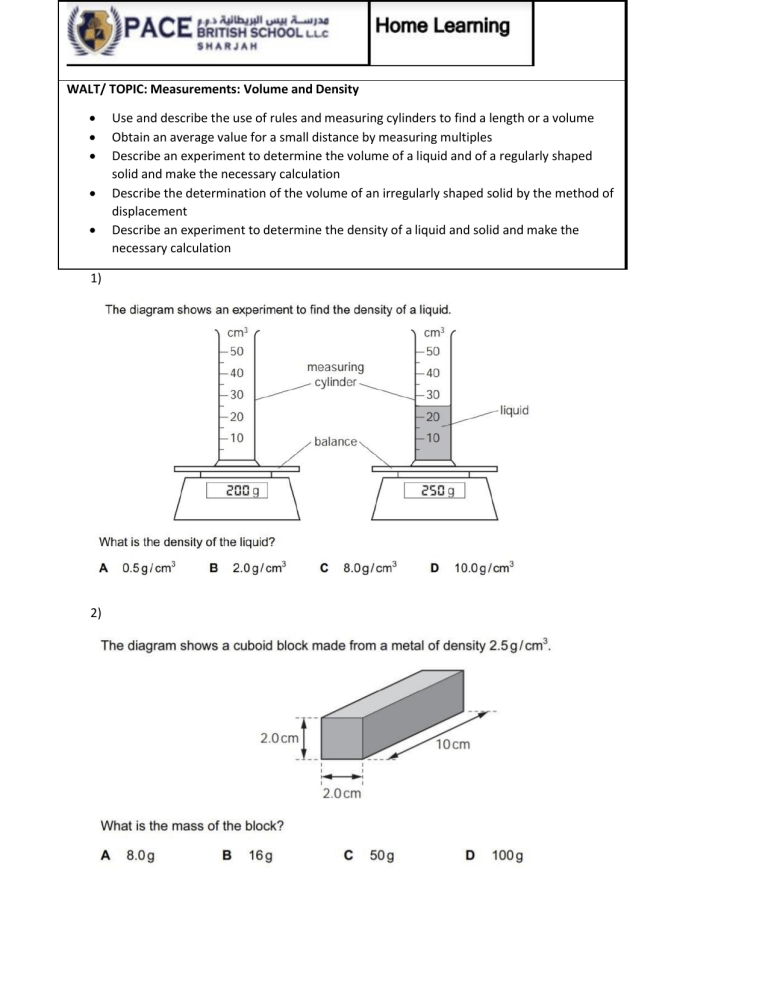
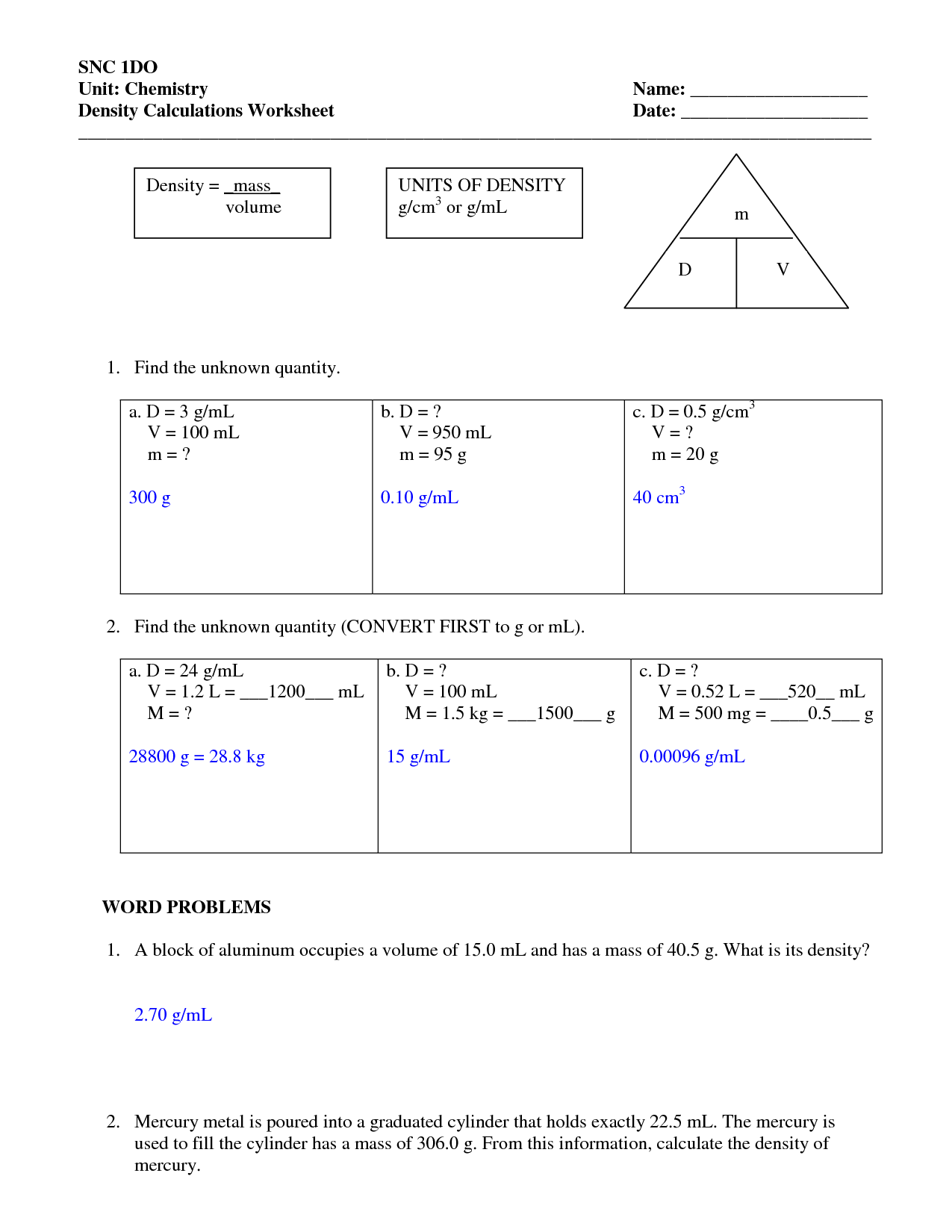
Explore Density with Our Graphing Worksheet

