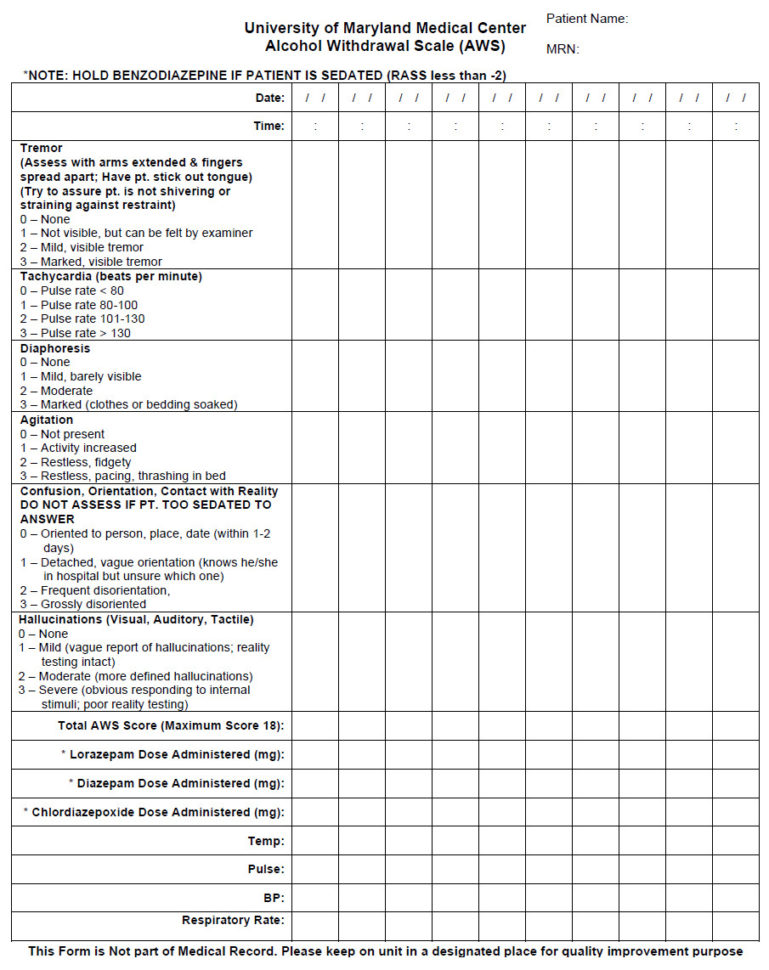
Gummy Bear Science: Simple Experiment Worksheet for Kids

Are you ready to explore the fascinating world of science with your kids in a fun and engaging way? Today, we're going to delve into the delightful realm of gummy bear science, where simple experiments can spark curiosity and teach children about basic scientific principles. Whether it's an educational activity at home or a project for school, gummy bear experiments are perfect for young learners to grasp concepts like osmosis, measurements, and observation skills. Let's jump into this sweet adventure!
Introduction to Gummy Bear Science

Gummy bears, those chewy, fruity snacks, become unexpectedly excellent tools for hands-on science experiments. They offer an entertaining way to introduce kids to scientific methods through observation, hypothesis making, and data recording. Why gummy bears? They’re colorful, they change size and shape in liquids, and most importantly, they’re something kids love. Here’s how you can make learning fun:
- Experimentation: Using common kitchen ingredients, children can explore how different environments affect the bears.
- Observation: Documenting changes over time instills patience and the value of detailed observation.
- Hypothesis Testing: Predicting outcomes teaches critical thinking.
Preparation for the Experiment

Before diving into the experiment, gather these simple materials:
- Gummy bears - at least 6
- 4 small clear cups
- Water, vinegar, and corn syrup
- Ruler (metric or imperial)
- Stopwatch or timer
- A notebook for data recording
Now, set up your experiment station:
- Label each cup with the liquid you'll be using (Water, Vinegar, Corn Syrup, and one for control - no liquid).
- Pour the liquids into their respective cups, ensuring you have enough to submerge the bears fully.
- Leave the control cup empty.
Step-by-Step Gummy Bear Experiment

1. Initial Observations

First, examine the gummy bears. Have your children describe their:
- Size
- Color
- Texture
- Shape
Record these initial observations in your notebook, noting their exact measurements.
2. Placing Gummy Bears in Solutions

Now, place a gummy bear in each of the cups:
- One in water
- One in vinegar
- One in corn syrup
- One in the control cup without liquid
Time how long you let them soak for consistency, usually 24 hours works well, but children can decide on shorter or longer durations.
3. Making Hypotheses

Discuss with the children what they think will happen:
- Will the bears grow, shrink, or stay the same?
- Which liquid will affect the gummy bears the most?
Write these hypotheses down in the notebook.
4. Observing Changes

