understand heat transfer in these unique situations. Let's delve into how thermal energy influences the state of matter.
Understanding Heat Transfer During Phase Changes

When dealing with phase changes, we’re essentially looking at how heat influences the transition from one state to another. Here are the key aspects:
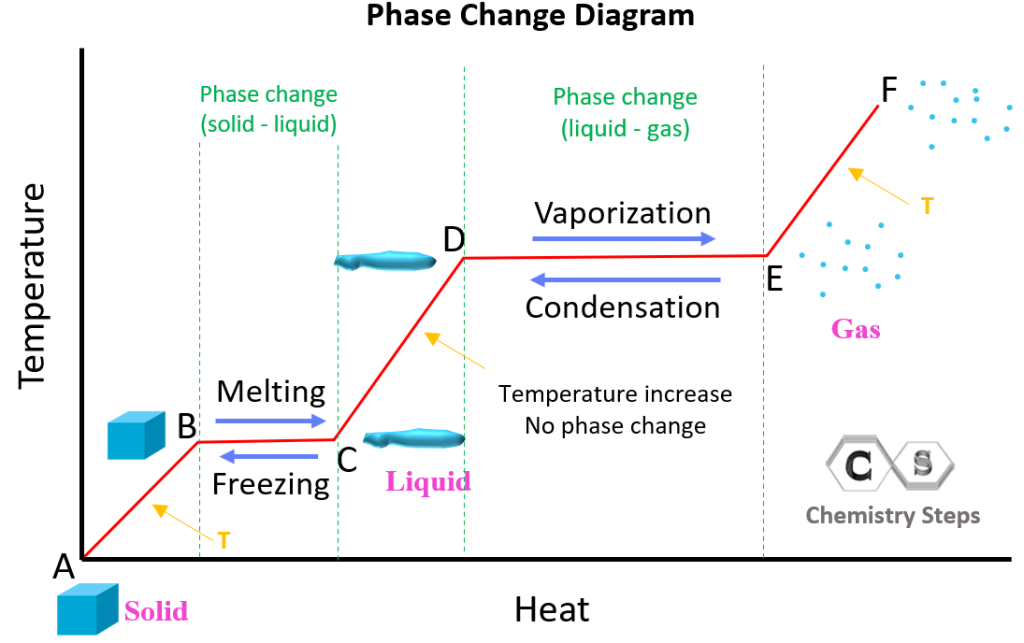
- Latent Heat: This is the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a phase transition without changing its temperature.
- Melting and Freezing: Solid to liquid (melting) or liquid to solid (freezing).
- Vaporization and Condensation: Liquid to gas (vaporization) or gas to liquid (condensation).
- Sublimation and Deposition: Solid directly to gas (sublimation) or gas directly to solid (deposition).
Worksheet Overview


The worksheet provided in this post will help you master the calculations involved in phase transitions. Here’s what you can expect to find:
- A mix of theoretical questions about phase changes.
- Energy calculations involving specific heat capacity and latent heat.
- Application of these concepts to real-world scenarios.
Key Calculations for Phase Changes

Here are some essential formulas and steps to follow when working through problems in the worksheet:
- Specific Heat Capacity:
Q = m * c * ΔT, where m is mass, c is specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- Latent Heat:
Q = m * L, where L is the latent heat of fusion or vaporization.
- Calculate the total heat transfer by combining the above formulas for different parts of the phase change process.
💡 Note: Remember that the temperature does not change during the phase transition, but energy is still absorbed or released.
Examples with the Worksheet

Let’s walk through a couple of examples from the worksheet:
- Calculating the energy required to melt ice at 0°C into water:
- Determining the heat energy needed to convert liquid water into steam at its boiling point:
| Scenario | Heat Calculation |
|---|---|
| Ice at 0°C to water at 0°C | Q = m * Lfusion |
| Water at 100°C to steam at 100°C | Q = m * Lvaporization |

Practical Applications
Understanding how heat works during phase changes is not just theoretical; it has practical applications in:
- Engineering: Managing heat in industrial processes.
- Energy Production: Enhancing efficiency in steam engines and refrigeration.
- Food Science: Managing food texture and preservation through thermal processes.
🌡️ Note: Specific heat capacity and latent heat values for common substances are often available online or in reference books. Make sure to use the correct units.
Learning through Mistakes

One of the best ways to master heat transfer calculations is by learning from common errors:
- Failing to account for the phase transition temperature: Remember, temperature doesn’t change during the phase change.
- Confusing units: Always convert measurements to standard units before applying formulas.
- Misreading values: Ensure accuracy in using specific heat capacity and latent heat values.
📝 Note: Keep track of your units throughout the calculation to avoid errors in your final result.
In this extensive blog post, we’ve delved into the intricacies of heat transfer during phase changes, providing a structured worksheet to enhance your understanding and calculation skills. By using specific heat capacity and latent heat in your calculations, you can now tackle even the most complex heat energy problems with confidence. Whether it’s melting ice or boiling water, the principles of thermodynamics guide these phenomena, offering practical insights into energy management across various fields.
Now, let’s answer some common questions that often arise when dealing with heat and phase changes:
What is the difference between heat and temperature during a phase change?

+
During a phase change, heat is the energy that either breaks or forms bonds between molecules, allowing the substance to change its state. The temperature, however, remains constant because this energy is being used for the phase transition, not to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules.
How can I calculate the energy needed for a substance to change from one phase to another?

+
Use the formula Q = m * L, where Q is the heat, m is the mass of the substance, and L is the latent heat of fusion or vaporization. Remember to use the correct value for L based on the phase change occurring.
Why is specific heat capacity important for heat calculations?

+
Specific heat capacity tells us how much heat energy a substance can absorb or release per unit mass for each degree of temperature change. It’s crucial for calculating how much energy is needed or given off when changing the temperature of a substance before, during, or after a phase change.