In the world of science, understanding and graphing density is crucial for a variety of applications, from fluid mechanics to materials science. Our density graphing worksheet is designed to help learners visualize the relationship between mass and volume in an intuitive way. Through this interactive tool, you will not only learn how to plot data points effectively but also comprehend the deeper concept of mass per unit volume. This post will guide you through the essentials of density, how to create a density graph, and what insights you can gain from this representation.
Understanding Density

At its core, density is defined as the mass of an object divided by its volume:
[ Density = \frac{Mass}{Volume} ]
This relationship is key in distinguishing different materials based on their inherent properties:
- Solids: Their density helps in the identification and comparison of metals, plastics, or minerals.
- Liquids: Understanding density is vital for applications like buoyancy and fluid dynamics.
- Gases: While less tangible, gas density affects how we understand atmospheric changes and weather patterns.

Importance of Density in Science
- Identifies Materials: By measuring density, scientists can identify unknown substances.
- Engineering Designs: From building materials to automotive components, density influences design decisions.
- Medicine: Density scans help in understanding bone health or determining fluid levels in the body.
Creating a Density Graph

Graphing density involves plotting data points where:
- The X-axis represents the volume.
- The Y-axis represents the mass.
Here's how to create your density graph:
1. Collect Data

Gather data on the mass and volume of several samples from different materials. Ensure your measurements are consistent and precise:
| Sample | Volume (cm³) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Lead | 5 | 55 |
| Aluminum | 20 | 54 |
| Water | 10 | 10 |
2. Plotting the Points

Plot the volume on the X-axis and mass on the Y-axis. Each material should form a separate data series:
- Use different markers or colors for different materials to make the graph distinguishable.
- Label each axis with units for clarity.

3. Calculating Density

To find the density of a material, draw a line of best fit through the data points of that material. The slope of this line represents the density. Here's a simple method:
- Identify two points on the line, say Point A and Point B.
- Calculate the change in mass (ΔMass) and volume (ΔVolume) between these points.
- Density (ρ) = ΔMass / ΔVolume
📌 Note: The more data points you have, the more accurate your density calculation will be. However, ensure that your measurements are precise to reduce errors in your graph.
4. Understanding the Graph

The graph provides insights:
- Slope: The steepness of the line indicates the density of the material. A steeper line means higher density.
- Outliers: Points not fitting the trend could indicate measurement errors or material impurities.
- Comparisons: Different materials can be compared on the same graph for a clear visual representation.
Enhancing Understanding with Practical Applications

Understanding density goes beyond academic exercises; it has practical implications:
- Materials Engineering: Selecting materials based on their density helps in crafting lighter yet stronger structures.
- Fluid Dynamics: Density affects how liquids and gases interact, influencing everything from plumbing to aerodynamics.
- Geology: Density differences help geologists understand stratification, mining, and earth's structure.

Advanced Visualization Techniques

For advanced learners or professionals, exploring different density visualization methods can yield further insights:
- 3D Density Plots: These can help visualize density variations within a material or across different layers.
- Isodensity Surfaces: Graphing isodensity surfaces can show where materials have similar density throughout.
📌 Note: While these techniques are beyond basic graphing, understanding them can lead to deeper insights into complex systems involving materials of varying densities.
To sum up, our density graphing worksheet serves as an invaluable tool to grasp the essentials of density. By plotting and analyzing data points, you learn not just how to calculate density but also how to interpret its implications across different disciplines. Through visual representations, you can compare materials, predict behaviors, and understand the underpinnings of physical phenomena. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or an engineer, mastering the art of graphing density equips you with a foundational skill for material characterization and the science of understanding the world around us.
Why do we need to graph density?

+
Graphing density provides a visual representation that helps in comparing the density of different materials, understanding their relationships, and making predictions based on their physical properties.
How accurate should my measurements be for the graph to be reliable?

+
The accuracy of your measurements directly impacts the reliability of your density graph. Precision in measurements ensures accurate density calculations and reliable comparisons.
Can I use different units for mass and volume?

+
Yes, as long as you consistently use the same units for all measurements, you can choose any unit. For example, grams for mass and cm³ for volume will give you the density in grams per cubic centimeter.