After the waiting period:
- Take the bears out one by one and observe their changes.
- Measure the new size, noting any changes in color, texture, and shape.
- Compare these results with the initial observations.
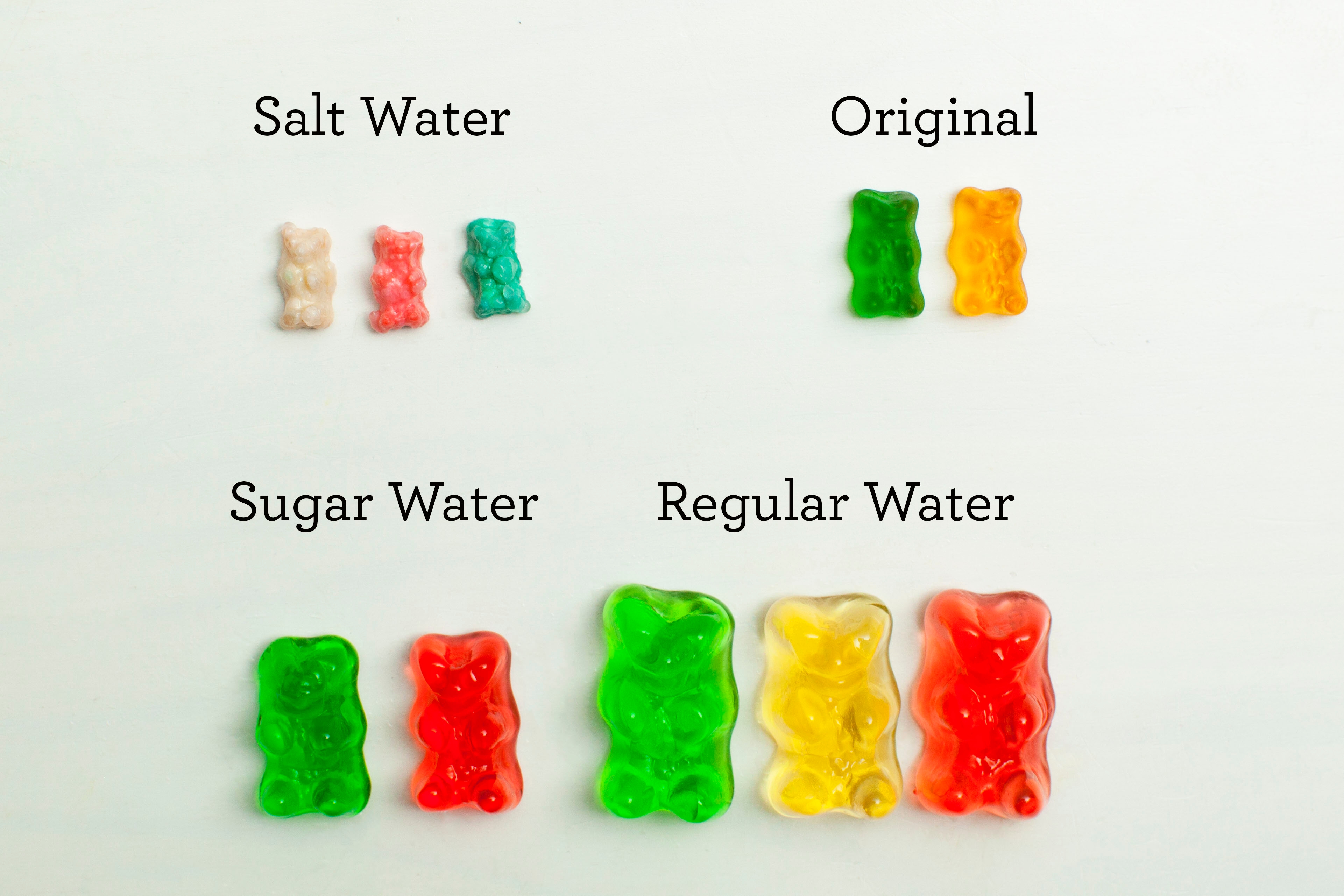
| Liquid | Initial Size (cm) | Final Size (cm) | Color Change | Texture Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 2 x 1 x 1 | 4 x 2 x 2 | Lighter | Softer |
| Vinegar | 2 x 1 x 1 | 1.8 x 0.8 x 0.8 | Slightly faded | Harder |
| Corn Syrup | 2 x 1 x 1 | 3 x 1.5 x 1.5 | Lighter, some bears colorless | Hard and sticky |
| Control (No Liquid) | 2 x 1 x 1 | 2 x 1 x 1 | No change | No change |

🧪 Note: The time of observation affects results. A longer exposure to the liquids can amplify the changes observed in gummy bears.
Conclusion

Through this gummy bear experiment, children have learned about osmosis, how different substances interact with each other, and the importance of patience in science. They’ve seen firsthand how water moves into or out of the bear’s material, causing them to grow or shrink. This simple activity not only fosters a curiosity for science but also develops critical observation and documentation skills, setting the stage for a lifelong love of learning.
What exactly is osmosis?

+
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. In this experiment, gummy bears act as this membrane, absorbing or losing water based on their environment.
Can we use other liquids for this experiment?

+
Absolutely! You can try salt water, sugar water, lemon juice, or any other household liquid to see different effects on the bears.
How can this experiment be adapted for different age groups?

+
For younger children, simplify the process by focusing on observation. For older kids, you can introduce more complex concepts like the osmotic pressure, detailed measurements, and encourage them to design their experiments.
Why did some gummy bears get sticky?

+
In corn syrup, the sugar content is very high, which can cause the gummy bear to lose water due to osmosis, making it feel hard and sticky as it dries out.
Are there educational benefits to these types of experiments?

+
Yes! Gummy bear experiments can teach kids about science, encourage logical thinking, boost curiosity, and develop fine motor skills and patience through observation and data recording.