5 Tips for Graphing Systems of Inequalities Easily

Graphing systems of inequalities can be a daunting task for many students learning algebra, but with the right strategies and understanding, it can become a straightforward and less intimidating process. In this blog post, we will explore five essential tips that can make graphing systems of inequalities easier and more intuitive. Whether you're preparing for an exam or just trying to improve your math skills, these tips will help you conquer this critical math concept effectively.
Understand the Basics of Inequalities
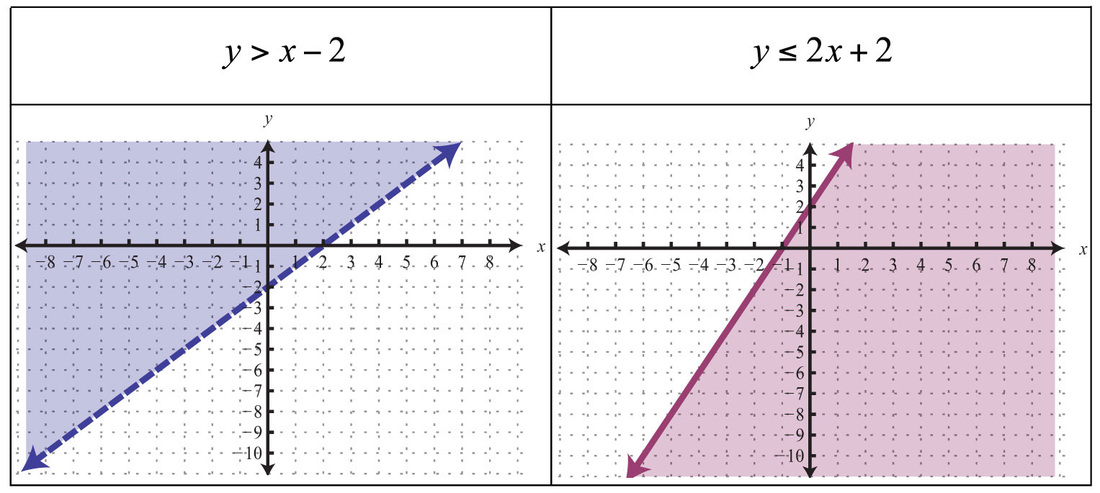
Before you start graphing, it’s crucial to have a solid grasp of what inequalities represent:
- Greater Than (>) and Less Than (<): These symbols tell us that one expression is larger or smaller than another. Remember, the open side faces the larger number.
- Greater Than or Equal (≥) and Less Than or Equal (≤): These include equality. The line under the inequality sign means that the solution can include the boundary line.
When graphing linear inequalities:
- Use a solid line for ≥ or ≤, which means the line itself is part of the solution set.
- Use a dashed line for > or < to indicate the line is not part of the solution set.
Identify Boundary Lines

Each inequality in the system represents a line on the coordinate plane. Here’s how to handle them:
- Convert each inequality into its corresponding equation by replacing the inequality sign with an equal sign to find the line's position.
- Graph these lines. Use the slope-intercept form y = mx + b to plot the line, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Determine if the line should be solid or dashed based on the inequality type.
💡 Note: Use the y-intercept for quick plotting; then, use the slope to extend the line in both directions.
Shade Regions Appropriately
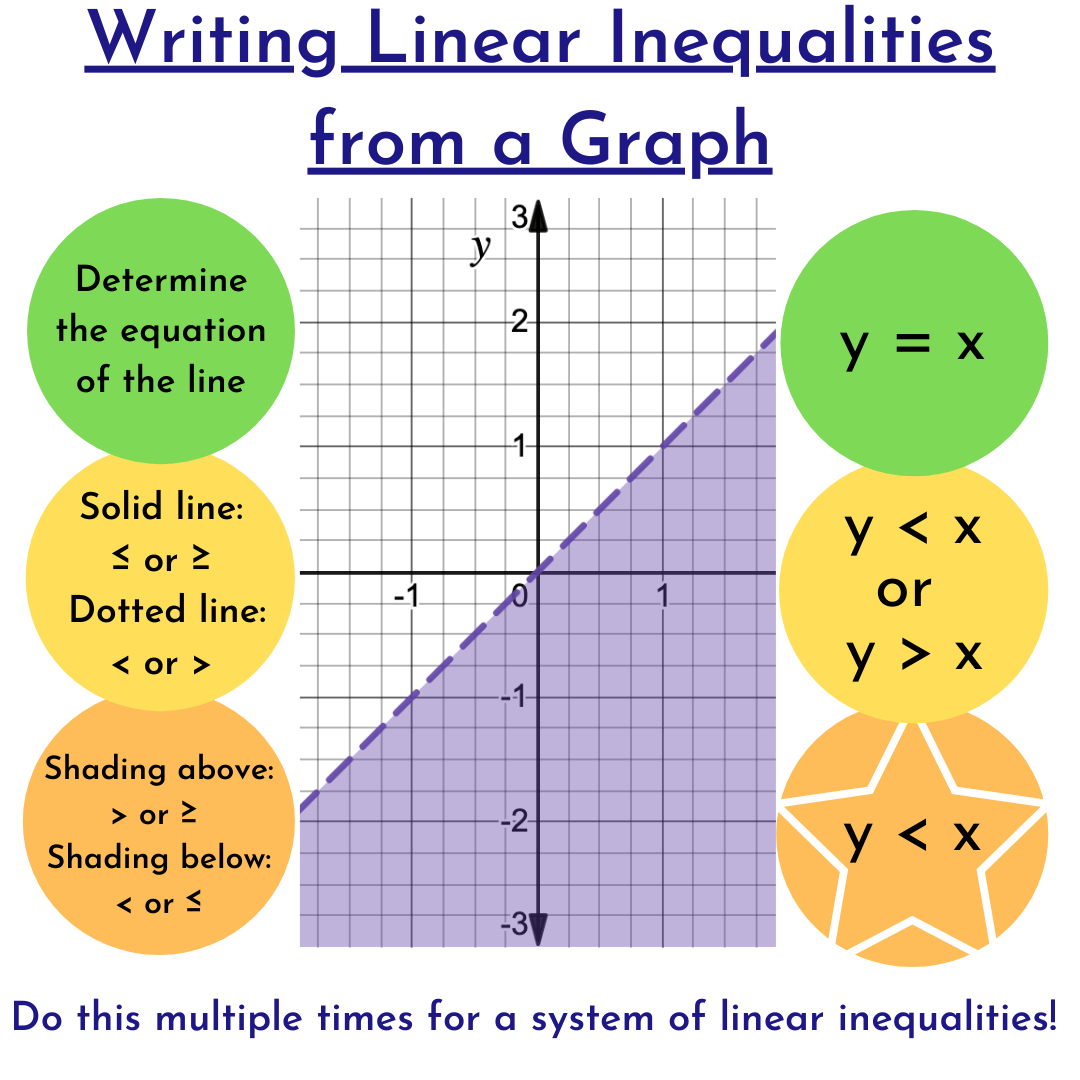
After plotting the boundary lines:
- Choose a test point not on the line, often (0,0) if it’s not on the line, to determine which side of the line satisfies the inequality.
- Shade the area where the inequality holds true:
- For (y > mx + b) or (y \geq mx + b), shade above the line.
- For (y < mx + b) or (y \leq mx + b), shade below the line.
- When dealing with multiple inequalities, find the area where all shadings overlap, which will be your solution set.
Use Technology to Verify

