Graphing Quadratic Functions Made Easy with This Worksheet
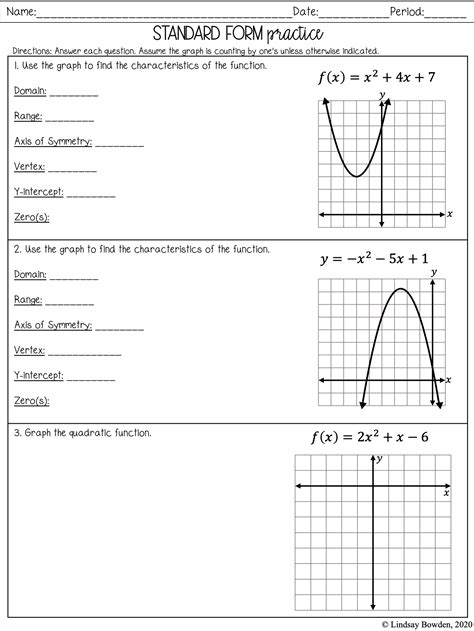
Understanding Quadratic Functions

Quadratic functions are a fundamental concept in algebra, and graphing them can be a daunting task for many students. However, with the right tools and techniques, graphing quadratic functions can be made easy. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of quadratic functions, the importance of graphing, and provide a worksheet to help you practice and master the skill.
What are Quadratic Functions?
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, which means the highest power of the variable (usually x) is two. The general form of a quadratic function is:
f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c
where a, b, and c are constants, and a cannot be zero. Quadratic functions can be represented in various forms, including the standard form, vertex form, and factored form.
Why Graph Quadratic Functions?
Graphing quadratic functions is essential in mathematics and real-life applications. It helps to visualize the relationship between the variables and understand the behavior of the function. By graphing quadratic functions, you can:
- Identify the vertex, axis of symmetry, and x-intercepts
- Determine the maximum or minimum value of the function
- Analyze the function’s behavior, such as opening up or down, and its concavity
- Solve problems involving quadratic functions in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields
How to Graph Quadratic Functions

Graphing quadratic functions involves several steps:
- Determine the vertex: The vertex is the lowest or highest point on the graph, depending on the direction of the parabola. To find the vertex, use the formula x = -b / 2a.
- Find the axis of symmetry: The axis of symmetry is the vertical line that passes through the vertex. It is given by the equation x = -b / 2a.
- Identify the x-intercepts: The x-intercepts are the points where the graph crosses the x-axis. To find the x-intercepts, set the function equal to zero and solve for x.
- Plot additional points: Plot additional points on either side of the vertex to determine the shape of the graph.
- Draw the graph: Draw a smooth curve through the points to create the graph.
Worksheet: Graphing Quadratic Functions
Here is a worksheet to help you practice graphing quadratic functions:
| Function | Vertex | Axis of Symmetry | x-Intercepts |
|---|---|---|---|
| f(x) = x^2 + 4x + 4 | (-2, 0) | x = -2 | (-2, 0) |
| f(x) = -x^2 + 2x - 1 | (1, 1) | x = 1 | (0, -1), (2, -1) |
| f(x) = 2x^2 - 4x - 3 | (1, -5) | x = 1 | (-0.5, 0), (3, 0) |
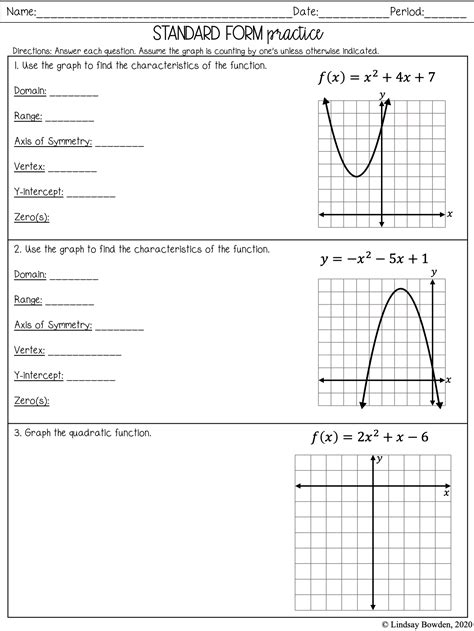
Graph each function on a separate coordinate plane. Label the vertex, axis of symmetry, and x-intercepts.
📝 Note: Use the steps outlined above to graph each function. Make sure to label the vertex, axis of symmetry, and x-intercepts correctly.
Tips and Tricks

- Use a consistent scale when graphing to ensure accuracy.
- Plot additional points to ensure the graph is smooth and continuous.
- Use the vertex and axis of symmetry to help draw the graph.
- Check your work by plugging in values to ensure the graph is accurate.
By following these steps and practicing with the worksheet, you will become proficient in graphing quadratic functions. Remember to take your time, be patient, and practice regularly to master this essential skill.
In summary, graphing quadratic functions is a crucial skill in mathematics and real-life applications. With the right tools and techniques, you can become proficient in graphing quadratic functions. Practice regularly, and you will be well on your way to mastering this essential skill.
What is the general form of a quadratic function?
+
The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a cannot be zero.
Why is graphing quadratic functions important?
+
Graphing quadratic functions helps to visualize the relationship between the variables and understand the behavior of the function. It is essential in mathematics and real-life applications.
What is the axis of symmetry in a quadratic function?
+
The axis of symmetry is the vertical line that passes through the vertex of the parabola. It is given by the equation x = -b / 2a.
Related Terms:
- Desmos
- GeoGebra
- Symbolab
- Photomath
- Microsoft Math Solver
- Wolfram Alpha