5 Tips for Mastering Geometry Area and Volume Worksheet

Introduction to Geometry Worksheet Mastery


Geometry is a cornerstone of mathematics that involves the study of shapes, sizes, angles, and dimensions. For students and enthusiasts alike, mastering the concepts of area and volume through dedicated worksheets is an indispensable exercise. Here, we delve into five comprehensive tips to not only conquer geometry worksheets but to truly comprehend the underlying principles that govern these fascinating spatial concepts.
1. Understand the Basics of Area and Volume

The foundation of mastering geometry worksheets lies in understanding the fundamental concepts of area and volume. Area refers to the two-dimensional space inside the boundaries of a shape, while volume extends this idea to three dimensions, measuring the space inside a solid shape.
- Area: Familiarize yourself with formulas for common shapes:
- Square/Rectangle: \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width}
- Triangle: \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
- Circle: \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2
- Volume: Learn the corresponding volume formulas:
- Cube/Rectangular Prism: \text{Volume} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \times \text{height}
- Cylinder: \text{Volume} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \times \text{height}
- Sphere: \text{Volume} = \frac{4}{3} \pi \times \text{radius}^3
Knowing these formulas is crucial because all geometry problems on worksheets will revolve around these basic principles. Understanding these foundations will make solving more complex problems more intuitive.
2. Identify and Classify Shapes Correctly


Before you can calculate the area or volume of a shape, you must correctly identify it. Geometry worksheets often include a wide variety of shapes, from simple to complex, and understanding how they are classified can streamline your problem-solving approach.
- Know the differences between polygons, circles, ellipses, and other figures.
- Be able to differentiate between:
- Regular polygons (all sides and angles equal) vs. irregular ones.
- Convex shapes (all interior angles less than 180°) vs. concave ones (at least one interior angle greater than 180°).
- Prism vs. pyramid, cylinder vs. cone, etc.
- Learn to spot composite shapes, where you might need to break down complex figures into simpler components.
💡 Note: Misidentifying a shape can lead to incorrect calculations. Always ensure you've classified the shape correctly before applying a formula.
3. Practice Visual Estimation

Geometry is not just about formulas; it's about intuition and spatial awareness. Developing an eye for estimating areas and volumes can be as important as knowing the precise calculations:
- Visualize: Try to estimate the size of a figure before calculating. For example, estimate whether a rectangle's area is closer to 100 cm² or 200 cm².
- Compare: Use familiar objects to gauge size. For instance, compare the area of a circle to the area of a dinner plate or the volume of a box to that of a milk carton.
- Use real-world objects: Drawing squares or cubes on real-world objects to help with understanding dimensions.
- Practice with tools: Utilize apps or software that can help you visualize and compare shapes.
Developing this skill not only improves your speed in worksheet scenarios but also enhances your overall geometrical comprehension.
4. Utilize Multiple Solution Methods
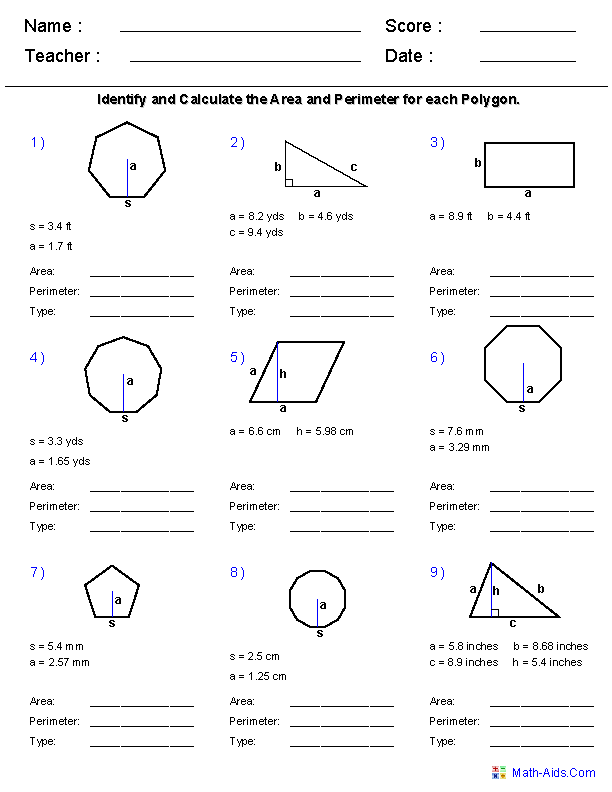
Geometry problems often have more than one way to solve them. Here's how you can approach these problems:
- Formula Approach: Use standard formulas for direct calculation.
- Geometric Proofs: Utilize geometric theorems to prove the result rather than just calculating.
- Decomposition: Break down complex shapes into simpler components and solve for each part separately.
- Similarity and Congruence: Use similar or congruent shapes to derive solutions through scaling or comparison.
- Area/Volume by Decomposition: In case of irregular shapes, approximate their areas or volumes by breaking them into standard shapes.
By practicing multiple methods, you not only solve the problem but also reinforce your understanding of geometry principles.
5. Reflect and Review

After working through a geometry worksheet, take time to reflect on your methods and review your work:
- Check your work: Verify calculations and ensure you've used the correct formulas or methods.
- Review errors: If you made mistakes, understand why. Was it a conceptual error or a calculation mistake?
- Seek feedback: From teachers or peers if possible, to gain different perspectives on your solutions.
- Ask yourself:
- Can you explain each step of your solution?
- Are there quicker or more intuitive methods you could use next time?
- How can you remember the formulas better?
- Create a summary: Make a summary of key concepts or hard-to-remember formulas in your own words.
Reflection is the bridge between practice and mastery, transforming routine calculations into a deeper understanding of geometry.
Throughout this journey of mastering geometry worksheets, one should approach each problem not just as a means to find an answer but as an opportunity to solidify one's understanding of spatial relationships and geometric properties. By employing these five tips, students can not only excel at worksheets but also develop a profound appreciation for geometry. The importance of recognizing shapes, estimating visually, mastering multiple solution strategies, and reflecting on one's approach will greatly enhance both problem-solving abilities and the intrinsic value gained from this branch of mathematics.
Why is it important to understand the basics of area and volume?
+
Understanding the basics of area and volume is foundational because all complex geometric problems are built on these principles. Without a solid grasp of how to calculate the space or volume of basic shapes, solving more intricate geometric puzzles becomes significantly more challenging.
Can visual estimation help with real-world problems?

+
Yes, visual estimation is crucial for quickly assessing quantities and dimensions in practical scenarios, like estimating how much paint is needed for a room or how many people can fit in a given space.
How can I remember formulas better?

+
To remember formulas better, use mnemonic devices, relate them to real-world objects or situations, practice regularly, and understand the underlying principles rather than memorizing blindly.