Mastering Graphs: A Science Student's Essential Guide

Understanding the Basics of Graphs

As a science student, you’re likely to encounter graphs in various forms throughout your academic journey. Graphs are a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data, and being able to read, create, and interpret them is an essential skill for any science enthusiast. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of graphs, exploring the different types, their applications, and provide tips on how to master them.
Types of Graphs

There are several types of graphs, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Let’s take a look at some of the most common types of graphs:
- Line Graphs: Used to show trends or patterns over time, line graphs consist of a series of data points connected by lines.
- Bar Graphs: Ideal for comparing categorical data, bar graphs use bars of different lengths to represent the values.
- Histograms: A type of bar graph, histograms are used to display the distribution of continuous data.
- Pie Charts: Circular graphs that use slices to represent the proportion of different categories.
- Scatter Plots: Used to visualize the relationship between two variables, scatter plots display data points on a grid.
Reading and Interpreting Graphs
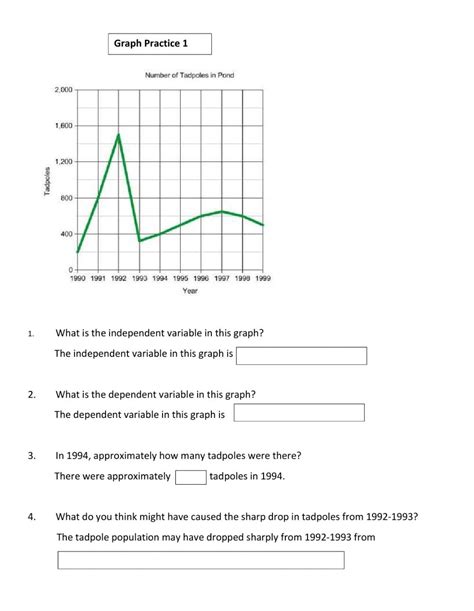
Being able to read and interpret graphs is crucial for extracting valuable insights from data. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Understand the Axes: Familiarize yourself with the x and y axes, and what they represent.
- Identify the Scale: Pay attention to the scale used on each axis, as it can affect the interpretation of the data.
- Look for Patterns: Identify trends, correlations, or anomalies in the data.
- Analyze the Data Points: Understand what each data point represents, and how it contributes to the overall trend.
Creating Graphs

Creating graphs can be a daunting task, but with the right tools and techniques, you can create informative and engaging visualizations. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Choose the Right Type: Select the type of graph that best suits the data and the message you want to convey.
- Use a Clear and Concise Title: Ensure the title accurately reflects the data and is easy to understand.
- Label the Axes: Clearly label the x and y axes, and provide a scale or legend if necessary.
- Use Color Effectively: Use color to highlight trends, patterns, or correlations, but avoid using too many colors.
Common Graphing Mistakes to Avoid

When creating graphs, it’s easy to fall into common pitfalls that can mislead or confuse the audience. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
- Inconsistent Scales: Ensure the scales on each axis are consistent and easy to read.
- 3D Graphs: Avoid using 3D graphs unless necessary, as they can be misleading and difficult to interpret.
- Too Many Colors: Limit the number of colors used to avoid visual overload.
- Insufficient Labeling: Ensure all axes, labels, and titles are clear and concise.
📝 Note: When creating graphs, it's essential to consider the audience and the message you want to convey. Use clear and concise language, and avoid cluttering the graph with unnecessary information.
Real-World Applications of Graphs

Graphs have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Science and Research: Graphs are used to visualize and analyze data in fields like physics, biology, and chemistry.
- Business and Finance: Graphs are used to track trends, forecast sales, and analyze market data.
- Medicine and Health: Graphs are used to visualize patient data, track disease outbreaks, and analyze medical research.
- Environmental Science: Graphs are used to track climate patterns, analyze weather data, and visualize environmental trends.
Tools and Software for Graphing
There are numerous tools and software available for creating graphs, including:
- Microsoft Excel: A popular spreadsheet software that offers a range of graphing tools.
- Google Sheets: A cloud-based spreadsheet software that allows real-time collaboration and graphing.
- Graphing Calculators: Specialized calculators designed for graphing and analyzing mathematical functions.
- Data Visualization Software: Specialized software like Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js that offer advanced graphing and data visualization tools.
📊 Note: When choosing a graphing tool or software, consider the complexity of the data, the type of graph required, and the level of customization needed.
In conclusion, mastering graphs is an essential skill for any science student. By understanding the different types of graphs, learning to read and interpret them, and creating effective visualizations, you’ll be able to extract valuable insights from data and communicate complex information in a clear and concise manner.
What is the most common type of graph used in science?

+
The most common type of graph used in science is the line graph, which is used to show trends or patterns over time.
How do I choose the right type of graph for my data?

+
Choose the type of graph that best suits the data and the message you want to convey. Consider the complexity of the data, the type of graph required, and the level of customization needed.
What are some common graphing mistakes to avoid?

+
Common graphing mistakes to avoid include inconsistent scales, using 3D graphs unnecessarily, using too many colors, and insufficient labeling.
Related Terms:
- Interpreting science graphs worksheet PDF
- Science graphing practice worksheet
- graphing practice worksheet pdf
- interpreting charts and graphs worksheets
- graphing practice worksheet science
- graphing and analyzing scientific data