Modern tools like graphing calculators and online graphing apps:
- Can plot these systems for you, providing instant feedback on whether your manual graphing is correct.
- Help in understanding the concept through visual representation, which can be particularly useful for complex systems.
🌍 Note: Technology not only aids in accuracy but also reinforces learning through visualization.
Consistency is Key

To ensure accuracy when graphing:
- Consistently apply the same rules for every inequality. If you shade above for one inequality, do so for all similar ones.
- Be meticulous with plotting points and lines, ensuring the scale on your graph is appropriate for the values in the inequalities.
- Check your work by verifying that the points in the shaded regions satisfy all given inequalities.
By following these tips, graphing systems of inequalities will become a less daunting task. It’s all about understanding the underlying principles, using the right tools, and maintaining a systematic approach. Over time, with practice, you’ll find that what once seemed complex becomes more straightforward and manageable. The key points to remember include:
- Understand the basic rules of inequalities.
- Plot boundary lines correctly.
- Shade regions carefully after testing points.
- Use technology to verify and learn.
- Be consistent in your approach to avoid common mistakes.
How do I know which side to shade when graphing an inequality?

+
To determine which side to shade, pick a test point not on the boundary line (usually (0,0)). If this point satisfies the inequality, shade the side containing that point. Otherwise, shade the opposite side.
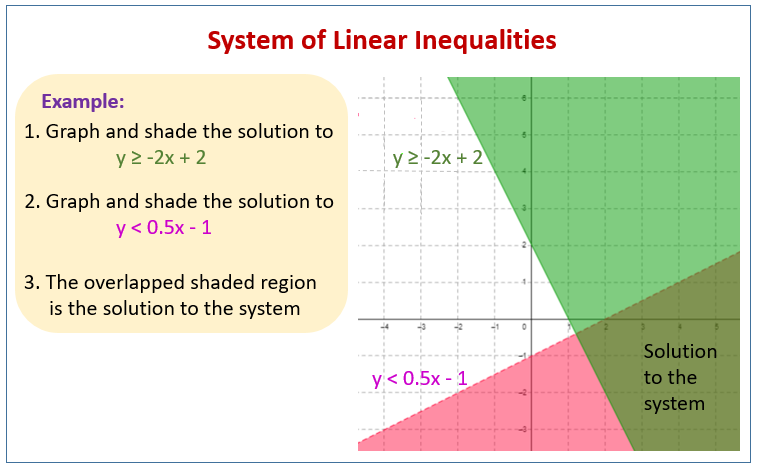
What if the boundary lines overlap?

+
When boundary lines overlap or intersect, you should identify the overlapping regions where all inequalities are true. The solution set for the system is where all regions overlap.
Can graphing inequalities be done on any calculator?
+
Modern graphing calculators and many graphing apps on computers or smartphones can graph inequalities, although the capabilities might differ. Look for features like inequality shading or solving systems of equations.
Why are these tips important for understanding inequalities?

+
These tips provide a structured method to approach a problem that often appears complex. By breaking it down into manageable steps, it not only simplifies the process but also deepens the understanding of mathematical relationships and logical reasoning.